Volume of the bulb of a mercury thermometer at 0∘C is V0 and area of cross section of the capillary tube is A0, coefficient of linear expansion of glass is αg per ∘C, and the cubical expansion of mercury is γm per ∘C. If the mercury fills the bulb at 0∘C, find the length of mercury column in capillary tube at T∘CSolution in Telugu
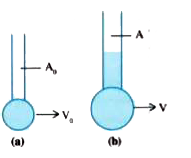
An exaggerated view of the expansion is shown figure (b).
Figure (a) represents the initial situation . When exposed to a temperature change ΔT, the cross-section of the capillary, the volume of the bulb , and the volume ocupied by the mercury all change (see figures). The final voluem occcupied by the mercury is
VHg=V0(1+βHgΔT)
where βHg is the coefficient of volume expansion of mercury. The new cross-section of the capillary will be A=A0(1+2αgΔT) ...(2)
where alphgg is the coefficient of linear expansion of glass. Similarly, the new volume of the bulb is
Vg=V0(1+3αgΔT) ...(3)
(Note that , initially the colume of Hg = the volume of the bulb).
Now, the volume of mercury outside the bulb in figure (b) will be
VHg−Vg=V0(1+βHgΔT−1−3αgΔT)
VHg−Vg=V0(βHg−3αg)ΔT ...(4)
If the length of the mercury column in figure (b) is h, then
VHg−Vg=hA=h(A0)(1+2αgΔH) ...(5)
where we have used (2). Equating (4) and (5)
hA0(1+2αgΔT)=V0(βHg−3αg)ΔTorh=V0A0(βhg−3αg1+2αgΔT)ΔT,
since ΔT=t∘C−0∘C
h=V0A0(BHg−3αg1+2αgt)t
Topper's Solved these Questions
- EXPANSION OF LIQUIDS Book:AAKASH SERIESChapter:EXPANSION OF LIQUIDS Exercise:TEST YOUR SELF
Explore 5 Videos
- EXPANSION OF LIQUIDS Book:AAKASH SERIESChapter:EXPANSION OF LIQUIDS Exercise:VERY SHORY ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Explore 15 Videos
- EXPANSION OF GASESBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:EXPANSION OF GASESExercise:QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWERS
Explore 4 Videos
- EXPANSION OF SOLIDS Book:AAKASH SERIESChapter:EXPANSION OF SOLIDS Exercise:Questions for Descriptive Answers
Explore 5 Videos
Similar Questions
Is the real coefficient of expansion of water between 0∘Cand4∘C positive or negative? Explain.
View SolutionWhy the expansions of the liquids is greater than the expansion of the solids ?
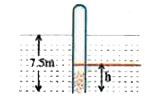
View SolutionA thin uniform tube of length 9 m closed at one end is immersed in water to a depth of 7.5 m. Find the height h to which water rises in the tube. Ignore any temperature change and take atmosphere pressure as 10 mg water column.
View SolutionThe length of an iron rod is measured by a brass scale. When both of them are at 20∘C, the length is 80 cm. What is the length of the rod at 100∘C as measured by the scale at 100∘C? The coefficient of linear expansion of brass and iron are 24×10−6(C∘)−1and18×10−6(C∘)−1 respectively.
View SolutionThe coefficient of linear expansion of glass is αg per .∘C and the cubical expansion of mercury is λm per .∘C. The volume of the bulb of a mercury thermometer at 0∘C is V0 and cross section of the capillary is A0. What is the length of mercury column in capillary at T∘C, if the mercury just fills the bulb at 0∘C ?
View SolutionVolume of the bulb of a mercury thermometer at 0^(@)C is V_(@) and area of cross section of the capillary tube is A_(0) , coefficient of linear expansion of glass is alpha_(g) , and the cubical expansion of mercury is gamma_(m) . If the mercury fills the bulb at 0^(@)C , find the length of mercury column in thermometer at T^(@)C
View SolutionThe volume of mercury in the bulb of thermometer is 10−6m3. The area of cross-section of the capillary tube is 2×10−7m2. If the temperature is raised by 1000C, the increase in the length of the mercury column is (γHg=18×10−5/∘C)
View SolutionA weight thermometer contains 51g of mercury at 200C and 50g of mercury at 1000C. The coefficient of apparent expansion of mercury in glass vessel is
View SolutionThe coefficient of volumetric expansion of mercury is 18×10−5/∘C . A thermometer bulb has a volume 10−6m3 and cross section of stem is 0.004cm2. Assuming that bulb is filled with mercury at 0∘C then the length of the mercury column at 100∘C is
View SolutionIn a mercury-glass thermometer the cross-section of the capillary portion is A0 and the volume of the bulb is V0 at 273K. If α and γ are the coefficients of linear and cubical expansion coefficients of glass and mercury respectively then length of mercury in the capillary at temperature t∘C is (Ignore the increase in cross-sectional area of capillary)
_E01_142_Q01.png)
View SolutionIn a mercury in glass thermometer the cross section of the capillary is A0 and volume of the bulb is V0 at 0∘C. If mercury just fills the bulb at 0∘C, find the that the length of mercury in the capillary at temperature t.∘C. Given that β=coefficient of cubical, expansion on mercury and α= coefficient of linear expansion of glass.
View SolutionA thin long glass tube of uniform cross-section contains 1 m long mercury thread at 0^(@)C. At 100^(@)C , the mercury thread increases by 16.5 mm. If the coefficient of real expansion of mercury is 0.000182^(@)C^(-1) , find the coefficient of linear expansion of glass.
View SolutionThe area of cross-section of the capillary tube of a mercury thermometer is A_(0) and the volume of the bulb filled with mercury is V_(0) " at " 0^(@)C . Find the length of the mercury column in the capillary tube as the bulb is heated to t^(@)C . Coefficient of linear expansion of glass is alpha and coefficient of volume expansion of mercury is beta.
View SolutionThe coefficient of real expansion of mercury is 18×10−5∘C−1. A thermometer has a bulb of volume 10−6m3 and the cross-section of the stem is 0.002 cm2. Assuming the bulb to be filled with mercury at 0∘C, find the length (in cm) of the mercury column at 100∘C.
View SolutionVolume of the bulb of a mercury thermometer at 0^(@)C" is "V_(0) and area of cross section of the capillary tube is A_(0) , coefficient of linear expansion of glass is alpha_(g) per ""^(@)C , and the cubical expansion of mercury is gamma_(m) per ""^(@)C . If the mercury fills the bulb at 0^(@)C , find the length of mercury column in capillary tube at T^(@)C
View Solution
