On a large tray of mass M an ice cube of mass m, edge L is kept. If the ice melts completely, the centre of mass of the system come down by
mL2(M+m)
(M−m)L2(M+m)
(M+2m)L2(M+m)
2MLM+m
The correct Answer is:A
Similar Questions
If the mass equivalent energy is kept in mind, then when ice melts, the mass of water
View SolutionA cubical block of ice of mass m and edge L is placed in a large tray of mass M. If the ice melts, how far does the centre of mass of the system ''ice plus tray'' come down?
View SolutionConsider a gravity free hall in which a tray of mas M, carrying a cubical block of ice of mass m and edge L, is at rest in the middle.. If the ice melts, by what distance does the centre of mass of the tray plus the ice system descend?
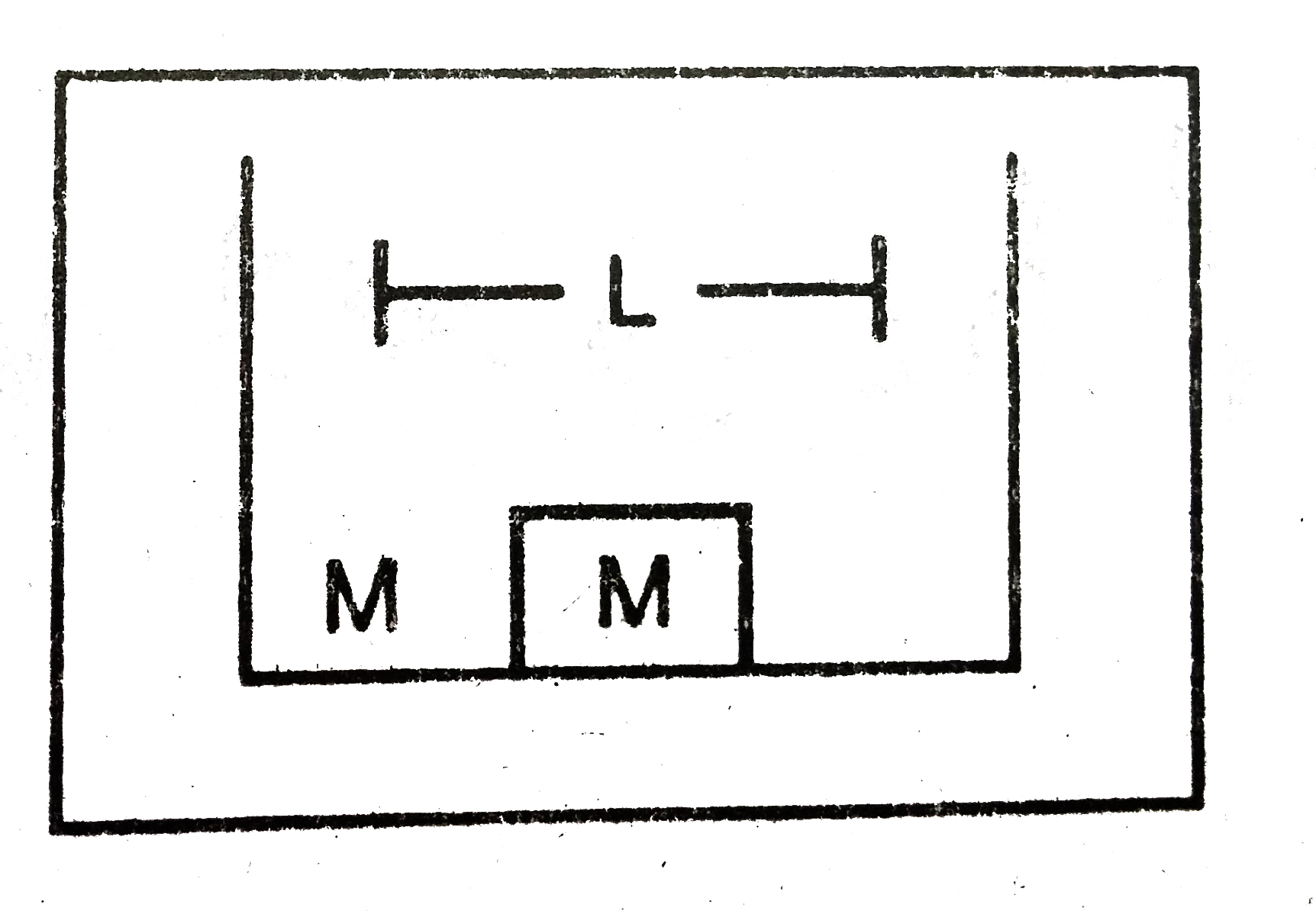
View Solutionm द्रव्यमान का बर्फ का ब्लॉक झील में गिर जाता है। जल की सतह से टकराने के बाद बर्फ का m/5 द्रव्यमान पिघल जाता है। बर्फ के ब्लॉक तथा झील दोनों का तापमान 0∘C है। या L गलन की गुप्त ऊष्मा हो, तो जल की सतह से टकराने से पूर्व बर्फ के गिरने की न्यूनतम दूरी होगी :
View SolutionIce density rho And water sigma Is that when the mass of ice M is melted, then the volume of ice will decrease
View SolutionA small quantity mass m, of water at a temperature theta ("in " ^(@)C) is poured on to a larger mass M of ice which is at its melting point. If c is the specific heat capacity of water and L the specific heat capacity of water and L the specific latent heat of fusion of ice, then the mass of ice melted is give by
View Solution10 g of ice at 0∘C is mixed with m mass of water at 50∘C. What is minimum value of m so that ice melts completely. (L = 80 cal/g and s = 1 cal/g−.∘C)
View Solution

