A ball with initial momentum P collides with rigid wall elasticall. If P1 be it's momentum after collision then
P1=P
P1=−P
P1=2P
P1=−2P
The correct Answer is:B
Topper's Solved these Questions
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:EXERCISE - II
Explore 136 Videos
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:PRACTICE EXERCISE
Explore 108 Videos
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWER
Explore 5 Videos
- KINETIC THEORY OF GASESBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:KINETIC THEORY OF GASESExercise:Practice Exercise
Explore 15 Videos
- MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS Book:AAKASH SERIESChapter:MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS Exercise:EXERCISE-3
Explore 43 Videos
Similar Questions
A ball with initial momentum P collides with rigid wall elastically. If P1 be it's momentum after collision then
View SolutionA ball A moving with momentum 2ˆi+4ˆj collides with identical ball B moving with momentum 6ˆj . After collision momentum of ball B is 10ˆj . Which of the following statement is correct?
View Solution
Knowledge Check
A ball with initial momentum →P collides with rigid wall elastically. If −→P1 be its momentum after collision then
A−→P1=→PB−→P1=−→PC−→P1=2→PD−→P1=−2→PA ball A moving with momentum 2ˆi+4ˆj collides with identical ball B moving with momentum 6ˆj . After collision momentum of ball B is 10ˆj . Which of the following statement is correct?
AAfter collision momentum of A is 4ˆiBAfter collision momentum of A is parallel to momentum of BCAfter collision momentum of A is 2ˆiDIf →PAand→PB are momenta of balls A and B, then Δ(∣∣→PA∣∣+∣∣→PB∣∣)=0A ball moving with a speed of 9m/s strikes an identical ball at rest, such that after the collision, the direction of each ball makes an angle of 30∘ with the original line of motion. Find the speeds of the two balls after collision.
A5.2ms−1B0.52ms−1C52ms−1D26ms−1
A ball of mass m moving with velocity v, collide with the wall elastically as shown in the figure. After impact the change in angular momentum about P is :
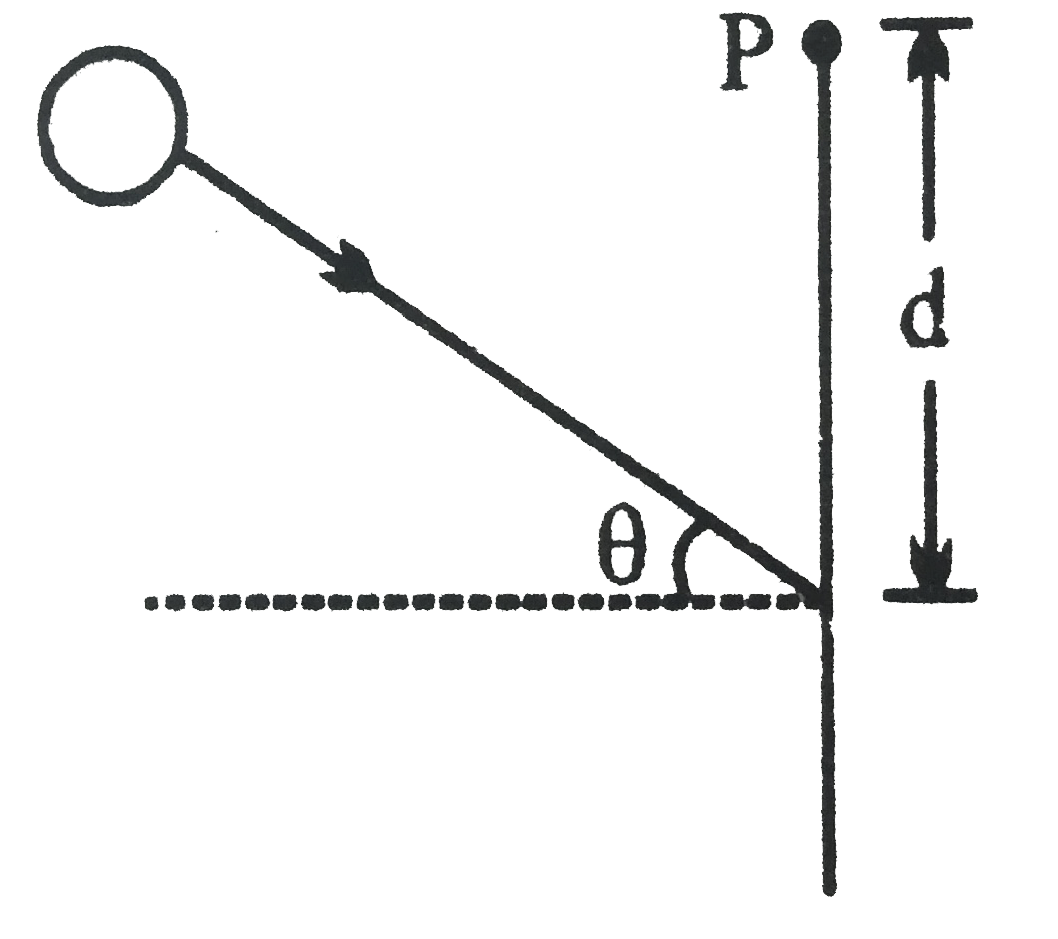 .
.
View SolutionTwo particles of equal masses moving with same momentum collide perfectly inelastically. After the collision the combined mass moves with half of the speed of the individual masses. The angle between the initial momenta of individual particle is
View SolutionA ball of mass m moving with velocity v, collide with the wall elastically as shown in the figure. After impact the change in angular momentum about P is :
 .
.
View SolutionTwo particles of equal masses moving with same momentum collide perfectly in-elastically. After the collision the combined mass moves with half of the speed of the individual masses. The angle between the initial momenta of individual particle is
View SolutionA ball of mass 3 kg collides with a wall with velocity 10 m/sec at an angle of 30° and after collision reflects at the same angle with the same speed. The change in momentum of ball in MKS unit is-
View Solution

