The degree of dissociation (α) of CH3COOH solution having 0.1M concentration and pKa as 6, in presence of strong acid HCl having concentration 0.1M is 10−x. Then what is the value of x?
The correct Answer is:5
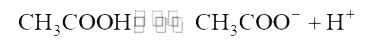
t=00.100t=t0.1−0.1α0.1α(0.1α+0.1)
HCl→H+0.1+Cl−0.1
Ka=0.1(1+α)×α×0.10.1(1−α)
Since α<<1 therefore
10−6=α×0.11
α=10−610−1=10−5
So the value of x=5
Similar Questions
When 0.1M CH_(3)COOH solution is shaken with activated charcoal and the charcoal is filtered out, the concentration of acid -
View SolutionAt equilibrium, the mixed water solution of the following pH=pKa is 1. 0.1 M CH_(3)COOH Of 100mL+0.1M CH_(3)COONa 100 mL of 2. 0.1M CH_(3)COOH Of 100mL +0.1M NaOH 50 mL of 3. 0.1M CH_(3)COOH Of 100mL +0.1 M NaOH 100 mL of 4. 0.1 M CH_(3)COOH Of 100mL +0.1 M NH_(3) Of 100mL
View SolutionWhat is the pH of the solution when 100mL of 0.1M HCl is mixed with 100mL of 0.1 M CH_(3) COOH .
View Solution18mL of mixture of CH_(3)COOH and CH_(3)COONa required 6mL of 0.1M NaOH for neutralisation of the acid 12mL of 0.1M HCl for reaction with salt, separately. If pK_(a) of the acid is 4.75 , what is the pH of the mixture
View SolutionThe degree of dissociation of weak electrolyde is inversely proportional to the square root fo concentration. It is called Ostwald's dilution law. alpha = sqrt((K_(a))/(c)) As the tempertaure increases, degree of dissociation will increase. (alpha_(1))/(alpha_(2)) = sqrt((K_(a_(1)))/(K_(a_(2)))) if concentration is same. (alpha_(1))/(alpha_(2)) = sqrt((c_(2))/(c_(1))) if acid is same. 0.01M CH_(3)COOH has 4.24% degree of dissociation, the degree of dissociation of 0.1M CH_(3)COOH will be
View SolutionThe degree of dissociation of acetic acid in a 0.1M solution is 1.32 xx 10^(-2) . Find out the dissociation constant of the acid and its pK_(a) value.
View SolutionThe degree of dissociation (alpha) of CH_(3)COOH solution having 0.1M concentration and pKa as 6, in presence of strong acid HCl having concentration 0.1M is 10^(-x) . Then what is the value of x?
View Solution

