If the enthalpies of formation of C3H8(g),CO2(g)andH2O(l) at standard conditions are −104kJmol−1,−394kJmol−1and−286kJmol−1 respectively then the standard anthalpy of combustion of 66 g of C3H8(g) will be
−2222kJ
−2500kJ
−784kJ
−3333kJ
The correct Answer is:C
To find the standard enthalpy of combustion of 66 g of C3H8(g), we will follow these steps:
Step 1: Calculate the number of moles of C3H8
The molar mass of C3H8 (propane) can be calculated as follows:
- Carbon (C): 12.01 g/mol × 3 = 36.03 g/mol
- Hydrogen (H): 1.008 g/mol × 8 = 8.064 g/mol
- Total molar mass of C3H8 = 36.03 g/mol + 8.064 g/mol = 44.094 g/mol
Now, we can calculate the number of moles of C3H8 in 66 g:
Number of moles=massmolar mass=66 g44.094 g/mol≈1.496 mol
Step 2: Write the balanced combustion reaction for C3H8
The balanced equation for the combustion of propane is:
C3H8(g)+5O2(g)→3CO2(g)+4H2O(l)
Step 3: Calculate the enthalpy change for the combustion reaction
Using the enthalpies of formation provided:
- ΔHf of C3H8(g)=−104 kJ/mol
- ΔHf of CO2(g)=−394 kJ/mol
- ΔHf of H2O(l)=−286 kJ/mol
The standard enthalpy change of combustion (ΔHcomb) can be calculated using the formula:
ΔHcomb=∑ΔHf(products)−∑ΔHf(reactants)
For the products:
- For 3CO2: 3×(−394)=−1182 kJ
- For 4H2O: 4×(−286)=−1144 kJ
Total for products:
−1182 kJ+(−1144 kJ)=−2326 kJ
For the reactants:
- For C3H8: −104 kJ
- For 5O2: 0 kJ (since elemental oxygen has an enthalpy of formation of 0)
Total for reactants:
−104 kJ+0=−104 kJ
Now, substituting into the enthalpy change formula:
ΔHcomb=−2326 kJ−(−104 kJ)=−2326+104=−2222 kJ
Step 4: Calculate the total enthalpy of combustion for 66 g of C3H8
Now, we need to find the enthalpy of combustion for the number of moles calculated:
ΔHcomb per mole of C3H8=−2222 kJ/mol
Total for 1.496 moles:
ΔHtotal=1.496 mol×(−2222 kJ/mol)≈−3325.5 kJ
Final Answer
The standard enthalpy of combustion of 66 g of C3H8(g) is approximately -3325.5 kJ.
---
The molar mass of C3H8 (propane) can be calculated as follows:
- Carbon (C): 12.01 g/mol × 3 = 36.03 g/mol
- Hydrogen (H): 1.008 g/mol × 8 = 8.064 g/mol
- Total molar mass of C3H8 = 36.03 g/mol + 8.064 g/mol = 44.094 g/mol
Number of moles=massmolar mass=66 g44.094 g/mol≈1.496 mol
The balanced equation for the combustion of propane is:
C3H8(g)+5O2(g)→3CO2(g)+4H2O(l)
Using the enthalpies of formation provided:
- ΔHf of C3H8(g)=−104 kJ/mol
- ΔHf of CO2(g)=−394 kJ/mol
- ΔHf of H2O(l)=−286 kJ/mol
ΔHcomb=∑ΔHf(products)−∑ΔHf(reactants)
For the products:
- For 3CO2: 3×(−394)=−1182 kJ
- For 4H2O: 4×(−286)=−1144 kJ
−1182 kJ+(−1144 kJ)=−2326 kJ
- For C3H8: −104 kJ
- For 5O2: 0 kJ (since elemental oxygen has an enthalpy of formation of 0)
−104 kJ+0=−104 kJ
ΔHcomb=−2326 kJ−(−104 kJ)=−2326+104=−2222 kJ
Now, we need to find the enthalpy of combustion for the number of moles calculated:
ΔHcomb per mole of C3H8=−2222 kJ/mol
Total for 1.496 moles:
ΔHtotal=1.496 mol×(−2222 kJ/mol)≈−3325.5 kJ
The standard enthalpy of combustion of 66 g of C3H8(g) is approximately -3325.5 kJ.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Which one of the following acids has highest heat of neutralization with one equivalent of NaOH?
View SolutionSelect the Incorrect statement among the following.
View SolutionWhich of the following bonds has the highest bond energy?
View SolutionThe molar enthalpies of combustion of C_(2)H_(2)(g), C("graphite") and H_(2)(g) are -1300,-394 , and -286 kJ mol^(-1) , respectively. The standard enthalpy of formation of C_(2)H_(2)(g) is
View SolutionThe standard enthalpy of formation of octane (C8H18) is −250kJ/mol. Calculate the enthalpy of combustion of C8H18. The enthalpy of formation of CO2(g) and H2O(l) are −394kJ/mol and −286kJ/mol respectively.
View SolutionThe standard enthalpy of formation of H_(2)(g) and Cl_(2)(g) and HCl(g) are 218 kJ//mol , 121.88 kJ//mol and -93.31 kJ//mol respectively. Calculate standard enthalpy change in kJ for (1)/(2)H_(2)(g)+(1)/(2)Cl_(2)(g)toHCl(g)
View SolutionThe standard enthalpies of combustion of C_(6)H_(6(l)),C_(("graphite"))and H_(2(g)) are respectively -3270 kJmol^(-1), -394 kJ mol^(-1) and - 286 kJ mol^(-1) . What is the standard enthalpy of formation of C_(6)H_(6(l)) in kJ mol^(-1)
View Solutionयदि 25∘C ताप तथा 1 वाइयोमॉडली दाब पर C2H4(g),CO2(g) तथा H2O(l) के सम्भावन की एन्थेलपी ( enthalpy of formation ) क्रमशः +52,−394 तथा −286 kJ mol−1 हो तो C2H4(g) के दहन की एन्थेलपी ( enthalpy of formation ) होगी :
View SolutionThe standard enthalpies of combustion of C6H6(l),C(graphite)andH2(g) are respectively −3270kJmol−1,−394kJmol−1 and −286kJmol−1. What is the standard enthalpy of formation of C6H6(l) in kJ mol−1?
View SolutionH_2O(l) And H_2O(g) Standard oscillation enthalpy respectively -285.8 kJ mol^-1 And -241.8 kJ mol^-1 Huh.
View SolutionThe heats of formation of CO_(2(g)) , H_2O_((l)) and CH_(4(g)) are respectively –394 kJ mol^(-1), -286 kJ mol^(-1) and -76 kJ mol^(-1) . Calculate the heat of combustion of methane.
View SolutionCalculate the standard enthalpy change for the reaction CH4(g)+2O2(g)→CO2(g)+2H2O(l) Given that the standard enthalpies of formation of CH4(g),CO2(g), and H2O(l) are -74.8 kJ mol^-1, -393.5 kJ mol^-1and−285.8kJmol^-1 respectively.
View SolutionCalculate the standard enthalpy change for the reaction
CH4(g)+2O2(g)→CO2(g)+2H2O(l),
given that the standard heatds of formation of CH4(g,CO2(g)andH2O(l) are−74.91mol−1,−394.12kJmol−1and−286.31kJmol−1 respectivley.
View SolutionCalculate the standard heat of formation of propane if its heat of combustion is −2220.2kjmol−1. The heats of formation of CO2(g) and H2O(l) are −394.12and−286.31kJmol−1 respectively.
View SolutionThe enthalpy change of the reaction C3H8(g)+H2(g)→C2H6(g)+CH4(g), at 25∘, will be Given that: heat of combustion values under standard condition
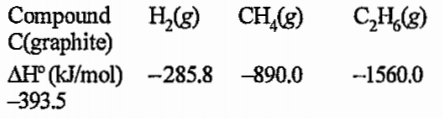 (The standard heat of formation of C3H8(g) is
-103.8kJ/mol)
(The standard heat of formation of C3H8(g) is
-103.8kJ/mol)
View Solution

