The lac operon consists of
Four regulatory genes only
One regulatory gene and three structural genes
Two regulatory genes and two structural genes
Three regulatory genes and three structural genes
The correct Answer is:B
Step-by-Step Solution:
1. Understanding the Lac Operon: The lac operon is a genetic regulatory system found in prokaryotes, particularly in E. coli. It is responsible for the metabolism of lactose.
2. Components of the Lac Operon: The lac operon consists of several key components:
- Regulatory Gene: This gene produces a repressor protein that can bind to the operator region and inhibit transcription.
- Promoter: This is the region where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription of the structural genes.
- Operator: This is the segment of DNA that the repressor binds to, blocking RNA polymerase from transcribing the structural genes.
- Structural Genes: There are three structural genes in the lac operon:
- lacZ: Codes for beta-galactosidase, which breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose.
- lacY: Codes for permease, which facilitates the entry of lactose into the cell.
- lacA: Codes for transacetylase, which is involved in the metabolism of lactose.
3. Counting the Genes:
- Regulatory Gene: 1
- Promoter: 1
- Operator: 1
- Structural Genes: 3 (lacZ, lacY, lacA)
4. Total Components:
- Total = 1 (regulatory) + 1 (promoter) + 1 (operator) + 3 (structural) = 6 components in total, but the question specifically asks for the number of regulatory and structural genes.
- Regulatory Genes = 1
- Structural Genes = 3
5. Conclusion: Based on the components of the lac operon, the correct answer is that it consists of 1 regulatory gene and 3 structural genes.
Final Answer: The lac operon consists of 1 regulatory gene and 3 structural genes.
---
- Regulatory Gene: This gene produces a repressor protein that can bind to the operator region and inhibit transcription.
- Promoter: This is the region where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription of the structural genes.
- Operator: This is the segment of DNA that the repressor binds to, blocking RNA polymerase from transcribing the structural genes.
- Structural Genes: There are three structural genes in the lac operon:
- lacZ: Codes for beta-galactosidase, which breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose.
- lacY: Codes for permease, which facilitates the entry of lactose into the cell.
- lacA: Codes for transacetylase, which is involved in the metabolism of lactose.
- Regulatory Gene: 1
- Promoter: 1
- Operator: 1
- Structural Genes: 3 (lacZ, lacY, lacA)
- Total = 1 (regulatory) + 1 (promoter) + 1 (operator) + 3 (structural) = 6 components in total, but the question specifically asks for the number of regulatory and structural genes.
- Regulatory Genes = 1
- Structural Genes = 3
Similar Questions
An operon consists of
View SolutionWhich of following statement is true for lac operon in E-coli
(a) lac operon consists of one regulatory gene and five structural gene.
(b) The i gene codes for inducer
(c) The z-gene codes for β -galacosidase
(d) A very low level of expression of lac operon has to be present in cell all the time
View SolutionLac operon is
View SolutionOperon unit consists of
View SolutionA considerable amount of lactose is added to the growth medium of E.coli. How is the lac operon switched on in the bacteria.? Mention the state of the operon when lactose is digested.
View SolutionE. coli cells with a mutated z gene of the lac operon cannot grow in medium containing only lactose as the source of energy because
View SolutionIn the following diagram of the lac operon, which is an operon for inducible enzymes , identify the components and enzymes.
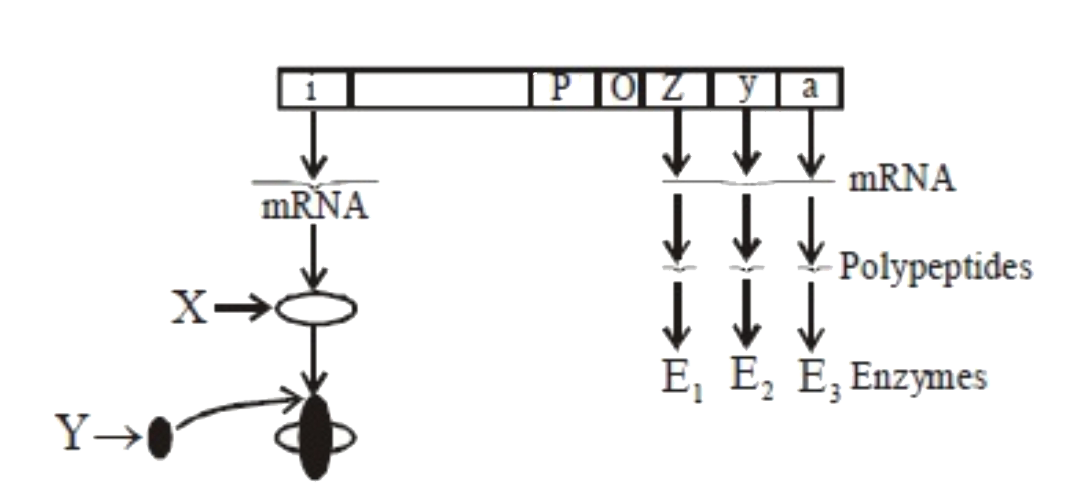
View SolutionWhy does the lac operon shut down some time after the addition of lactose in the medium where E.coli was growing ? Why low level expression of lac operon is always required ?
View SolutionDescribe how the lac operon operates, both in the presence and absence of an inducer in E. coli.
View SolutionDescribe how the lac operon operates, both in the presence and absence of an inducer in E. coli.
View Solution

