[A]: Convergent evolution leads to pro_duct1on of analogous similarities among different groups of organisms.
[R]: Animals of the same grou~ or closely r~- lated groups exhibit great divergences in their morphology
If both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
If both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
If A is true and R is false
If both A and R are false
The correct Answer is:B
To address the question regarding convergent evolution and the divergence of morphology among closely related groups, we can break down the solution into clear steps:
1. Understanding Convergent Evolution:
- Convergent evolution occurs when different species evolve similar traits or functions independently, often because they adapt to similar environments or ecological niches. This results in analogous structures, which serve similar functions but do not share a common evolutionary ancestor.
2. Definition of Analogous Structures:
- Analogous structures are features in different species that perform similar functions but have different evolutionary origins. For example, the wings of bats and insects serve the same function (flight) but evolved independently.
3. Assertion Analysis:
- The assertion states that convergent evolution leads to the production of analogous similarities among different groups of organisms. This is true because convergent evolution results in organisms from different lineages developing similar traits due to similar environmental pressures.
4. Reason Analysis:
- The reason provided states that animals of the same group or closely related groups exhibit great divergences in their morphology. This statement is also true, as closely related species can adapt to different environments, leading to diverse morphological traits.
5. Linking Assertion and Reason:
- While both the assertion and the reason are true statements, the reason does not adequately explain the assertion. The reason discusses divergence within closely related groups, while the assertion focuses on convergence among unrelated groups.
6. Conclusion:
- Therefore, the assertion is true, and the reason is true, but the reason does not justify the assertion. They are related concepts in evolution, but one does not explain the other.
- Convergent evolution occurs when different species evolve similar traits or functions independently, often because they adapt to similar environments or ecological niches. This results in analogous structures, which serve similar functions but do not share a common evolutionary ancestor.
- Analogous structures are features in different species that perform similar functions but have different evolutionary origins. For example, the wings of bats and insects serve the same function (flight) but evolved independently.
- The assertion states that convergent evolution leads to the production of analogous similarities among different groups of organisms. This is true because convergent evolution results in organisms from different lineages developing similar traits due to similar environmental pressures.
- The reason provided states that animals of the same group or closely related groups exhibit great divergences in their morphology. This statement is also true, as closely related species can adapt to different environments, leading to diverse morphological traits.
- While both the assertion and the reason are true statements, the reason does not adequately explain the assertion. The reason discusses divergence within closely related groups, while the assertion focuses on convergence among unrelated groups.
- Therefore, the assertion is true, and the reason is true, but the reason does not justify the assertion. They are related concepts in evolution, but one does not explain the other.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
[A] : Endomycorrhiza of forest trees contribute to the efficient nutrient cycling in tropical test ecosystems .
[R] : The fungi that form endomycorrhizal association with plants store nutrient ions and make them available to the host plants .
View Solution(a) Give reason for -
(i) Both strands of DNA are not copied during transcription.
(ii) Transcription and translation in bacteria can be coupled.
(b) Differentiate between the process of transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
View SolutionA group of individual organisms with fundamental morphological similarities is called?
View SolutionAssertion :- Analogous structures are a result of convergent evolution. Reason :- Different strutures evolving for the same function and hence having similarity.
View Solution[A]: Convergent evolution leads to pro_duct1on of analogous similarities among different groups of organisms.
[R]: Animals of the same grou~ or closely r~- lated groups exhibit great divergences in their morphology
View SolutionA and B are examples of ………………i………… organs and represent ………..ii…………… evolution .
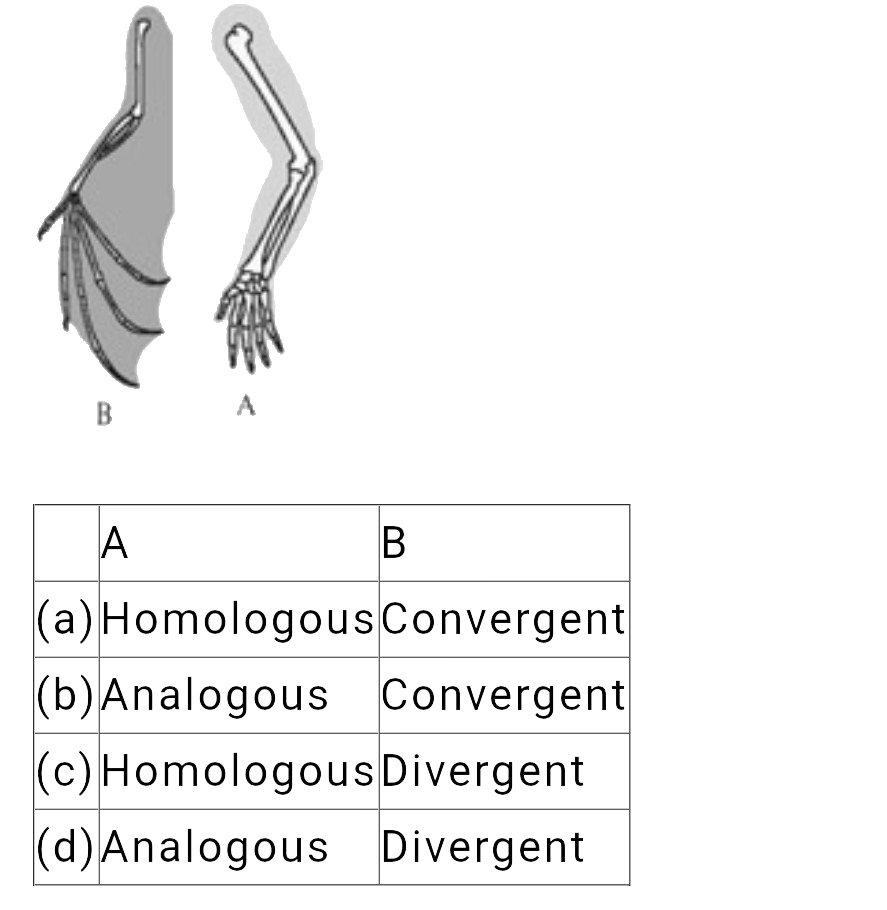
AB(a)HomologousConvergent(b)AnalogousConvergent(c)HomologousDivergent(d)AnalogousDivergent
View SolutionAnalogous organs suggest divergent evolution.
View SolutionDivergent Evolution and Convergent Evolution
View SolutionWhat are the analogous organs or convergent evolution?
View Solution[A]: Macro evolution produces groups of parallel special adaptations among convergent but related species. [R]: Adaptive radiation/macroevolution don't produce evolutionary lines that converge in special adaptation with other related groups differing in general adaptation
View SolutionEnumerate on convergent and divergent evolution with suitable examples in animals.
View SolutionEvidences OF Organic Evolution || Evidences From Comparative Morphology and Anatomy || Homology ( Divergent Evolution+ Adaptive Radiation) || Analogy (Convergent Evolution + Adaptive Convergence)
View SolutionCompare and contrast divergent and convergent evolution :
Which of the following would result in a group of species that are physiclly similar but NOT genetically related?
View Solution[A]: Convergent evolution leads to production of analogous similarities among different groups of organisms.
[R]: Animals of the same group or closely related groups exhibit great divergences in their morphology
View Solution[A]: Macro evolution produces groups of parallel special adaptations among convergent but related species.
[R]: Adaptive radiation/macroevolution don't produce evolutionary lines that converge in special adaptation with other related groups differing in general adaptation
View Solution

