A liquid of density 800kg/m3 flowing steadily in a tube of varying cross-section. If area of cross-section at A is 4cm2 and at B is 2cm2, if speed of liquid at A is 10cm/s, calculate:- the difference in pressure at A and B.Solution in Marathi
Step by step video & image solution for A liquid of density 800 kg//m^3 flowing steadily in a tube of varying cross-section. If area of cross-section at A is 4 cm^2 and at B is 2 cm^2, if speed of liquid at A is 10 cm//s, calculate:- the difference in pressure at A and B. by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
A liquid of densilty 1200 kg/m3 flowing steadily in a tube of varying cross section. The cross section at a ponit A is 1.0cm2 and that at B is 20mm2, the ponts A and B are in the same horizontal plane. The speed of the liquid at A is 10cm/s. Calculate the difference i pressure at A and B.
View SolutionAn incompressible liquid flows through a uniform cross section tube with velocity 12 cm/s. the thickness of liquid layer is 0.8 cm then velocity of gradient of flow is
View SolutionThe given figure shows a streamline flow of a non-viscous liquid having density 1000kg/m3.The cross sectional area at point A is 2cm2 and at point B is 1mm2.The speed of liquid at the point A is 5cm/s. Both points A and B are at the same horizontal level. Calculate the difference in pressure at A and B.
View SolutionA liquid of density 800kg/m3 flowing steadily in a tube of varying cross-section. If area of cross-section at A is 4cm2 and at B is 2cm2, if speed of liquid at A is 10cm/s, calculate:- the rate of flow at B
View SolutionWater flows through a pipe of varying cross-section. If the velocity of flow is 0.24 m/s at a cross- section of 5cm2, what will beits velocity at a cross-section of 10cm2?
View SolutionFigure shows a liquid flowing through a tube at the rate of 0.1m3/s. The tube is branched into two semicircular tubes of cross-sectional area A/3 and 2A/3. The velocity of liquid at Q is (the cross section of the main tube is A=10−2m2 and vp=20m/s)
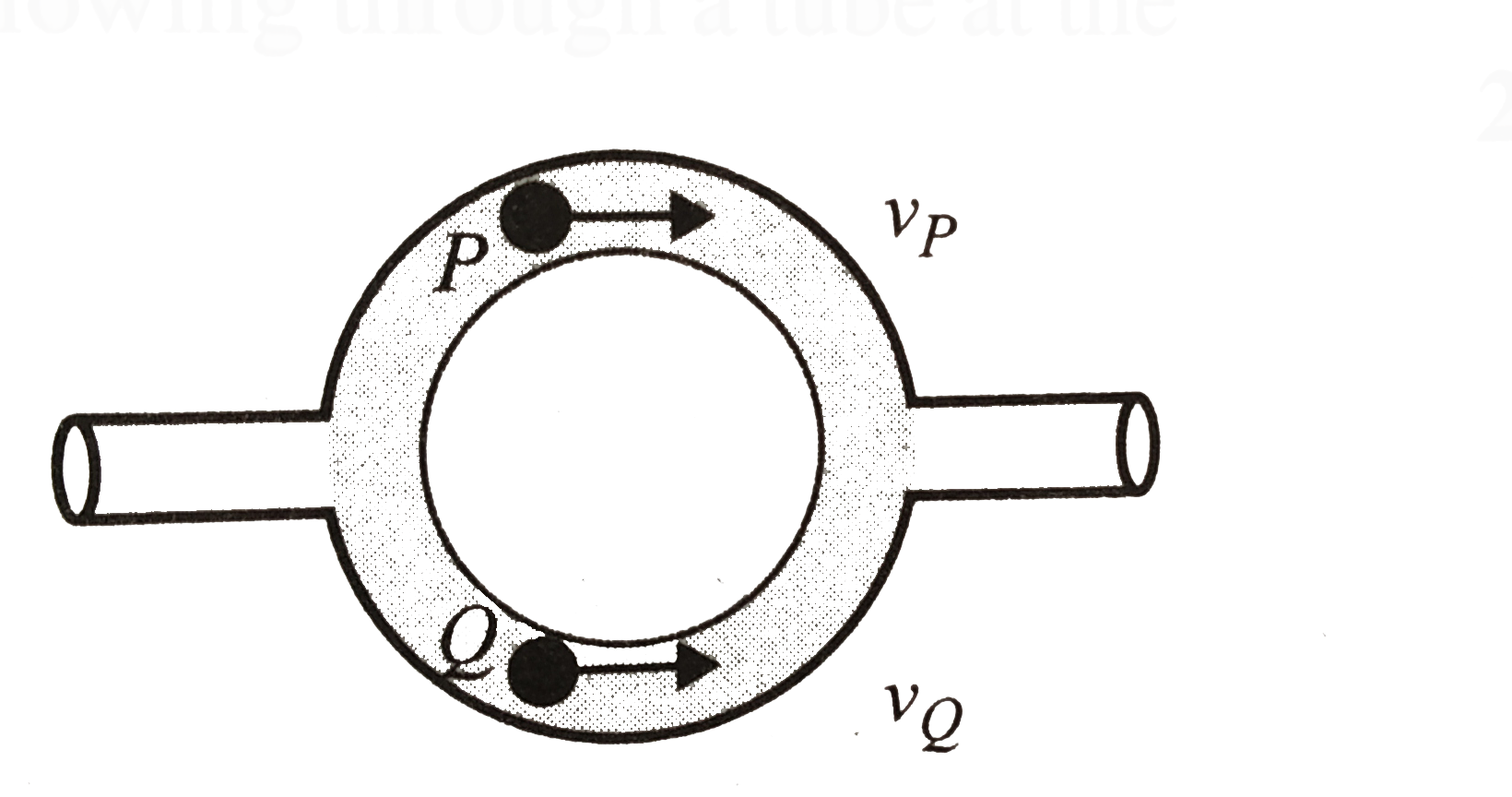
View SolutionA pipe of varying area of cross-section is held such that its axis is horizontal. At two cross sections A and B, its radii are 8 cm and 4 cm. If velocity of water at A through the pipe is 16 cm s−1 and pressure at A is 106 dyne/cm2 , find the pressure at cross-section B.
View Solution
