Read the given passage and answer the questions:
Most of the chemical reactions are accelerated by increase in temperature. For example, in decomposition of N2O5, the time taken for half of the original amount of material to decompose is 12 min at 50∘C, 5 h at 25 ∘C and 10 days at 0 ∘C. You also know that is a mixture of potassium permaganate and oxalic acid H2C4O4, potassium permaganate KMnO4 gets decolourised faster at a higher temperature than at a lower temperature. It has been found that for a chemical reaction with rise in temperature by 10 ∘C, the rate constant is nearly doubled. The temperature dependence of the rate of a chemical reaction can be accurately explained by Arrhenius equation:
k=Ae−Ea/RT
where A is the frequency factor, Ea is the activation energy measured in joules per mole.
Q. How will change this equation into natural logaritham form?
In k=−EaRT+In A
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CHEMICAL KINETICS BOOK - U-LIKE SERIESCHAPTER - CHEMICAL KINETICS EXERCISE - MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
19 Videos
- CHEMICAL KINETICS BOOK - U-LIKE SERIESCHAPTER - CHEMICAL KINETICS EXERCISE - ASSERTION-REASON QUESTIONS
10 Videos
- CHEMICAL KINETICS BOOK - U-LIKE SERIESCHAPTER - CHEMICAL KINETICS EXERCISE - NCERT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
29 Videos
- CBSE EXAMINATION PAPER 2020 (CODE No.56/4/1) BOOK - U-LIKE SERIESCHAPTER - CBSE EXAMINATION PAPER 2020 (CODE No.56/4/1) EXERCISE - SECTION -D
3 Videos
- CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFEBOOK - U-LIKE SERIESCHAPTER - CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFEEXERCISE - LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS - I
21 Videos
Similar Questions
Units of rate constant for a second order reaction is
View SolutionAssertion (A) : The extent to which a reaction will proceed can be determined from chemical equilibrium.
Reason (R ) : The word kinetics is derived from the Greek word kinesis.
View SolutionFrom the rate expression for the following reactions, determine their order of reaction and the dimensions of the rate constants:
(i) 3NO(g)→N2O(g),Rate=k[NO]2
(ii) H2O2(aq)+3I−(aq)+2H+→2H2O(l)+I−3,Rate=k[H2O2][I−]
(iii) CH3CHO(g)→CH4(g)+CO(g),Rate=k[CH3CHO]3/2
(iv) C2H5Cl(g)→C2H4(g)+HCl(g),Rate=k[C2H5Cl]
View Solution(a) The electrical resistance of a column of 0.05MKOH solution of length 50 cm and area of cross-section 0.625cm2 is 5×103 ohm. Calculate its resistivity, conductivity and molar conductivity.
(b) Predict the products of electrolysis of an aqueous solution of CuCI2 with platinum electrodes.
[Given : EoCu2+/Cu=+0.34V,Eo(12CI2/CI−)=+1.36V,EoH+/H2(g),Pt=0.00V,E(12O2/H2O)=+1.23V]
OR
(a) Calculate e.m.f. of the following cell :
Zn(s)/Zn2+(0.1M)∣∣(0.01M)Ag+/Ag(s)
[Given : EoZn2+/Zn=−0.76V,EoAg+/Ag=+0.80V,log10=1]
(b) X and Y are two electrolytes. On dilution molar conductivity of 'X' increases 2.5 times while that Y increases 25 times. Which of the two is a weak electrolyte and why ?
View Solution(a) Why is bithional added to soap ?
(b) What is tincture of iodine ? Write its one use.
(c) Among the following, which one acts as a food preservative ?
Aspartame, Aspirin, Sodium Benzoate, Paracetamol
View SolutionThe rate equation for the decomposition of N_(2)O_(5) in C Cl_(4) is rate =K[N_(2)O_(5)] , where K=6.3xx10^(-4) s^(-1) at 320K . What would be the initial rate of decomposition of N_(2)O_(5) in a 0.10 M solution of N_(2)O_(5) ?
View SolutionConcentrations measured as a function of time when gaseous N2O5 at initial concentration of 0.0200M decomposes ot gaseous NO2andO2at50∘C.The change in concentration with time is given by the following graph.
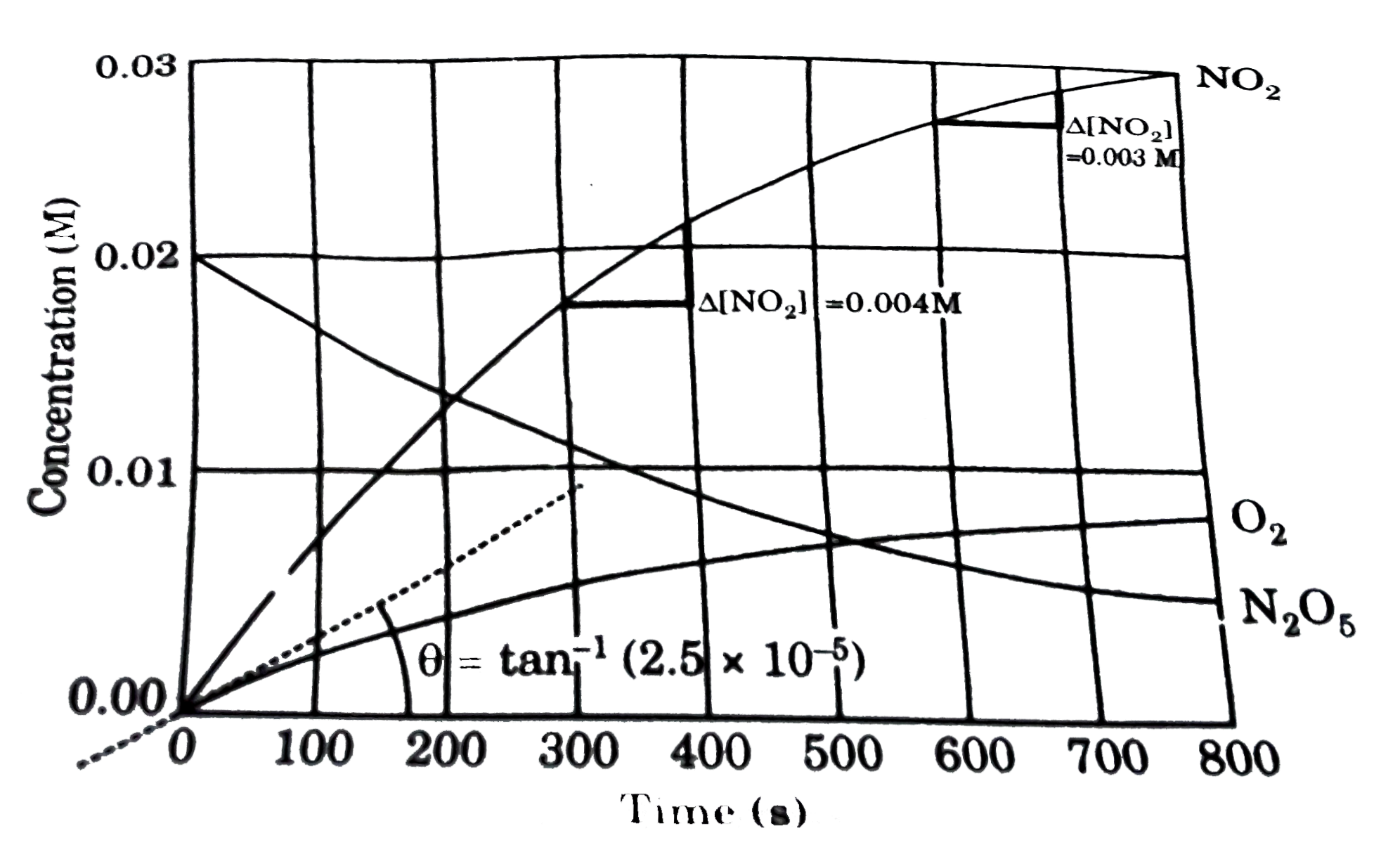
The rate of decomposition of N2O5during the period 300-400 s is :
View SolutionThe decomposition of N2O5 in chloroform was followed by measuring the volume of O2 gas evolved :
2N2O5(CC4)→2N2O4(CCl4)+O2(g). The maximum volume of O2 gas obtained was 100cm3. In 500 minutes, 90cm3 of O2 were evolved. The first order rate constant (in −1min) for the rate of disappearance of N2O5 is
View SolutionHeat of neutralisation of oxalic acid is -53.35 kJ/g.eq. using NaOH. Calculate the value of Detla H for the given reaction H_(2)C_(2)O_(4) hArr C_(2)O_(4)^(2-) + 2H^(+)
View SolutionDecomposition of N2O5 in liquid CCl4 is a first order reaction : 2N2O5→4NO2+O2 . The rate constant for this reaction is 3.66×10−2min−1.
At what concentration of N2O5 will the reaction -rate be 3.854×10−2mol.L−1.min−1 ?
View SolutionThe following data are obtained for the decomposition of H2O2 at 25∘C :
Time (min)0102030%decomposed0376075
Calculate the order , rate constant and half -life of the reaction.
View SolutionWhen 1 g of anhydrous oxalic acid is burnt at 25^(@)C , the amount of heat liberated is 2.835 kJ . Delta H combustion is (oxalic acid : C_(2)H_(2)O_(4))
View SolutionWhen 1.0g of oxalic acid (H_(2)C_(2)O_(4)) is burned in a bomb calorimeter whose heat capacity is 8.75kJ/K, the temperature increases by 0.312K. The enthalpy of combustion of oxalic acid at 27^(@)C
View SolutionRead the given passage and answer the questions:
Most of the chemical reactions are accelerated by increase in temperature. For example, in decomposition of N2O5, the time taken for half of the original amount of material to decompose is 12 min at 50∘C, 5 h at 25 ∘C and 10 days at 0 ∘C. You also know that is a mixture of potassium permaganate and oxalic acid H2C4O4, potassium permaganate KMnO4 gets decolourised faster at a higher temperature than at a lower temperature. It has been found that for a chemical reaction with rise in temperature by 10 ∘C, the rate constant is nearly doubled. The temperature dependence of the rate of a chemical reaction can be accurately explained by Arrhenius equation:
k=Ae−Ea/RT
where A is the frequency factor, Ea is the activation energy measured in joules per mole.
Q. In the volumetric titration of oxalic acid against potassium permanganate (KMnO4), we heat the oxalic acid solution to about 40 ∘C before performing the titration. Why?
View SolutionRead the given passage and answer the questions:
Most of the chemical reactions are accelerated by increase in temperature. For example, in decomposition of N2O5, the time taken for half of the original amount of material to decompose is 12 min at 50∘C, 5 h at 25 ∘C and 10 days at 0 ∘C. You also know that is a mixture of potassium permaganate and oxalic acid H2C4O4, potassium permaganate KMnO4 gets decolourised faster at a higher temperature than at a lower temperature. It has been found that for a chemical reaction with rise in temperature by 10 ∘C, the rate constant is nearly doubled. The temperature dependence of the rate of a chemical reaction can be accurately explained by Arrhenius equation:
k=Ae−Ea/RT
where A is the frequency factor, Ea is the activation energy measured in joules per mole.
Q. How does the time required for half change vary with the change in time?
View Solution

