Two identical concave mirrors M1 & M2 with principal axes perpendicular to each other and pole P1 of mirror M1 at origin is as shown. Let 'f' be the focal length and C be the common centre of curvature for both mirrors. A point object 'O' is at (-5f, 0) and is moving with a velocity →V=V0ˆim/s
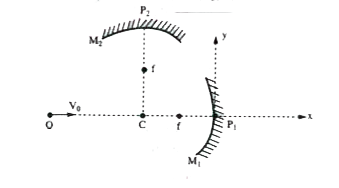
Consider rays incident on mirror M,, the final image formed is
real
virtual
may be real or virtual
all of these
The correct Answer is:A
Topper's Solved these Questions
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - GEOMETRICAL OPTICSEXERCISE - PRACTICE SHEET (EXERICSE-II (LEVEL-II (ADVANCED) MATRIX MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS))
1 Video
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - GEOMETRICAL OPTICSEXERCISE - PRACTICE SHEET (EXERICSE-II (LEVEL-II (ADVANCED) INTEGER TYPE QUESTIONS))
5 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - GEOMETRICAL OPTICSEXERCISE - PRACTICE SHEET (EXERICSE-II (LEVEL-II (ADVANCED) STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS))
2 Videos
- ELEMENTS OF VECTORSBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - ELEMENTS OF VECTORSEXERCISE - QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWERS
9 Videos
- LAWS OF MOTIONBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - LAWS OF MOTIONEXERCISE - PRACTICE EXERCISE
98 Videos
Similar Questions
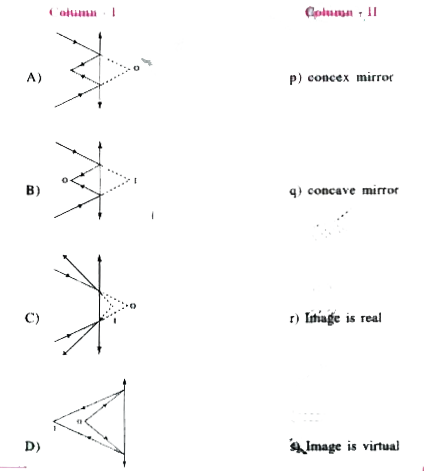
Column-I contains the path traced by light rays and the positions of object and image, with a reflecting spherical mirror. Choose the possible options for type of mirror and the nature of image rom Column-II to each case in Column- I
View SolutionTwo plane mirrors are making an angle of 60∘ to each other. A light ray falls on one of the mirrors. The light ray is incident parallel to angular bisector of mirrors. How many reflection does the light ray undergo ?
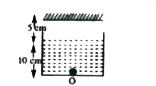
View SolutionConsider the situation shown in figure. Water (μw = 4/3) is filled in a beaker upto a height of 10 cm. A plane mirror is fixed at a height of 5 cm from the surface of water. Distance of image from the mirror after reflection from it of an object O at the bottom of the beaker is:
View SolutionFind the components of vector ¯¯¯A=2ˆi+3ˆj along the directions of ˆi+ˆjandˆi−ˆj
View SolutionA force of 50 N acts on a body of mass 10 kg at rest. Its velocity after 5 seconds if the same force acts, is
View SolutionA plane mirror (M_1) and a concave mirror (M_2) of focal length 10 cm are arranged as shown in figure. An object is kept at origin. Answers the following questions. (consider image formed by single reflection in all cases). If concave mirror is replaced by convex mirror of same focal length then coordinates of image formed by (M_2) will be
View SolutionA plane mirror (M1) and a concave mirror (M2) of focal length 10 cm are arranged as shown in figure. An object is kept at origin. Answers the following questions. (consider image formed by single reflection in all cases).
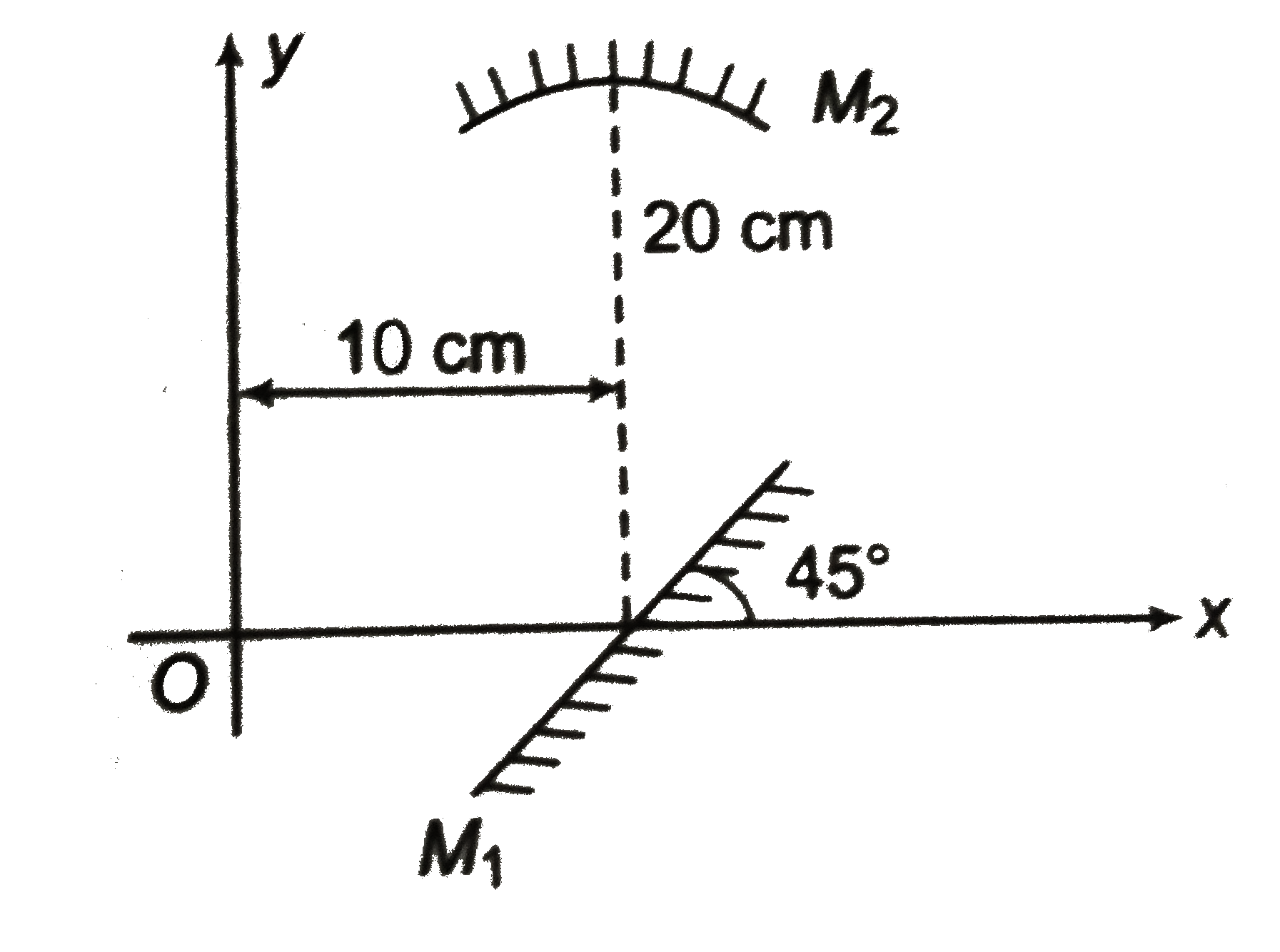
if concove mirror is replaced by another plane mirror parallel to x-axis, then coordinates of image formed by (M2) are
View SolutionA point object 'O' is at the center of curvature of a concave mirror. The mirror starts to move at a speed u, iin a direction perpendicular to the principal axis. Then, the initial velocity of the image is
View Solutiona) An object is kept between centre of curvature and principal focus of a concave mirror. Write the nature of the image formed.
b) Define focal length of a convex mirror. Write the relationship between focal length and radius of curvature of a convex mirror.
View SolutionWhen an object is placed at a distance of 25cm from a mirror, the magnification is m1. The object is moved 15 cm farther away with respect to the earlier position, and the magnification becomes m2. If m1m2 = 4, then calculate the focal length of the mirror.
View SolutionAn object O is placed in front of a small plane mirror M1 and a large convex mirror M2 of focal length f. The distance between O and M1 is x and the distance between M1andM2 is y. The images of O formed by M1andM2 coincide. The magnitude of f is
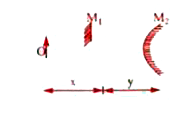
View SolutionAn object 'O' is placed in front of a small plane mirror M_1 and a large convex mirror M_2 of focal length 'f'. The distanace between 'O' and M_1 is x and the distance between M_1 and M_2 is y. The images of 'O' formed by M_1 and M_2 coincide. The magnitude of 'f is
View SolutionWhen an object is placed at a distance of 25 cm from a concave mirror, the magnification is m_1 . The object is moved 15 cm farther away with respect to the earlier position, and the magnification becomes m_2 . If m_1//m_2 = 4 the focal length of the mirror is (Assume that image is real and m_1, m_2 are numerical values)
View SolutionTwo identical concave mirrors M1 & M2 with principal axes perpendicular to each other and pole P1 of mirror M1 at origin is as shown. Let 'f' be the focal length and C be the common centre of curvature for both mirrors. A point object 'O' is at (-5f, 0) and is moving with a velocity →V=V0ˆim/s
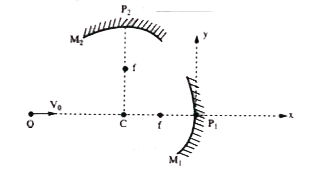
Consider rays incident on mirror M2, the co-ordinates of the final image formed is
View SolutionTwo identical concave mirrors M1 & M2 with principal axes perpendicular to each other and pole P1 of mirror M1 at origin is as shown. Let 'f' be the focal length and C be the common centre of curvature for both mirrors. A point object 'O' is at (-5f, 0) and is moving with a velocity →V=V0ˆim/s
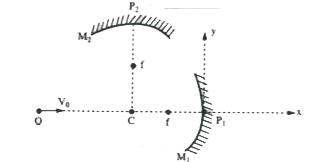
Consider rays incident on mirror M1, the coordinates of the final image is
View Solution

