A gas with CP/CV=γ goes from an initial state (P1,V1,T1) to a final state (P2,V2,T2) through an adiabatic process. The work done by the gas is
a) nR(T1−T2)γ−1
b) P1V1−P2v2γ−1
c) nRγ(T1−T2)
a and b are true
b and c are true
both a and c are true
a, b, c are true
The correct Answer is:A
Similar Questions
A gas with cpcV=γ goes from an intial state (p1,V1,T1) to a final state (p2,V2,T2) through an adiabatic process. The work done by the gas is
View SolutionA gas with cpcV=γ goes from an intial state (p1,V1,T1) to a final state (p2,V2,T2) through an adiabatic process. The work done by the gas is
View Solution
Knowledge Check
An ideal gas is transformed from state A(P1,V1) to the state B(P2,V2) through path AB. In this process the work done by the gas is
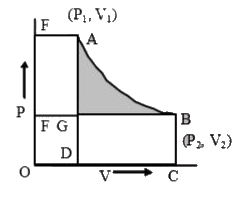 AW = area ABCDABW = area ABEFACW = area ABGADW = area ABCOFA
AW = area ABCDABW = area ABEFACW = area ABGADW = area ABCOFAOne mole of a gas in the state A(P1,V1,T1) is subjected to adiabatic expansion to attain state B(P2,V2,T2). The work done by the gas is:
A−R(T1−T2)γ−1BnR(T2−T1)γ−1CR(T2−T1)1−γDP2V2−P1V11−γAn ideal gas is expand from (p1,V1,T1) to (p2,V2,T2) under different conditions. The correct statement(s) among the following is (are):
AThe work done by the gas is less when it is expanded reversibly from V1 to V2 under adiabatic conditions as compared to that when expanded reversibly from V1 to V2 under isothermal conditionsBThe change in internal energy of the gas is (i) zero, if it is expanded reversibly with T1=T2, and (ii) positive, if it is expanded reversibly under adiabatic conditions with T1≠T2CIf the expansion is carried out freely, it is simultaneously both isothermal as well as adiabaticDThe work done on the gas is maximum when it is compressed irreversibly from (P2,V2) to (P1,V1) against constant pressure P1
An ideal gas expands adiabatically from an initial temperature T1 to a final temperature T2. Prove that the work done by the gas is CV(T1−T2).
View SolutionAn ideal gas follows a process described by PV2=C from (P1,V1,T1) to (P2,V2,T2) (C is a constant). Then
View SolutionA gaseous system changes from state A(P1,V1,T1) to B(P2,V2,T2) to C(P3,V3,T3) and finally from C to A. The whole process may be called :
View SolutionA gaseous system changes from state A(P1,V1,T1) to B(P2,V2,T2), B to C(P3,V3,T3) and finally from C to A. The whole process may be called
View SolutionA gaseous system changes from state A(P1,V1,T1) to B(P2,V2,T2), B to C (P3,V3T3) and finally from C to A. The whole process may be called
View Solution

