Two cylinders having radii 2R and R and moment of inertia 4I and I about their central axes are supported by axles perpendicular to their planes. The large cylinder is initially rotating clockwise with angular velocity ω0. The small cylinder is moved to the right until it touches the large cylinder and is caused to rotate by the frictional force between the two. Eventually slipping ceases and the two cylinders rotate at constant rates in opposite directions. During this
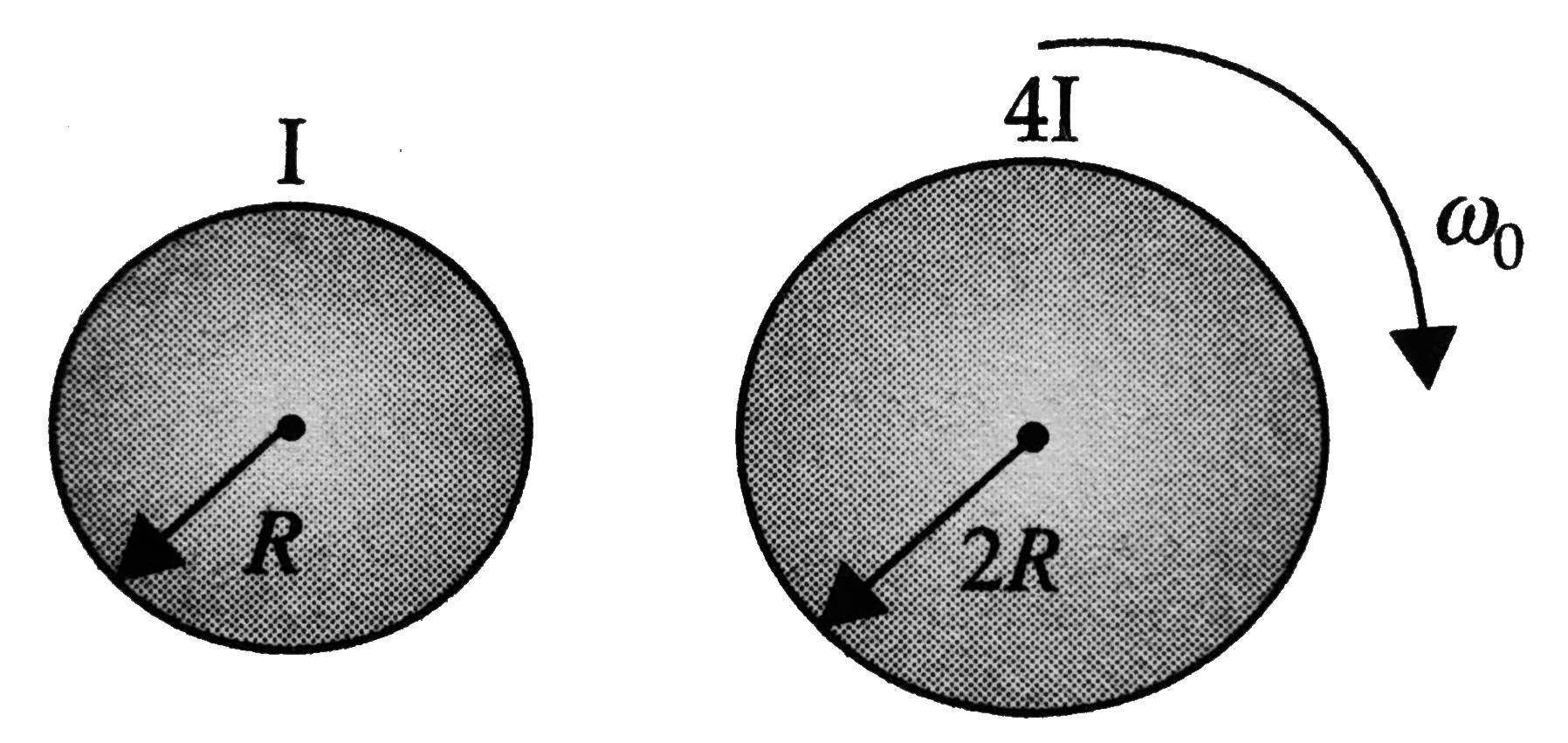
angular momentum of system is conserved
kinetic energy is conserved
neither the angular momentum nor the kinetic energy is conserved
both the angular momentum and kinetic energy are conserved
The correct Answer is:C
Step by step video solution for Two cylinders having radii 2R and R and moment of inertia 4I and I about their central axes are supported by axles perpendicular to their planes. The large cylinder is initially rotating clockwise with angular velocity omega_(0). The small cylinder is moved to the right until it touches the large cylinder and is caused to rotate by the frictional force between the two. Eventually slipping ceases and the two cylinders rotate at constant rates in opposite directions. During this by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- ROTATIONAL MOTIONBOOK - DC PANDEY ENGLISHCHAPTER - ROTATIONAL MOTIONEXERCISE - A Only One Option is Correct
86 Videos
- ROTATIONAL MOTIONBOOK - DC PANDEY ENGLISHCHAPTER - ROTATIONAL MOTIONEXERCISE - More than one option is correct
36 Videos
- ROTATIONAL MECHANICSBOOK - DC PANDEY ENGLISHCHAPTER - ROTATIONAL MECHANICSEXERCISE - Subjective Questions
2 Videos
- SEMICONDUCTORS AND ELECTRONIC DEVICESBOOK - DC PANDEY ENGLISHCHAPTER - SEMICONDUCTORS AND ELECTRONIC DEVICESEXERCISE - More than One Option is Correct
3 Videos
Similar Questions
A cylinder of water, is rotating about its own axis with uniform angular velocity ω. The shape of free surface of water will be
View SolutionFind the moment of inertia of a uniform cylinder about an axis through its centre of mass and perpendicular to its base. Mass of the cylinder is M and radius is R.
View SolutionFigure shows two cylinders of radii r1andr2 having moments of inertia I1andI2 about their respective axes. Initially the cylinders rotate about their axes with angular speed ω1andω2 as shown in the figure. The cylinders are moved closer to touch each other keeping the axes parallel. The cylinders first slip over each other at the contact but the slipping finally ceases due to the friction between them. Find the angular speeds of the cylinders after the slipping ceases.

View SolutionA solid cylinder of mass 20kg rotates about its axis with angular velocity of 100 radian s−1. The radius of the cylinder is 0.25m. The magnitude of the angular momentum of the cylinder about its axis of rotation is
View SolutionA cylinder rests on a horizontal rotating disc, as shown in the figure. Find at what angular velocity, ω, the cylinder falls off the disc, if the distance between the axes of the disc and cylinder is R, and the coefficient of friction μ>D/h where D is the diameter of the cylinder and It is its height.

View SolutionVelocity of the centre of a small cylinder is v. There is no slipping anywhere. The velocity of the centre of the larger cylinder is

View SolutionA clockwise torque of 6N−m is applied to the circular cylinder as shown in the figure. There is no friction between the cylinder and the block.

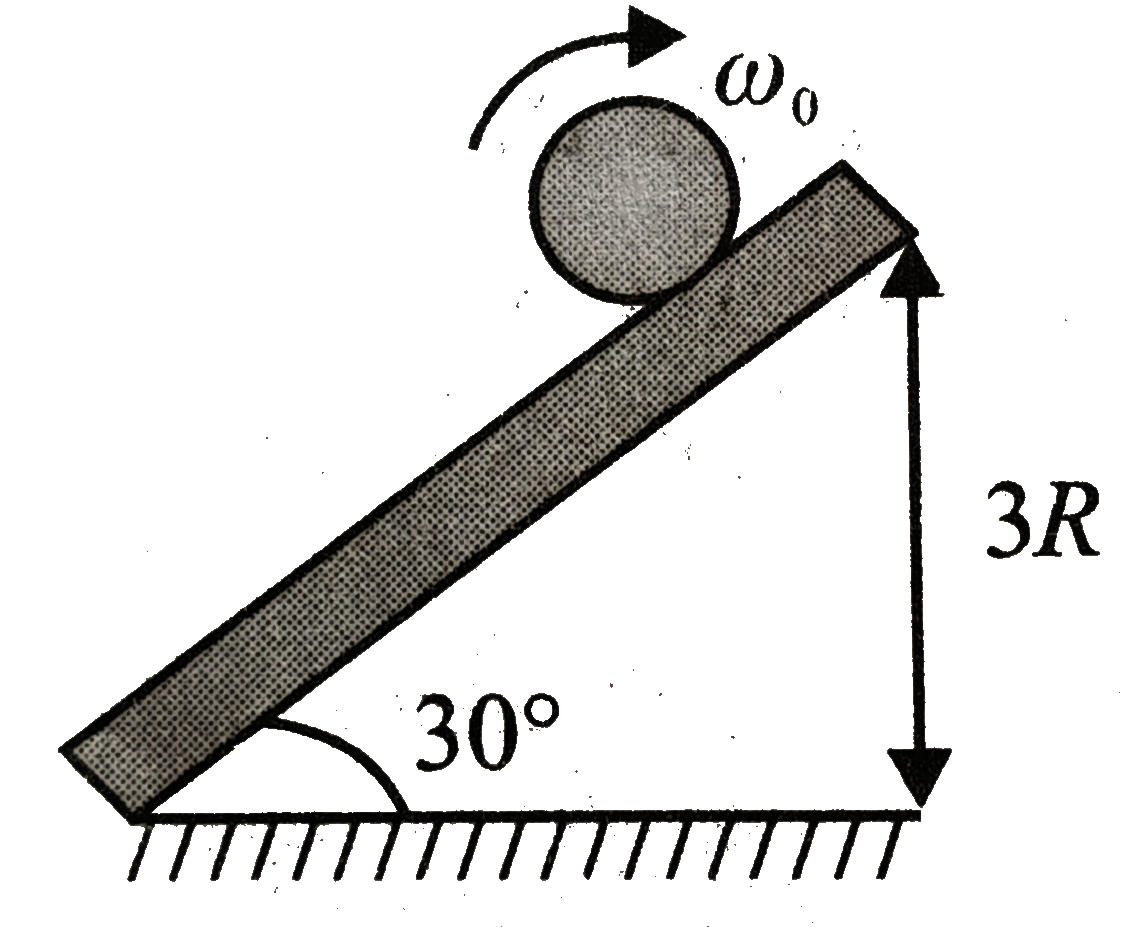
View SolutionA spinning cylinder with angular velocity ω0 of mass M and radius R is lowered on a rough inclined plane of angle 30∘ with the horizontal and μ=1/√3. The cylinder is released at a height of 3R from horizontal. Find the total time taken by the cylinder to reach the bottom of the incline.
View Solution_S01_038_Q01.png)
As per the shown figure the central solid cylinder starts with initial angular velocity ω0 Find the time after which the angular velocity becomes half.
View SolutionWhat is moment of inertia of a cylinder of radius r, along its height?
View Solution

