A bullet of mass 'm' moving with velocity 'u' passes through a wooden block of mass M=nm as shown in figure. The block is resting on a smooth horizontal floor. After passing through the block, velocity relative to the block is
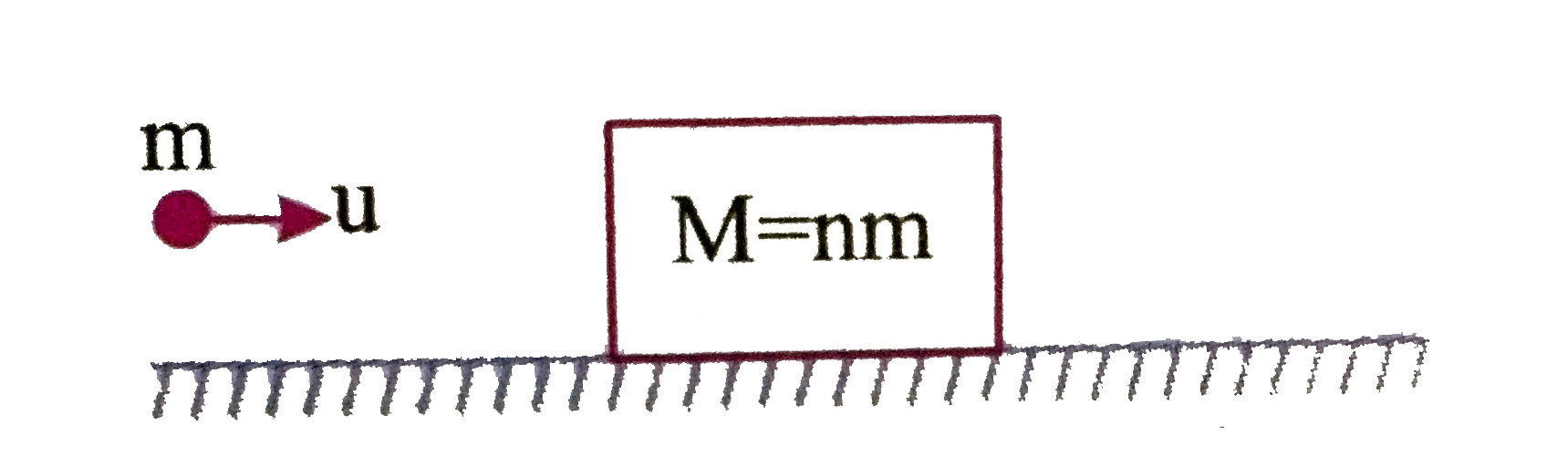 .
.
(1+n)v−un
nv−un+1
nu−vn+1
(1+n)v+u2n+1
Step by step video solution for A bullet of mass 'm' moving with velocity 'u' passes through a wooden block of mass M = nm as shown in figure. The block is resting on a smooth horizontal floor. After passing through the block, velocity relative to the block is . by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- CENTRE OF MASS, IMPULSE AND MOMENTUMBook:DC PANDEY ENGLISHChapter:CENTRE OF MASS, IMPULSE AND MOMENTUMExercise:More a than one option is Correct
Explore 1 Video
- CENTRE OF MASS, IMPULSE AND MOMENTUMBook:DC PANDEY ENGLISHChapter:CENTRE OF MASS, IMPULSE AND MOMENTUMExercise:Comprehension type questions
Explore 15 Videos
- CENTRE OF MASS, IMPULSE AND MOMENTUMBook:DC PANDEY ENGLISHChapter:CENTRE OF MASS, IMPULSE AND MOMENTUMExercise:Comprehension type questions
Explore 15 Videos
- CENTRE OF MASSBook:DC PANDEY ENGLISHChapter:CENTRE OF MASSExercise:Medical entrances gallery
Explore 27 Videos
- CENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONBook:DC PANDEY ENGLISHChapter:CENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONExercise:Level 2 Subjective
Explore 21 Videos
Similar Questions
A ball mass 2 kg moving horizontally with velocity 10 m/s hits a wedge of mass 5 kg placed on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure. Just after collision klvelocity of wedge is 3.2 m/s. There is no friction at any contact surface. Then (take sin 30∘=3/5)
View SolutionComprehension # 1
If net force on a system in a particular direction is zero (say in horizontal direction), we can apply: ΣmRxR=ΣmLxL,ΣmRvR=ΣmLvL and ΣmRaR=ΣmLaL
Here R stands for the masses which are moving towards right and L for the masses towards left, x is displacement, v is velocity and a the acceleration (all with respect to ground).
A small block of mass m=1kg is placed over a wedge of mass M=4kg as shown in figure. Mass m is released from rest. All surface are smooth. Origin O is as shown.
Final velocity of the wedge is ..........m/s :-
View SolutionComprehension # 1
If net force on a system in a particular direction is zero (say in horizontal direction), we can apply: ΣmRxR=ΣmLxL,ΣmRvR=ΣmLvL and ΣmRaR=ΣmLaL
Here R stands for the masses which are moving towards right and L for the masses towards left, x is displacement, v is velocity and a the acceleration (all with respect to ground).
A small block of mass m=1kg is placed over a wedge of mass M=4kg as shown in figure. Mass m is released from rest. All surface are smooth. Origin O is as shown.

Final velocity of the wedge is ..........m/s :-
View SolutionA rod of weight w is supported by two parallel knife edges A and B and is in equilibrium in a horizontal position. The knives are at a distance d from each other. The centre of mass of the rod is at distance x from A. The normal reaction on A is.. And on B is......
View SolutionA ladder AP of length 5m inclined to a vertical wall is slipping over a horizontal surface with velocity of 2m/s, when A is at distance 3m from ground. What is the velocity of COM at this moment?
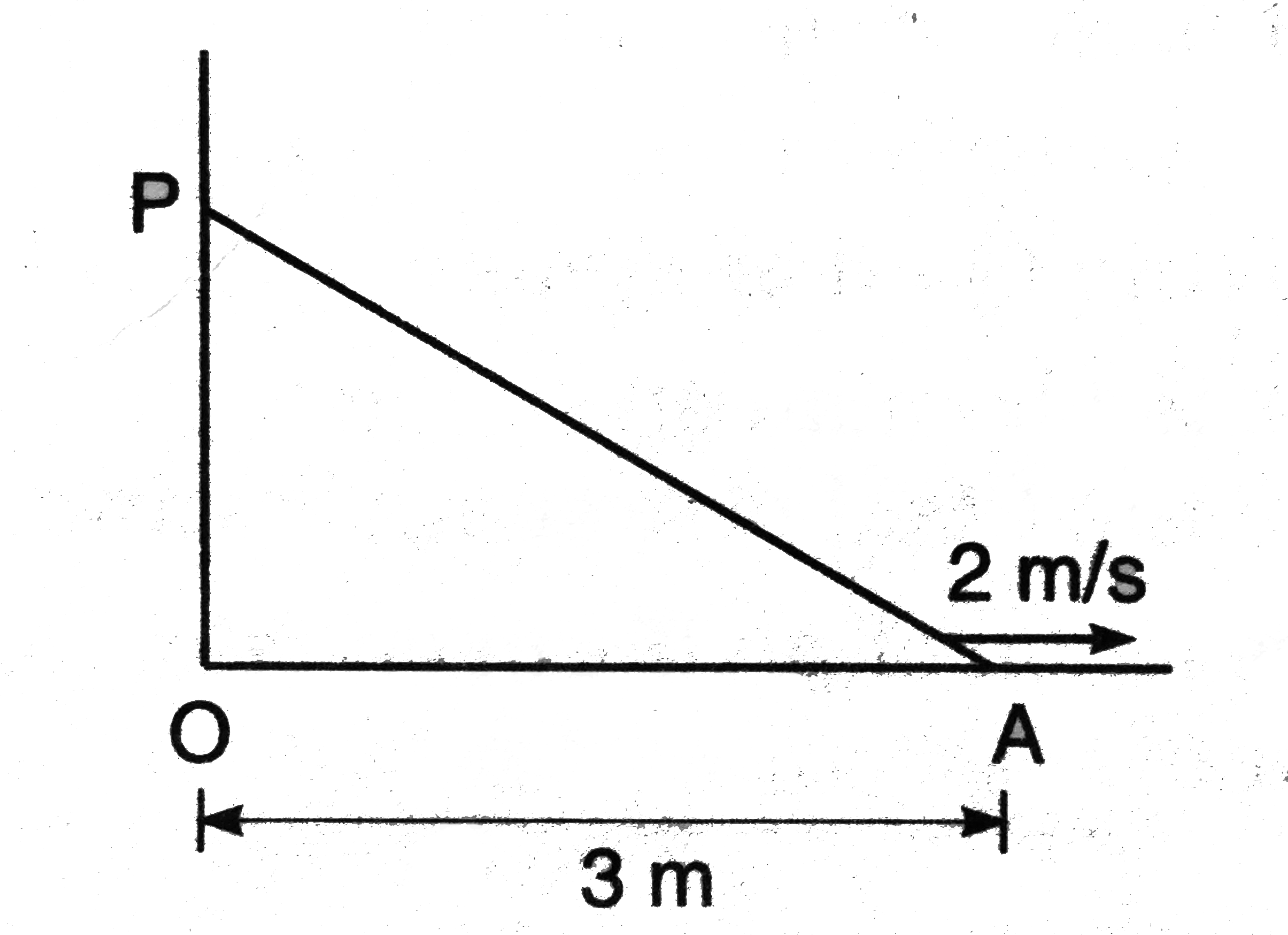

View SolutionA bullet of mass 10gm moving with a horizontal velocity 100m/s passes through a wooden block of mass 100gm. The block is resting on a smooth horizontal floor. After passing through the block the velocity of the bullet is 10m/s the velocity of the emerging bullet with respect to the block is .
View SolutionA bullet of mass 'm' moving with velocity 'u' passes through a wooden block of mass M=nm as shown in figure. The block is resting on a smooth horizontal floor. After passing through the block, velocity relative to the block is
 .
.
View SolutionA bullet of mass m moving with velocity υ1 strikes a suspended wooden block of mass M as shown in the figure and sticks to it. If the block rises to a height y. the initial of the bullet is
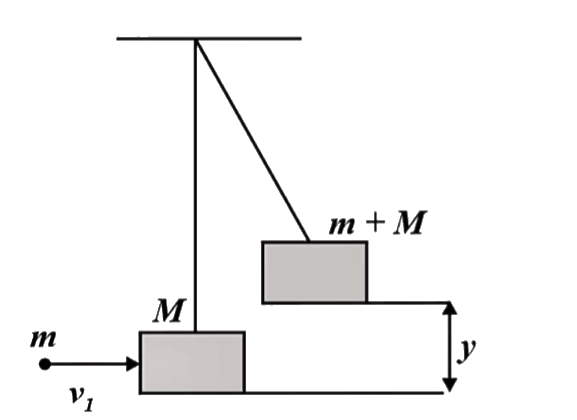
View SolutionA bullet of mass 50 g , moving with a velocity of 50m⋅s−1 hits and enters a wooden block of mass 2kg and comes to rest within it. The wooden block was initially at rest on a smooth table. Find the final velocity of the wooden block. What are the initial and final kinetic energies of the block-bullet system?
View SolutionA bullet of mass 10 gm moving with a horizontal velocity 100m//s passes through a wooden block of mass 100 gm. The block is resting on a smooth horizontal floor. After passing through the block the velocity of the bullet is 10m//s . the velocity of the emerging bullet with respect to the block is
View SolutionA bullet of mass 'm' moving with velocity *v' strikes a block of mass 'M' at rest and gets embeded into it. The K.E. of composite block will be:
View SolutionA bullet of mass 25 g moving with velocity of 500 ms^(-1) enters into a wooden block and comes out of it with a velocity of 100 ms^(-1) . Find the work done by the bullet while passing through the wooden block.
View SolutionA bullet of mass 2.5 g moving with a velocity of 500 ms−1 enters a wooden block and comes out of it with a velocity of 100 ms−1. Find the work done by the bullet while passing through the wooden block.
View SolutionA bullet of mass 50 g moving with a velocity of 500 ms−1 enters into a wooden block and comes out of it with a velocity of 100 ms−1. Find the work done by the bullet while passing through the wooden block.
View SolutionA bullet of mass m moving with velocity u passes through a wooden block of mass M=nm as shown in figure. The block is resting on a smooth horizontal floor. After passing through the block, velocity of the bullet becomes v. Its velocity relative to the block is

View SolutionA bullet of mass 0.04kg travelling horizontally at 100 m/s hits a stationary block of wood of mass 8kg, passes through it and emerges horizontally with a speed of 40 m/s. If the block is free to move on a smooth horizontal plane, what is the speed with which it moves after the bullet had passed through it?
View Solution
