State the law of conservation of mass.
Step-by-Step Text Solution:
1. Understanding the Concept: The law of conservation of mass is a fundamental principle in chemistry that relates to the mass of substances involved in chemical reactions.
2. Definition: The law states that in an isolated system, mass is neither created nor destroyed during chemical reactions or physical transformations. This means that the total mass of the reactants (the substances that undergo the reaction) is equal to the total mass of the products (the substances that are formed).
3. Implication: This principle implies that during any chemical reaction, the mass of the substances before the reaction (reactants) will be the same as the mass of the substances after the reaction (products).
4. Conclusion: Therefore, the law of conservation of mass can be summarized as: "The mass of the reactants is equal to the mass of the products in a chemical reaction."
---
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
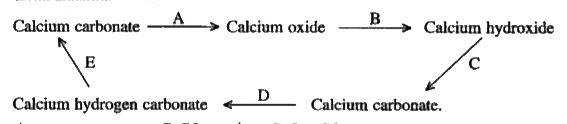
Write equation for each conversion A to E.
View SolutionName a gas which reduces hot copper (II) oxide to copper.
View SolutionGive reasons :
Sodium is kept in an inert solvent.
View SolutionState the law of conservation of mass. Give one example to illustrate this law.
View SolutionState the explain the law of conservation of mass. Describe an activity to chek the validity of the law .
View SolutionState the law of conservation of momentum.
View SolutionState Law of Conservation of Energy of mass.
View SolutionState the law of conservation of mass. How is it verified experimentally ?
View SolutionState and explain the law of conservation of mass.
View SolutionState the law of conservation of energy.
View SolutionState the law of conservation of energy.
View SolutionState the law of conservation of mass.
View SolutionState of law of conservation of mass.
View SolutionThe law of conservation of energy states that, _______ .
View SolutionState the law of conservation of charge.
View Solution
