A student puts his pencil into an empty trough and observes the pencil from the position as indicated in Figure.

(i) What change will be observed in the appearance of the pencil when water is poured into the trough?
(ii) Name the phenomenon which accounts for the above stated observation.
(iii) Complete the diagram showing how the student's eye sees the pencil through water.
Step by step video solution for A student puts his pencil into an empty trough and observes the pencil from the position as indicated in Figure. (i) What change will be observed in the appearance of the pencil when water is poured into the trough? (ii) Name the phenomenon which accounts for the above stated observation. (iii) Complete the diagram showing how the student's eye sees the pencil through water. by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 10 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACESBook:ICSEChapter:REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACESExercise:EXERCISE-4(C) MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
Explore 2 Videos
- REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACESBook:ICSEChapter:REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACESExercise:EXERCISE-4(C) NUMERICALS
Explore 3 Videos
- REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACESBook:ICSEChapter:REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACESExercise:EXERCISE-4(B) NUMERICALS
Explore 2 Videos
- REFRACTION OF LIGHTBook:ICSEChapter:REFRACTION OF LIGHTExercise:DIAGRAM BASED MCQ:
Explore 5 Videos
- REFRACTION THROUGH A LENS Book:ICSEChapter:REFRACTION THROUGH A LENS Exercise:EXERCISE-5(D) (MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE)
Explore 2 Videos
Similar Questions
Jatin puts a pencil into a glass container having water and is surprised to see the pencil in a different state.
What change is observed in the appearance of the pencil?
View SolutionJatin puts a pencil into a glass container having water and is surprised to see the pencil in a different state.
Name the phenomenon responsible for the change.
View SolutionJatin puts a pencil into a glass container having water and is surprised to see the pencil in a different state.
Draw a ray diagram showing how the eyes saw the pencil.
View Solution(a) A student dropped a few pieces of marble in dilute hydrochloric acid contained in
a test tube. The evolved gas was passed through lime water. What change would
be observed in lime water ? Write balanced chemical equations for both the
changes observed.
(b) State the chemical property in each case on which the following uses of baking
soda are based:
(i) as an antacid (ii) as a constituent of baking powder.
View SolutionA coil of insulated wire is connected to a galvanometer. What would be seen if a bar magnet with its south pole towards one face of the coil is
(i) moved quickly toward it
(ii) moved quickly away from it
(iii) placed near its one face ?
These activities are then repeated with north pole of the magnet. What will be the observations?
(b) Name and define the phenomenon involved in above activities.
(c) Name the rule which can determine the direction of current in each case.
View SolutionA point source of light O of single colour is seen through a rectangular glass slab PQRS. The paths of two rays, in and outside the slab, are shown in figure.
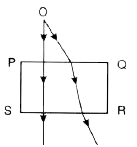
In the diagram, label the position I of the source O where it will appear when seen through the surface RS.
(ii) Does the source O appear to be nearer or farther with respect to the surface PQ ?
(iii) How does the shift depend on the thickness PS or QR of the slab?
(iv) Justify your answer in (iii) with the help of an appropriate ray diagram.
(v) For the same rectangular glass slab, which colour from the visible spectra (violet to red) will produce the maximum shift ?
View SolutionIn figure, PQ and PR are the two light rays emerging from an object P. the ray PQ is refracted as QS.
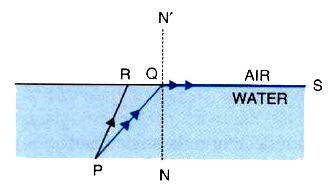
(a) state the special name given to the angle of incidence ∠PQN for the ray PQ.
(b) What is the angle of refraction for the refracted ray QS?
(c) Name the phenomenono that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased.
(d) The ray PR suffers partial reflection and refraction on the water-air surface. give reason.
(e) Draw in the diagram the refracted ray for the incident ray PR and hence show the position of the image of the object P by the letter P' when seen vertically from above.
View SolutionBunty was fond of painting. He observed that hairs of paint brush do not cling together when dry and even when dipped in water but form a fine tip when taken out of it. He was quite surprised to see it but found it very useful for doing neat and beautiful painting. He asked his elder sister Shanti, who was a science student of class XI, that why do hairs of a paint brush cling together when taken out of water. His elder sister explained him the reason nicely.
(i) What are the values displayed by Bunty here?
(ii) Why do the hairs of a paint brush cling together when taken out of water?\
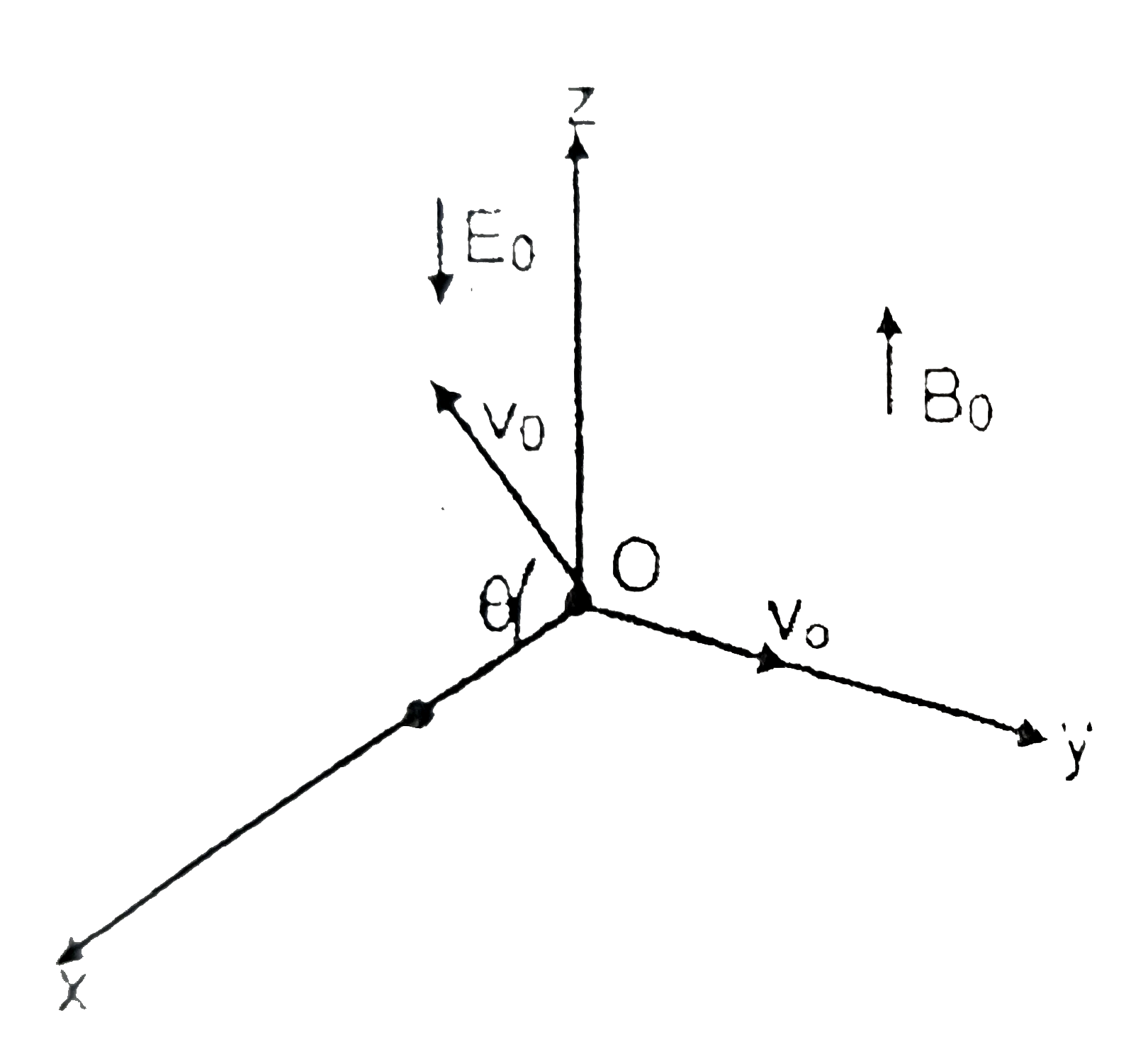
View SolutionA charged point particle having positive charge q, mass m is projected in x−z plane with a speed v0 at an angle θ with the x−axis , while another identical particle is projected simultaneously along the y−axis from the origin (see figure) with an equal speed v0.
An electric field →E=−E0ˆk exists in the x−z plane, while a magnetic field →B=B0ˆk exists in the region y>0 (F0, B0>0). It is observed that both the particles collide after some time. Assume that the space is gravity free.
(i) Find the time after which the particles collide and the coordinates of the point of collision.
(ii) Find the velocity v0 and the angle θ in terms of the other variables.
(iii) What is the maximum value of the z− coordinate of the first particle ?
View SolutionThin films, including soap bubbles and oil show patterns of alternative dark and bright regions resulting from interference among the reflected ligth waves. If two waves are in phase, their crests and troughs will coincide. The interference will be cosntructive and the amlitude of resultant wave will be greater then either of constituent waves. If the two wave are not of phase by half a wavelength (180∘), the crests of one wave will coincide width the troughs of the other wave. The interference will be destructive and the ampliutde of the resultant wave will be less than that of either consituent wave.
1. When incident light I, reaches the surface at point a, some of the ligth is reflected as ray Ra and some is refracted following the path ab to the back of the film.
2. At point b, some of the light is refracted out of the film and part is reflected back through the film along path bc. At point c, some of the light is reflected back into the film and part is reflected out of the film as ray Rc.
Ra and Rc are parallel. However, Rc has travelled the extra distance within the film fo abc. If the angle of incidence is small, then abc is approxmately twice the film's thickness .
If Ra and Rc are in phase, they will undergo constructive interference and the region ac will be bright. If Ra and Rc are out of phase, they will undergo destructive interference and the region ac will be dark.
I. Refraction at an interface never changes the phase of the wave.
II. For reflection at the interfere between two media 1 and 2, if n1>n2, the reflected wave will change phase. If n1<n2, the reflected wave will not undergo a phase change.
For reference, nair=1.00.
III. If the waves are in phase after reflection at all intensities, then the effects of path length in the film are:
Constrictive interference occurs when 2t=mλ/n,m=0,1,2,3,...
Destrcutive interference occurs when 2t=(m+12)λn,
m=0,1,2,3,...
If the waves are 180∘ out of the phase after reflection at all interference, then the effects of path length in the film ara:
Constructive interference occurs when
2t=(m+12)λn,m=0,1,2,3,...
Destructive interference occurs when
2t=mλn,m=0,1,2,3,...
The average human eye sees colors with wavelength between 430 nm to 680 nm. For what visible wavelength (s) will a 350 nm thick (n=1.35) soap film produce maximum destructive interference?
View Solution

