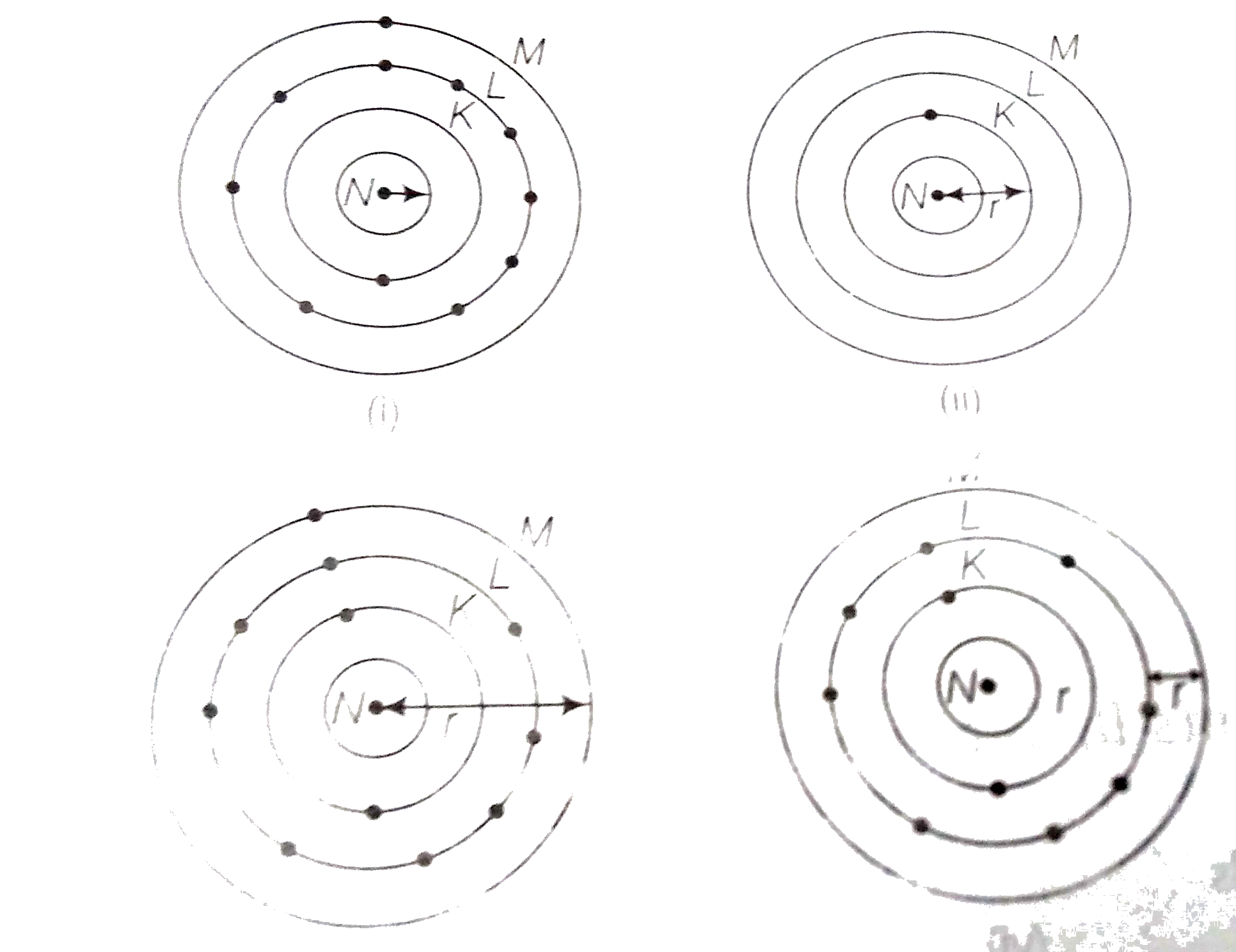
Which one of the figures I and II represents the correct measure of atomic radius (r)?
To determine which figure represents the correct measure of atomic radius, we need to understand the definition of atomic radius and analyze the two figures provided.
1. Understand the Definition of Atomic Radius:
- The atomic radius is defined as the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the boundary of its valence shell, which contains the valence electrons.
2. Analyze Figure I:
- In Figure I, measure the distance from the nucleus to what is depicted as the outer boundary.
- Check if this boundary represents the valence shell where the valence electrons are located.
- If there are additional shells or electrons beyond this boundary, it indicates that this measurement does not accurately represent the atomic radius.
3. Analyze Figure II:
- In Figure II, measure the distance from the nucleus to the outermost shell that contains the valence electrons.
- Ensure that this measurement only includes the valence shell and does not extend into other shells that do not contain valence electrons.
4. Comparison of Figures:
- Compare the measurements from both figures.
- Figure II should show a measurement that correctly aligns with the definition of atomic radius, capturing only the distance to the valence shell.
5. Conclusion:
- Based on the analysis, Figure II correctly represents the atomic radius as it measures the distance from the nucleus to the outermost shell containing the valence electrons.
Final Answer:
- Figure II is the correct measure of atomic radius.
---
- The atomic radius is defined as the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the boundary of its valence shell, which contains the valence electrons.
- In Figure I, measure the distance from the nucleus to what is depicted as the outer boundary.
- Check if this boundary represents the valence shell where the valence electrons are located.
- If there are additional shells or electrons beyond this boundary, it indicates that this measurement does not accurately represent the atomic radius.
- In Figure II, measure the distance from the nucleus to the outermost shell that contains the valence electrons.
- Ensure that this measurement only includes the valence shell and does not extend into other shells that do not contain valence electrons.
- Compare the measurements from both figures.
- Figure II should show a measurement that correctly aligns with the definition of atomic radius, capturing only the distance to the valence shell.
- Based on the analysis, Figure II correctly represents the atomic radius as it measures the distance from the nucleus to the outermost shell containing the valence electrons.
- Figure II is the correct measure of atomic radius.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- PERIODIC PROPERTIES OF ELEMENTS BOOK - ICSECHAPTER - PERIODIC PROPERTIES OF ELEMENTS EXERCISE - QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE ON EXAMINATION PATTERN (SECTION I)
2 Videos
- PERIODIC PROPERTIES AND VARIATIONS OF PROPERTIES (PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL) BOOK - ICSECHAPTER - PERIODIC PROPERTIES AND VARIATIONS OF PROPERTIES (PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL) EXERCISE - Questions from Previous ICSE Board Papers (2018)
5 Videos
- PERIODIC PROPERTIES AND VARIATIONS OF PROPERTIESBOOK - ICSECHAPTER - PERIODIC PROPERTIES AND VARIATIONS OF PROPERTIESEXERCISE - ASSERTION AND REASON BASED QUESTIONS
5 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Which of the following values does not represent the correct value of R ?
A8.314 Pa m3K−1mol−1B8.314×102bar LK−1mol−1C0.0821jk−1mol−1D8.314jk−1mol−1Which one of the following arrangements represents the correct order of electron gain enthalpy of the given atomic species?
AS<OCl<FBCl<F<S<OCF<Cl<O<SDO<S<F<Cl
The set representing the correct order of ionic radius is
View SolutionWhich is/are the correct order/s of atomic radius?
View SolutionWhich is /are the correct order/s of atomic radius?
View SolutionWhich of the following arrangements represents the correct order of increasing radius?
View SolutionWhich one of the following arrangements represents the correct order of electron gain enthalpy of the given atomic species?
View SolutionWhich one of the following arrangements represents the correct order of electron gain enthalpy of the given atomic species?
(a)Cl<F<S<O
(b) O<S<F<Cl
(c) S<O<Cl<F
(d) F<Cl<O<S
View Solution