Write the correctly balanced net ionic equations for the reations whose equilibrium constant at 298 K are
Ka(H2C2O4)=5.4×10−2
To write the correctly balanced net ionic equation for the dissociation of oxalic acid (H₂C₂O₄) in water, we follow these steps:
Step 1: Write the formula for oxalic acid
The chemical formula for oxalic acid is H₂C₂O₄.
Step 2: Identify the dissociation process
When oxalic acid dissolves in water, it dissociates into its ions. The dissociation can be represented as:
H2C2O4(aq)→C2O2−4(aq)+2H+(aq)
Step 3: Include water in the reaction
Since we are considering the formation of hydronium ions (H₃O⁺), we need to include water in the reaction. The dissociation can be represented as:
H2C2O4(aq)+2H2O(l)→C2O2−4(aq)+2H3O+(aq)
Step 4: Write the net ionic equation
The net ionic equation focuses on the species that undergo a change. In this case, we can simplify the equation to:
H2C2O4(aq)→C2O2−4(aq)+2H+(aq)
Step 5: Confirm the balance of the equation
- Hydrogens: 2 on the left (from H₂C₂O₄) and 2 on the right (from 2 H⁺).
- Carbons: 2 on both sides (from H₂C₂O₄ and C₂O₄²⁻).
- Oxygens: 4 on both sides (from H₂C₂O₄ and C₂O₄²⁻).
The equation is balanced.
Final Net Ionic Equation:
H2C2O4(aq)→C2O2−4(aq)+2H+(aq)
---
The chemical formula for oxalic acid is H₂C₂O₄.
When oxalic acid dissolves in water, it dissociates into its ions. The dissociation can be represented as:
H2C2O4(aq)→C2O2−4(aq)+2H+(aq)
Since we are considering the formation of hydronium ions (H₃O⁺), we need to include water in the reaction. The dissociation can be represented as:
H2C2O4(aq)+2H2O(l)→C2O2−4(aq)+2H3O+(aq)
The net ionic equation focuses on the species that undergo a change. In this case, we can simplify the equation to:
H2C2O4(aq)→C2O2−4(aq)+2H+(aq)
- Hydrogens: 2 on the left (from H₂C₂O₄) and 2 on the right (from 2 H⁺).
- Carbons: 2 on both sides (from H₂C₂O₄ and C₂O₄²⁻).
- Oxygens: 4 on both sides (from H₂C₂O₄ and C₂O₄²⁻).
H2C2O4(aq)→C2O2−4(aq)+2H+(aq)
Topper's Solved these Questions
- EQUILIBRIUM Book:ICSEChapter:EQUILIBRIUM Exercise:VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Explore 38 Videos
- EQUILIBRIUM Book:ICSEChapter:EQUILIBRIUM Exercise:SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Explore 44 Videos
- EQUILIBRIUM Book:ICSEChapter:EQUILIBRIUM Exercise:NCERT TEXT-BOOK EXERCISE
Explore 109 Videos
- ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY Book:ICSEChapter:ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY Exercise:NCERT TEXT-BOOK EXERCISE
Explore 20 Videos
- HYDROCARBONS Book:ICSEChapter:HYDROCARBONS Exercise:NCERT TEXT-BOOK EXERCISES
Explore 46 Videos
Similar Questions
Write the correctly balanced net ionic equations for the reations whose equilibrium constant at 298 K are
Kb(CH3NH2)=4.4×10−5
View SolutionWrite the correctly balanced net ionic equations for the reations whose equilibrium constant at 298 K are
Ka(H2S)=1.0×10−7
View SolutionWrite the correctly balanced net ionic equations for the reations whose equilibrium constant at 298 K are
Kb(NH3)=1.8×10−5
View SolutionWrite a balanced equation for the
C2H4+Br2→
View SolutionBalance the equations :
P2O5+H2O→H3PO4
View SolutionAt a certain temperature , the following reactions have the equilibrium constants as shown below:
S(s)+O2(g)⇔SO2(g),Kc=5×1052
2S(s)+3O2(g)⇔2SO3(g),Kc=1029
what is the equilibrium constant Kcfor the reaction at tahea same temperature?
2SO2(g)+O2(g)⇔2SO3(g)
View SolutionCalculate equilibrium constant for the reaction
CO+H2O⇔CO2+H2
If equilibrium constants for
2CO+O2⇔2CO2,K1=40×10−3
2H2+O2⇔2H2O,K2=36×10−2
View SolutionCalculate the equilibrium constant (K) for the formation of NH^ in the following reaction: N2(g)+3H2(g)<⇒2NH3(g)
At equilibrium, the concentration of NH3, H2 and N2 are 1.2×10−2,3.0×10−2 and 1.5×10−2 M respectively.
View SolutionConsider the following reaction. The reaction is first order in each direction, with an equilibrium constant of 104. For the conversion of chair form to boat form, e−Ea/RT=4.35×10−8 at 298 K with pre-exponential factor of 1012s−1. Apparent rate constant (kA) at 298 K is :
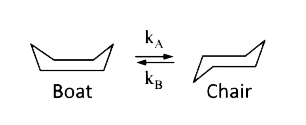
View SolutionFor the equilibrium
H2O(1)⇔H2O(g)
at 1 atm 298K
View Solution
