Arrange the following in the order as mentioned :
1∘,2∘,3∘ free radicals in the order of decreasing stability.
To arrange the free radicals (1°, 2°, and 3°) in order of decreasing stability, we need to understand the factors that influence the stability of free radicals.
1. Identify the Types of Free Radicals:
- 1° Free Radical: This is a free radical that is attached to one carbon atom that is connected to only one other carbon atom.
- 2° Free Radical: This free radical is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two other carbon atoms.
- 3° Free Radical: This free radical is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to three other carbon atoms.
2. Understand Stability Factors:
- The stability of free radicals increases with the number of alkyl groups attached to the carbon bearing the unpaired electron. Alkyl groups can donate electron density through the +I (inductive) effect, which stabilizes the radical.
- More alkyl substituents mean more electron donation, which leads to greater stability of the free radical.
3. Rank the Free Radicals:
- 3° Free Radical: Most stable because it is surrounded by three alkyl groups that can donate electron density.
- 2° Free Radical: Moderately stable as it is surrounded by two alkyl groups.
- 1° Free Radical: Least stable since it is only surrounded by one alkyl group.
4. Conclusion:
- Based on the above analysis, the order of stability from most stable to least stable is:
- 3° > 2° > 1°
Final Answer:
The order of decreasing stability of the free radicals is: 3° > 2° > 1°.
- 1° Free Radical: This is a free radical that is attached to one carbon atom that is connected to only one other carbon atom.
- 2° Free Radical: This free radical is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to two other carbon atoms.
- 3° Free Radical: This free radical is attached to a carbon atom that is connected to three other carbon atoms.
- The stability of free radicals increases with the number of alkyl groups attached to the carbon bearing the unpaired electron. Alkyl groups can donate electron density through the +I (inductive) effect, which stabilizes the radical.
- More alkyl substituents mean more electron donation, which leads to greater stability of the free radical.
- 3° Free Radical: Most stable because it is surrounded by three alkyl groups that can donate electron density.
- 2° Free Radical: Moderately stable as it is surrounded by two alkyl groups.
- 1° Free Radical: Least stable since it is only surrounded by one alkyl group.
- Based on the above analysis, the order of stability from most stable to least stable is:
- 3° > 2° > 1°
The order of decreasing stability of the free radicals is: 3° > 2° > 1°.
टॉपर्स ने हल किए ये सवाल
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES BOOK - ICSECHAPTER - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES EXERCISE - VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
87 Videos
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES BOOK - ICSECHAPTER - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES EXERCISE - SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
110 Videos
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES BOOK - ICSECHAPTER - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES EXERCISE - NCERT TEXT-BOOK EXERCISES (WITH HINTS AND SOLUTIONS )
72 Videos
- HYDROGENBOOK - ICSECHAPTER - HYDROGENEXERCISE - NCERT TEXT-BOOK EXERCISE (With Hints and Solutions)
53 Videos
- REDOX REACTIONS (OXIDATION AND REDUCTION)BOOK - ICSECHAPTER - REDOX REACTIONS (OXIDATION AND REDUCTION)EXERCISE - NCERT TEXT-BOOK. EXERCISES ((With Hints and Solutions)
69 Videos
समान प्रश्न
ज्ञान जांच
Arrange the following in decreasing order of E2 reaction :
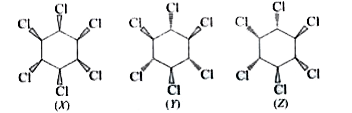 AX>Y>ZBX>Z>YCZ>X>YDY>X>Z
AX>Y>ZBX>Z>YCZ>X>YDY>X>ZArrange the following in decreasing order of E2 reaction :
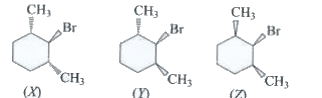 AX>Y>ZBX>Z>YCY>Z>XDZ>Y>X
AX>Y>ZBX>Z>YCY>Z>XDZ>Y>XArrange the following in increasing order of stability.
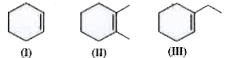 AI<II<IIIBII<I<IIICI<III<IIDII<III<I
AI<II<IIIBII<I<IIICI<III<IIDII<III<I
Arrange the following in decreasing order of acidity
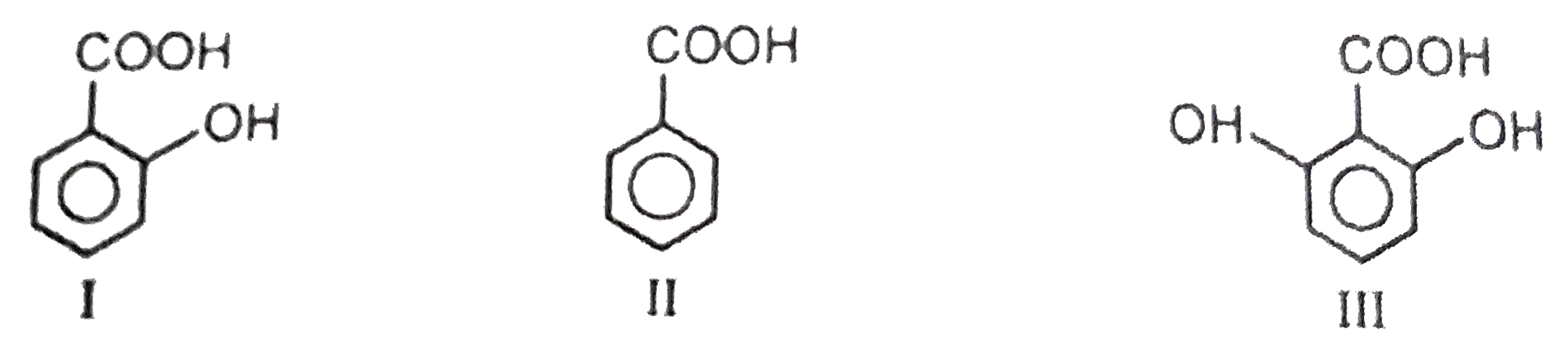
View SolutionArrange the following in decreasing order of stability
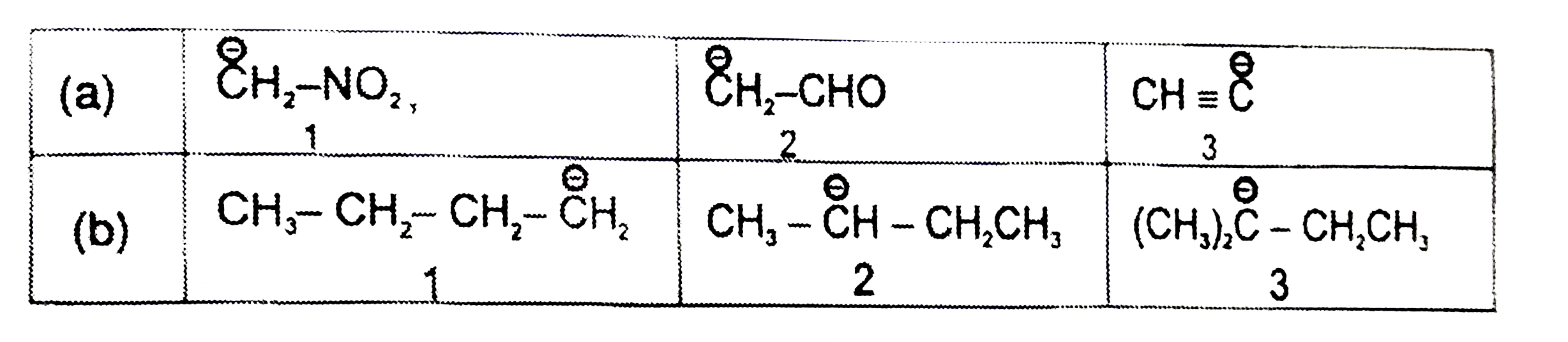
View SolutionArrange the following in decreasing order of stability
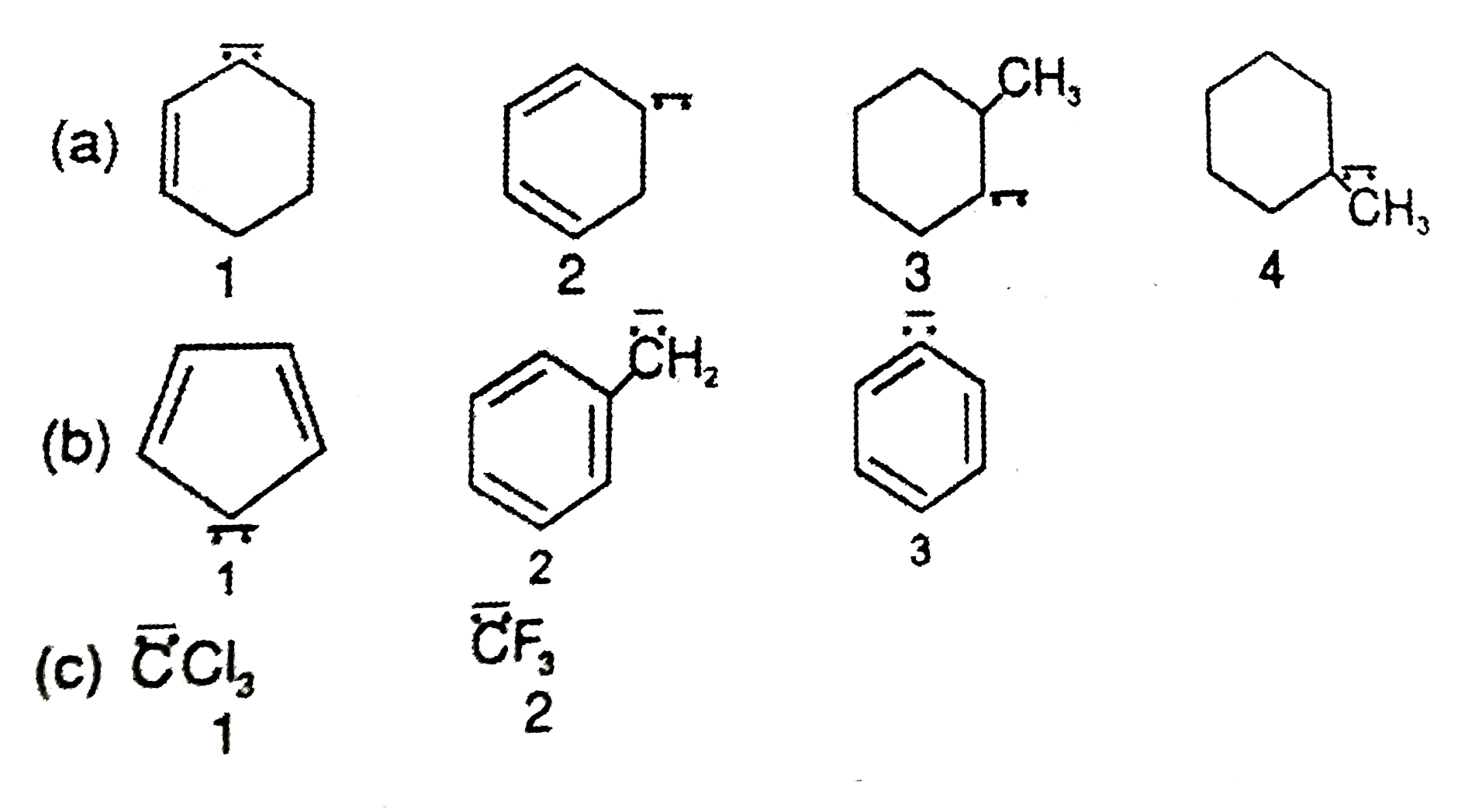
View SolutionArrange the following in decreasing order of rate of nitration :-
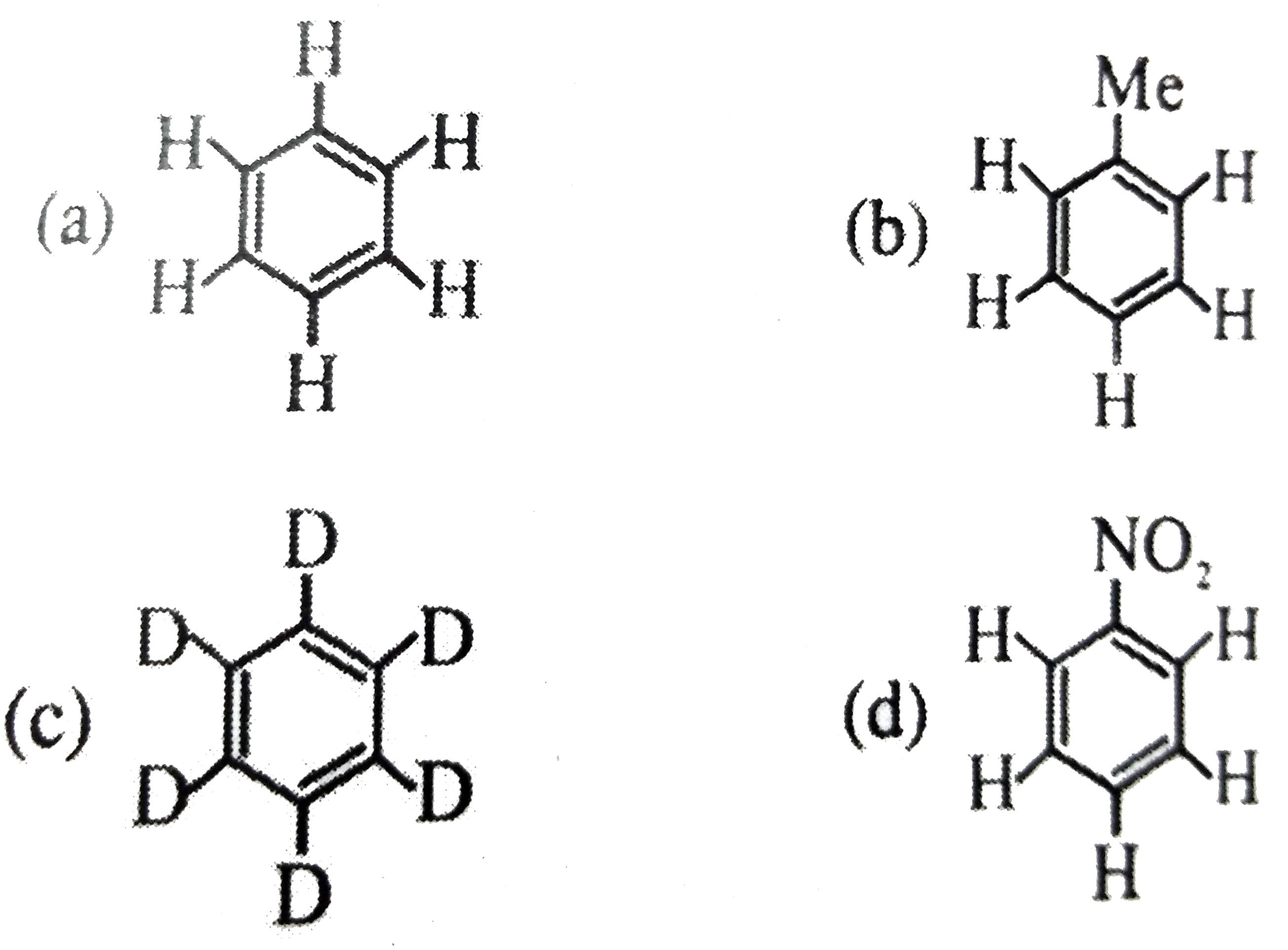
View SolutionArrange the following in decreasing order of dipole moment <
View Solution


