A ball of mass 10 g is moving with a velocity of 50ms−1. On applying a constant force on ball for 2.0 s, it acquires a velocity of 70ms−1. Calculate the final momentum of ball
To solve the problem, we need to calculate the final momentum of the ball after it has been acted upon by a constant force. Here are the steps to arrive at the solution:
Step 1: Convert mass from grams to kilograms
The mass of the ball is given as 10 g. We need to convert this into kilograms because the standard unit of mass in the SI system is kilograms (kg).
Mass(m)=10 g1000=0.01 kg
Step 2: Identify the final velocity
The final velocity of the ball after the force has been applied is given as 70 m/s.
Final velocity(v)=70 m/s
Step 3: Use the formula for momentum
The formula for momentum (P) is given by:
P=m×v
Where:
- P is the momentum,
- m is the mass,
- v is the velocity.
Step 4: Substitute the values into the momentum formula
Now we will substitute the values of mass and final velocity into the momentum formula.
P=0.01 kg×70 m/s
Step 5: Calculate the final momentum
Now we perform the multiplication:
P=0.01×70=0.7 kg m/s
Final Answer
The final momentum of the ball is:
P=0.7 kg m/s
---
The mass of the ball is given as 10 g. We need to convert this into kilograms because the standard unit of mass in the SI system is kilograms (kg).
The final velocity of the ball after the force has been applied is given as 70 m/s.
The formula for momentum (P) is given by:
- P is the momentum,
- m is the mass,
- v is the velocity.
Now we will substitute the values of mass and final velocity into the momentum formula.
Now we perform the multiplication:
The final momentum of the ball is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:ICSEChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:TOPIC 3 (2 Marks Questions )
Explore 9 Videos
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:ICSEChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:TOPIC 3 (3 Marks Questions )
Explore 7 Videos
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:ICSEChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:TOPIC 2 (3 Marks Questions )
Explore 11 Videos
- ICSE ANNUAL EXAMINATION -2020Book:ICSEChapter:ICSE ANNUAL EXAMINATION -2020Exercise:SECTION-II
Explore 45 Videos
- LIGHTBook:ICSEChapter:LIGHTExercise:TOPIC 2 Spherical Mirrors (4 Marks Questions )
Explore 9 Videos
Similar Questions
Define gravitational constant G.
View SolutionState Newton's law of gravitation.
View SolutionA truck carrying 500 kg sand was moving with a velocity 15ms−1. After disposal of 200 kg sand what should be the velocity of the truck to maintain same momentum as before? (say mass of truck = 1000 kg)
View SolutionThe figure below shows the velocity-time graph of a body moving in a straight line.
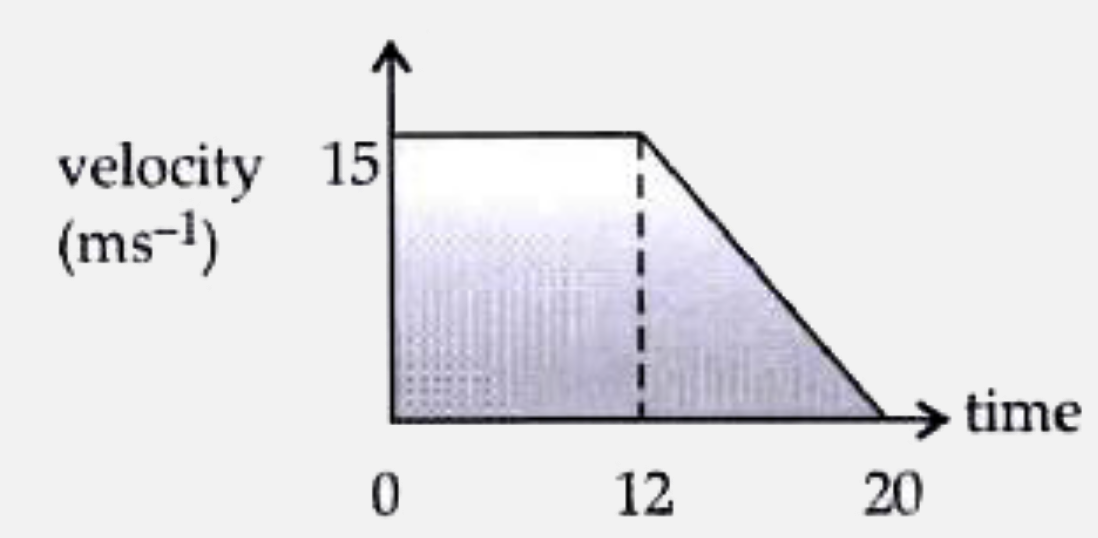
Find the time interval in which the body is moving with zero acceleration
View SolutionDifferentiate between concave mirror and convex mirror.
View SolutionA ball is projected horizontally from a tower with a velocity of 4 ms^(-1) . Find the velocity of the ball after 0.7 s. Take g = 10 ms^(-2) .
View SolutionA cricket ball of mass 150 g moving with a speed of 12 ms^(-1) is hit by a bat so that the ball is turned back with a velocity of 20 ms^(-1) . Calculate the impulse received by the ball ?
View SolutionA ball of mass 100 g is moving with a velocity of 10 ms^(-1) . On being hit with bat rebounds with a velocity of 10 ms^(-1) . The force of the ball by the bat acts for 0.01 s, then the force exerted on the ball by the bat is
View Solution25 g நிறையுடைய ஒரு கிரிக்கெட் பந்து மட்டையால் தாக்கப்பட்டு 12ms−1 வேகத்தில் செல்கிறது. எனவே பந்தானது 20ms−1 திசைவேகத்தில் திருப்பப்படுகிறது. பந்தினால் பெறப்பட்ட கணத்தாக்கினை கணக்கிடுக.
View SolutionA ball of mass of 150g and velocity 12 ms^(-1) coming towards a batsman is hit by him with a force in such a way that the ball moves with velocity 30 ms^(-1) in the direction opposite to its original one. The time of contact between the ball and the bat is 0.01 s. Then the force applied on it by the batsman i s .......
View SolutionA ball of mass 10 g is moving with a velocity of 50ms−1. On applying a constant force on ball for 2.0 s, it acquires a velocity of 70ms−1. Calculate the initial momentum of ball
View SolutionA ball of mass 10 g is moving with a velocity of 50 "ms"^(-1) . On applying a constant force on ball for 2.0 s, it acquires a velocity of 70 "ms"^(-1) . Calculate the rate of change of momentum
View SolutionA ball of mass 10 g is moving with a velocity of 50ms−1. On applying a constant force on ball for 2.0 s, it acquires a velocity of 70ms−1. Calculate the acceleration of ball
View SolutionA ball of mass 10 g is moving with a velocity of 50ms−1. On applying a constant force on ball for 2.0 s, it acquires a velocity of 70ms−1. Calculate the magnitude of force applied.
View Solution10ms−1 से गतिमान 200g द्रव्यमान की एक हॉकी की गेंद, हॉकी स्टिक से मारने के पश्चात् पूर्वपथ पर 5ms−1 वेग से वापस आ जाती है। हॉकी स्टिक से बल लगाने पर हॉकी की गेंद की गति में होने वाले परिवर्तन की गणना कीजिए।
View Solution