In a triangle ABC, AD is the altitude from A. If b>c. ∠C=23∘andAD=abcb2−c2,then ∠B=
110∘
113∘
120∘
130∘
The correct Answer is:B
Step by step video solution for In a triangle ABC, AD is the altitude from A. If b gt c. angleC = 23^(@) and AD = (abc)/(b^(2) - c^(2), then angle B = by Maths experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- PROPERTIES AND SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES Book:ARIHANT MATHS ENGLISHChapter:PROPERTIES AND SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES Exercise:Exercise (More Than One Correct Option Type Questions)
Explore 23 Videos
- PROPERTIES AND SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES Book:ARIHANT MATHS ENGLISHChapter:PROPERTIES AND SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES Exercise:Exercise (Statement I And Ii Type Questions)
Explore 11 Videos
- PROPERTIES AND SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES Book:ARIHANT MATHS ENGLISHChapter:PROPERTIES AND SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES Exercise:PROPERTIES AND SOLUTIONS OF TRIANGLES EXERSISE 1: SINGLE OPTION CORRECT TYPE QUESTIONS
Explore 1 Video
- PRODUCT OF VECTORSBook:ARIHANT MATHS ENGLISHChapter:PRODUCT OF VECTORSExercise:Exercise (Questions Asked In Previous 13 Years Exam)
Explore 51 Videos
- SEQUENCES AND SERIESBook:ARIHANT MATHS ENGLISHChapter:SEQUENCES AND SERIESExercise:Exercise (Questions Asked In Previous 13 Years Exam)
Explore 38 Videos
Similar Questions
If area of ΔABC(Δ) and angle C are given and if c opposite to given angle is minimum, then
View SolutionIn a triangle ABC,a3+b3+c3=c2(a+b+c) (All symbol used have usual meaning in a triangle.) Statement-1: The value of ∠C=60∘. Statement-2: ΔABC must be equilateral.
View SolutionIn the adjoining figure, the circle meets the sides of an equilateral triangle at six points.
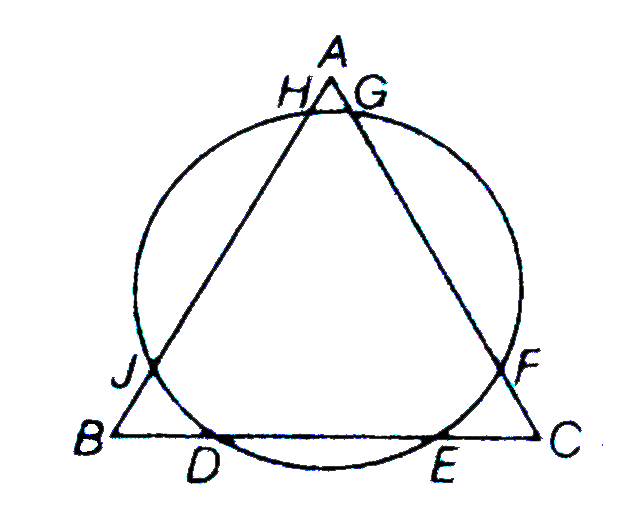
If AG=2,GF=13,FC=1andHJ=7, then DE equals to
View SolutionLet O be the origin and let PQR be an arbitrary triangle. The point S is such that ¯¯¯¯¯¯OP⋅¯¯¯¯¯¯OQ+¯¯¯¯¯¯OR⋅¯¯¯¯¯¯OS=¯¯¯¯¯¯OR⋅¯¯¯¯¯¯OP+¯¯¯¯¯¯OQ⋅¯¯¯¯¯¯OS=¯¯¯¯¯¯OQ⋅¯¯¯¯¯¯OR+¯¯¯¯¯¯OP⋅¯¯¯¯¯¯OS Then the triangle PQR has S as its
View SolutionLet a,b,c be in A.P. and |a|<1,|b|<1|c|<1.ifx=1+a+a2+....to ∞,y=1+b+b2+....to ∞and,z=1+c+c2+...to ∞, then x,y,z are in
View SolutionIn triangle ABC,AD is the altitude from A. If b>c,∠C=230,andAD=abcb2−c2, then ∠B=___
View SolutionIn a triangle ABC,AD is the altitude form- abcA (Fig.12.9). Given b>0,2C=23^(@) and AD=(abc)/(b^(2)-c^(2)) then /_B. is equal to
View SolutionIn an acute angle triangle ABC,AD,BE and CF are the altitudes,then (EF)/(a)+(FD)/(b)+(DE)/(c) is equal to -
View SolutionIn a triangle ABC, AD is the altitude from A. If b>c. ∠C=23∘andAD=abcb2−c2, then ∠B=
View SolutionIn a ΔABC,AD is the altitude from A. Given b>,c∠C=23∘andAD=abcb2−c2, then ∠B=....
View SolutionGive a right angle triangle ABC with right angled at C. ∠C=90∘ and a,b,c are lengths of corresponding sides. (b>a).
cos(A−B) will be equal to
View SolutionGive a right angle triangle ABC with right angled at C. ∠C=90∘ and a,b,c are lengths of corresponding sides. (b>a). tan(A2) will be equal to
View Solutionकिसी त्रिभुज ABC में AD बिन्दु A से डाला गया लम्ब है दिया गया है। b>c,∠C=23∘तथाAD=abcb2−c2 तो ∠B=
View SolutionIn a triangle ABC, AD is the perpendicular from point A. b gt c , /_C=23^(@) And AD= (abc)/(b^(2)-c^(2)) so /_B=
View SolutionIn ΔABC,AD is the altitude from A, if b>c,C=230,AD=abcb2−c2 then ∠B=
View SolutionIn a ΔABC, AD is the altitude from A. Given b>c,∠C=23∘ and AD=abc(b2−c2), find ∠B.
View Solution
