Which of the following leads to bonding?
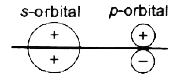
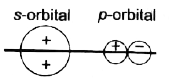

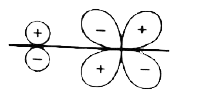
The correct Answer is:B
To determine which of the given orbital interactions leads to bonding, we will analyze each option based on the type of overlap between the orbitals involved.
1. Identify the Orbitals:
- We have different combinations of S and P orbitals in the options provided.
2. Analyze the First Option:
- The first option involves an S orbital and a P orbital.
- The overlap is unsymmetrical, meaning it does not have a proper head-on or sideways overlap.
- Conclusion: This does not lead to bonding.
3. Analyze the Second Option:
- The second option also involves an S orbital and a P orbital.
- Here, the P orbital overlaps with the S orbital in a head-on manner, and the phases of the orbitals are the same (both in the positive phase).
- Conclusion: This symmetrical overlap leads to bonding.
4. Analyze the Third Option:
- The third option consists of two P orbitals.
- The overlap is between two P orbitals with different phases (one positive and one negative).
- Conclusion: This results in a negative overlap, which does not lead to bonding.
5. Analyze the Fourth Option:
- The fourth option involves an S orbital, a P orbital, and a D orbital.
- Similar to the third option, the overlap is not symmetrical and involves different phases.
- Conclusion: This negative overlap does not lead to bonding.
6. Final Conclusion:
- After analyzing all options, the only combination that leads to bonding is the second option, where there is a head-on overlap between the S and P orbitals.
Answer:
The correct answer is Option 2.
---
- We have different combinations of S and P orbitals in the options provided.
- The first option involves an S orbital and a P orbital.
- The overlap is unsymmetrical, meaning it does not have a proper head-on or sideways overlap.
- Conclusion: This does not lead to bonding.
- The second option also involves an S orbital and a P orbital.
- Here, the P orbital overlaps with the S orbital in a head-on manner, and the phases of the orbitals are the same (both in the positive phase).
- Conclusion: This symmetrical overlap leads to bonding.
- The third option consists of two P orbitals.
- The overlap is between two P orbitals with different phases (one positive and one negative).
- Conclusion: This results in a negative overlap, which does not lead to bonding.
- The fourth option involves an S orbital, a P orbital, and a D orbital.
- Similar to the third option, the overlap is not symmetrical and involves different phases.
- Conclusion: This negative overlap does not lead to bonding.
- After analyzing all options, the only combination that leads to bonding is the second option, where there is a head-on overlap between the S and P orbitals.
The correct answer is Option 2.
টপার এই প্রশ্নগুলো সমাধান করেছে
- CHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)BOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - CHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)EXERCISE - Level 2
62 Videos
- CHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)BOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - CHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)EXERCISE - Level 3 (Passive 1)
6 Videos
- CHEMICAL BONDING (ADVANCED)BOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - CHEMICAL BONDING (ADVANCED)EXERCISE - SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS
48 Videos
- CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDSBOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDSEXERCISE - SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS
42 Videos
সম্পর্কিত প্রশ্ন
জ্ঞান পরীক্ষা করুন
Which of the following leads to the formation of an alkyl halide ?
AC2H5OHRedP+Br2−−−−−−→BC2H5OHSOCl2−−−→CC2H5OHKBr+Conc.H2SO4−−−−−−−−−−−→DAll of these
Which of the following has pπ−dπ bonding?
View Solutionwhich of the following leads to redox reaction ?
View SolutionWhich of the following reaction leads to the formation of secondary alcohol?
View SolutionWhich of the following process lead to formation of isobars ?
View SolutionWhich of the following shows bond in silicone?
View SolutionWhich of the following is most polar bond ?
View SolutionIn which of the following back - bonding is possible
View Solution

