The correct statement regarding ClO−n molecular ion is:
On decreasing value of 'n', Cl−O bond order increases
On increasing value of 'n', Cl-O bond length increases
On increasing value of n, oxidation number of central atom increases
On increasing value of n, hybrid orbitals on central atom increases
The correct Answer is:C
To analyze the molecular ion ClO_n^(-) and determine the correct statement regarding it, we will follow these steps:
Step 1: Understand the Molecular Ion ClO_n^(-)
The molecular ion ClO_n^(-) consists of chlorine (Cl) and oxygen (O) atoms. The subscript n indicates the number of oxygen atoms bonded to the chlorine atom, and the negative charge indicates that the overall charge of the ion is -1.
Step 2: Determine the Structure for Different Values of n
1. For n = 1 (ClO^(-)):
- Chlorine has 7 valence electrons, and oxygen has 6 valence electrons.
- Total valence electrons = 7 + 6 + 1 (for the negative charge) = 14 electrons.
- The structure will have a single bond between Cl and O, with Cl having a formal charge of +1 and O having a formal charge of -1.
2. For n = 2 (ClO2^(-)):
- Total valence electrons = 7 + 2*6 + 1 = 20 electrons.
- The structure will have one double bond between Cl and one O, and a single bond with the other O. The formal charges will balance out to keep the overall charge -1.
3. For n = 3 (ClO3^(-)):
- Total valence electrons = 7 + 3*6 + 1 = 26 electrons.
- The structure will have one Cl atom bonded to three O atoms, with one of the O atoms having a double bond. The formal charges will also balance out to maintain the -1 charge.
Step 3: Calculate Bond Order
The bond order can be calculated using the formula:
Bond Order=Number of bonding electrons−Number of antibonding electrons2
1. For ClO^(-):
- Bond order = 1 (single bond).
2. For ClO2^(-):
- Bond order = 1.5 (one double bond and one single bond).
3. For ClO3^(-):
- Bond order = 1.67 (more double bonds increase the bond order).
Step 4: Analyze the Trends
- As n increases, the bond order increases.
- The oxidation state of Cl also increases with n (from +1 in ClO^(-) to +5 in ClO3^(-)).
- The hybridization remains the same (sp3) across these ions.
Step 5: Evaluate the Statements
1. On decreasing value of n, ClO bond order decreases: True, as we observed that bond order increases with increasing n.
2. On increasing value of n, ClO bond length increases: False, bond length decreases with increasing bond order.
3. On increasing value of n, oxidation number of central atom increases: True, as the oxidation state increases from +1 to +5.
4. Hybridization of central atom increases with n: False, hybridization remains the same.
Conclusion
The correct statement regarding ClO_n^(-) molecular ion is: On increasing value of n, the oxidation number of the central atom increases.
The molecular ion ClO_n^(-) consists of chlorine (Cl) and oxygen (O) atoms. The subscript n indicates the number of oxygen atoms bonded to the chlorine atom, and the negative charge indicates that the overall charge of the ion is -1.
1. For n = 1 (ClO^(-)):
- Chlorine has 7 valence electrons, and oxygen has 6 valence electrons.
- Total valence electrons = 7 + 6 + 1 (for the negative charge) = 14 electrons.
- The structure will have a single bond between Cl and O, with Cl having a formal charge of +1 and O having a formal charge of -1.
- Total valence electrons = 7 + 2*6 + 1 = 20 electrons.
- The structure will have one double bond between Cl and one O, and a single bond with the other O. The formal charges will balance out to keep the overall charge -1.
- Total valence electrons = 7 + 3*6 + 1 = 26 electrons.
- The structure will have one Cl atom bonded to three O atoms, with one of the O atoms having a double bond. The formal charges will also balance out to maintain the -1 charge.
The bond order can be calculated using the formula:
Bond Order=Number of bonding electrons−Number of antibonding electrons2
- Bond order = 1 (single bond).
- Bond order = 1.5 (one double bond and one single bond).
- Bond order = 1.67 (more double bonds increase the bond order).
- As n increases, the bond order increases.
- The oxidation state of Cl also increases with n (from +1 in ClO^(-) to +5 in ClO3^(-)).
- The hybridization remains the same (sp3) across these ions.
1. On decreasing value of n, ClO bond order decreases: True, as we observed that bond order increases with increasing n.
2. On increasing value of n, ClO bond length increases: False, bond length decreases with increasing bond order.
3. On increasing value of n, oxidation number of central atom increases: True, as the oxidation state increases from +1 to +5.
4. Hybridization of central atom increases with n: False, hybridization remains the same.
The correct statement regarding ClO_n^(-) molecular ion is: On increasing value of n, the oxidation number of the central atom increases.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- p-BLOCK ELEMENTSBOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - p-BLOCK ELEMENTSEXERCISE - LEVEL 3 (PASSAGE TYPE)
14 Videos
- p-BLOCK ELEMENTSBOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - p-BLOCK ELEMENTSEXERCISE - ONE OR MORE ANSWERS IS/ARE CORRECT
95 Videos
- p-BLOCK ELEMENTSBOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - p-BLOCK ELEMENTSEXERCISE - SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS
35 Videos
- METALLURGYBOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - METALLURGYEXERCISE - ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
29 Videos
- PERIODIC PROPERTIESBOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - PERIODIC PROPERTIESEXERCISE - MATCH THE COLUMN
11 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
The correct statement regarding electrophile is
AElectrophile is a negatively charged species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile.BElectrophile is a negatively charged species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from another electrophile.CElectrophiles are generally neutral species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile.DElectrophile can be either neutral or positively charged species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile.Find the correct statements regarding following molecules.
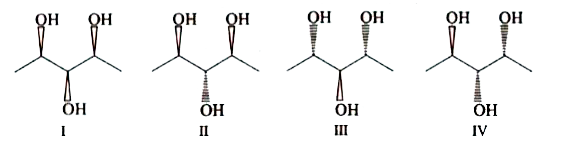 AI, II and III are mesoBI and IV are diastereomersCII and III are enantiomersDIII and IV are diastereomers
AI, II and III are mesoBI and IV are diastereomersCII and III are enantiomersDIII and IV are diastereomers
Choose the correct statement regarding SHM
View SolutionChoose the correct statement regarding SHM
View SolutionChoose the correct statement regarding SHM
View SolutionThe incorrect statement regarding molecular orbital (s) is :
View SolutionChoose the correct statement regarding ice.
View SolutionThe correct statement regarding electrophile is:
View Solution

