Which of the following species is /are superoctet molecule ?
AlF3
SiCl4
XeF2
ICl3
The correct Answer is:C, D
To determine which of the following species are superoctet molecules, we need to identify species that have more than eight electrons in their valence shell. Let's analyze each species step by step.
Step 1: Analyze AlF3
1. Identify the central atom: Aluminium (Al).
2. Determine the valence electrons of Al: Aluminium is in group 13, so it has 3 valence electrons.
3. Identify the surrounding atoms: There are 3 fluorine (F) atoms.
4. Determine the valence electrons of F: Each fluorine atom has 7 valence electrons.
5. Calculate the total number of valence electrons:
- Al: 3 electrons
- 3 F: 3 x 7 = 21 electrons
- Total = 3 + 21 = 24 electrons
6. Distribute the electrons: The structure has Al at the center with three F atoms bonded to it. Each bond uses 2 electrons, so:
- 3 bonds = 6 electrons used
- Remaining electrons = 24 - 6 = 18 electrons.
7. Count the electrons around Al: Al has 6 electrons around it (from the bonds with F), which is not more than 8.
8. Conclusion: AlF3 is not a superoctet molecule.
Step 2: Analyze SiCl4
1. Identify the central atom: Silicon (Si).
2. Determine the valence electrons of Si: Silicon is in group 14, so it has 4 valence electrons.
3. Identify the surrounding atoms: There are 4 chlorine (Cl) atoms.
4. Determine the valence electrons of Cl: Each chlorine atom has 7 valence electrons.
5. Calculate the total number of valence electrons:
- Si: 4 electrons
- 4 Cl: 4 x 7 = 28 electrons
- Total = 4 + 28 = 32 electrons.
6. Distribute the electrons: The structure has Si at the center with four Cl atoms bonded to it. Each bond uses 2 electrons, so:
- 4 bonds = 8 electrons used
- Remaining electrons = 32 - 8 = 24 electrons.
7. Count the electrons around Si: Si has 8 electrons around it (from the bonds with Cl), which is exactly 8.
8. Conclusion: SiCl4 is not a superoctet molecule.
Step 3: Analyze XeF2
1. Identify the central atom: Xenon (Xe).
2. Determine the valence electrons of Xe: Xenon is in group 18, so it has 8 valence electrons.
3. Identify the surrounding atoms: There are 2 fluorine (F) atoms.
4. Determine the valence electrons of F: Each fluorine atom has 7 valence electrons.
5. Calculate the total number of valence electrons:
- Xe: 8 electrons
- 2 F: 2 x 7 = 14 electrons
- Total = 8 + 14 = 22 electrons.
6. Distribute the electrons: The structure has Xe at the center with two F atoms bonded to it. Each bond uses 2 electrons, so:
- 2 bonds = 4 electrons used
- Remaining electrons = 22 - 4 = 18 electrons.
7. Count the electrons around Xe: Xe has 4 electrons from the bonds with F and 4 lone pairs (8 electrons), totaling 10 electrons.
8. Conclusion: XeF2 is a superoctet molecule.
Step 4: Analyze ICl3
1. Identify the central atom: Iodine (I).
2. Determine the valence electrons of I: Iodine is in group 17, so it has 7 valence electrons.
3. Identify the surrounding atoms: There are 3 chlorine (Cl) atoms.
4. Determine the valence electrons of Cl: Each chlorine atom has 7 valence electrons.
5. Calculate the total number of valence electrons:
- I: 7 electrons
- 3 Cl: 3 x 7 = 21 electrons
- Total = 7 + 21 = 28 electrons.
6. Distribute the electrons: The structure has I at the center with three Cl atoms bonded to it. Each bond uses 2 electrons, so:
- 3 bonds = 6 electrons used
- Remaining electrons = 28 - 6 = 22 electrons.
7. Count the electrons around I: I has 6 electrons from the bonds with Cl and 4 lone pairs (8 electrons), totaling 10 electrons.
8. Conclusion: ICl3 is a superoctet molecule.
Final Conclusion
The species that are superoctet molecules are XeF2 and ICl3.
1. Identify the central atom: Aluminium (Al).
2. Determine the valence electrons of Al: Aluminium is in group 13, so it has 3 valence electrons.
3. Identify the surrounding atoms: There are 3 fluorine (F) atoms.
4. Determine the valence electrons of F: Each fluorine atom has 7 valence electrons.
5. Calculate the total number of valence electrons:
- Al: 3 electrons
- 3 F: 3 x 7 = 21 electrons
- Total = 3 + 21 = 24 electrons
6. Distribute the electrons: The structure has Al at the center with three F atoms bonded to it. Each bond uses 2 electrons, so:
- 3 bonds = 6 electrons used
- Remaining electrons = 24 - 6 = 18 electrons.
7. Count the electrons around Al: Al has 6 electrons around it (from the bonds with F), which is not more than 8.
8. Conclusion: AlF3 is not a superoctet molecule.
1. Identify the central atom: Silicon (Si).
2. Determine the valence electrons of Si: Silicon is in group 14, so it has 4 valence electrons.
3. Identify the surrounding atoms: There are 4 chlorine (Cl) atoms.
4. Determine the valence electrons of Cl: Each chlorine atom has 7 valence electrons.
5. Calculate the total number of valence electrons:
- Si: 4 electrons
- 4 Cl: 4 x 7 = 28 electrons
- Total = 4 + 28 = 32 electrons.
6. Distribute the electrons: The structure has Si at the center with four Cl atoms bonded to it. Each bond uses 2 electrons, so:
- 4 bonds = 8 electrons used
- Remaining electrons = 32 - 8 = 24 electrons.
7. Count the electrons around Si: Si has 8 electrons around it (from the bonds with Cl), which is exactly 8.
8. Conclusion: SiCl4 is not a superoctet molecule.
1. Identify the central atom: Xenon (Xe).
2. Determine the valence electrons of Xe: Xenon is in group 18, so it has 8 valence electrons.
3. Identify the surrounding atoms: There are 2 fluorine (F) atoms.
4. Determine the valence electrons of F: Each fluorine atom has 7 valence electrons.
5. Calculate the total number of valence electrons:
- Xe: 8 electrons
- 2 F: 2 x 7 = 14 electrons
- Total = 8 + 14 = 22 electrons.
6. Distribute the electrons: The structure has Xe at the center with two F atoms bonded to it. Each bond uses 2 electrons, so:
- 2 bonds = 4 electrons used
- Remaining electrons = 22 - 4 = 18 electrons.
7. Count the electrons around Xe: Xe has 4 electrons from the bonds with F and 4 lone pairs (8 electrons), totaling 10 electrons.
8. Conclusion: XeF2 is a superoctet molecule.
1. Identify the central atom: Iodine (I).
2. Determine the valence electrons of I: Iodine is in group 17, so it has 7 valence electrons.
3. Identify the surrounding atoms: There are 3 chlorine (Cl) atoms.
4. Determine the valence electrons of Cl: Each chlorine atom has 7 valence electrons.
5. Calculate the total number of valence electrons:
- I: 7 electrons
- 3 Cl: 3 x 7 = 21 electrons
- Total = 7 + 21 = 28 electrons.
6. Distribute the electrons: The structure has I at the center with three Cl atoms bonded to it. Each bond uses 2 electrons, so:
- 3 bonds = 6 electrons used
- Remaining electrons = 28 - 6 = 22 electrons.
7. Count the electrons around I: I has 6 electrons from the bonds with Cl and 4 lone pairs (8 electrons), totaling 10 electrons.
8. Conclusion: ICl3 is a superoctet molecule.
The species that are superoctet molecules are XeF2 and ICl3.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)BOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - CHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)EXERCISE - MATCH THE COLUMN
22 Videos
- CHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)BOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - CHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)EXERCISE - ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
23 Videos
- CHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)BOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - CHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)EXERCISE - Level 3 (Passive 12)
2 Videos
- CHEMICAL BONDING (ADVANCED)BOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - CHEMICAL BONDING (ADVANCED)EXERCISE - SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS
48 Videos
- CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDSBOOK - VK JAISWAL ENGLISHCHAPTER - CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDSEXERCISE - SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS
42 Videos
Similar Questions
Column-I and Column -II contains four entries each. Entries of Column-I are to be matched with some entries of Column-II. One or more than one entries of Column-I may have the matching with the same entries of Column-II.
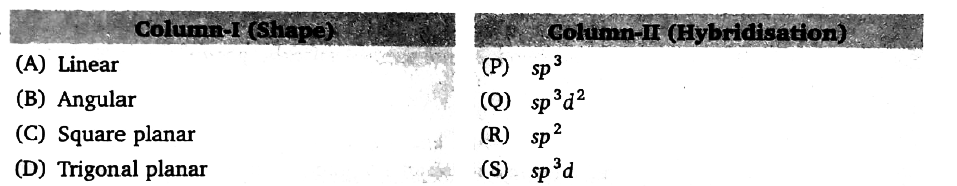
View SolutionAssertion : Multiple bond between two bonded atoms can have more than three bonds.
Reason : Multiple bond between two bonded atoms can not have more than two π-bonds.
View SolutionHybridisation involves the mixing of orbitals having comparable energhies of same atom. Hybridised orbitals perform efficient overlapping than overlapping by pure s, p or orbitals.
Which of the following is not correctly match between given species and type of overlapping ?
View SolutionThere are two groups of compounds A and B. Groups A contains three compounds Px4,Qy3,Rz2. Groups B also contains three compounds Sx4,Ty3,Uz2. Hybridization of each central atom of group A compounds is same as that of iodine in IBrCl− while in group B compounds it is same as that of iodine IBrCl+. Substituents X, Y and Z exhibit covalency of one in ground state. Then find the value of x/y.
Where, x and y are total number of lone pair present at central atoms of compounds of group A and B respectively.
View SolutionConsider the following compounds with their regular geometries.

Calculate value of (x+y−z)2, where x is total number of axial d-orbitals having zero nodal plane, y and z are total no. of non-axial and axial d-orbitals respectively each one having two nodal planes used in hybridisation of central atoms of compounds A to E.
View SolutionWhich of the following species are isoelectronic with N2 molecule?
View SolutionWhich of the following is not hypovalent molecule or species ?
View SolutionWhich pair of molecules are polar species ?
View SolutionWhich of the following species is /are superoctet molecule ?
View SolutionWhich of the following is a hypovalent molecule species?
View SolutionAmong the following species, the diamagnetic molecule is:
View SolutionWhich pair of molecules are polar species ?
View SolutionWhich of the following species is /are superoctet molecule ?
View SolutionWhich among the following molecules/species is/are aromatic?
View SolutionWhich of the following molecules/species are aromatic in character?
View Solutionनिम्न स्पीशीज में , प्रतिचुंबकिय अणु है
View Solution

