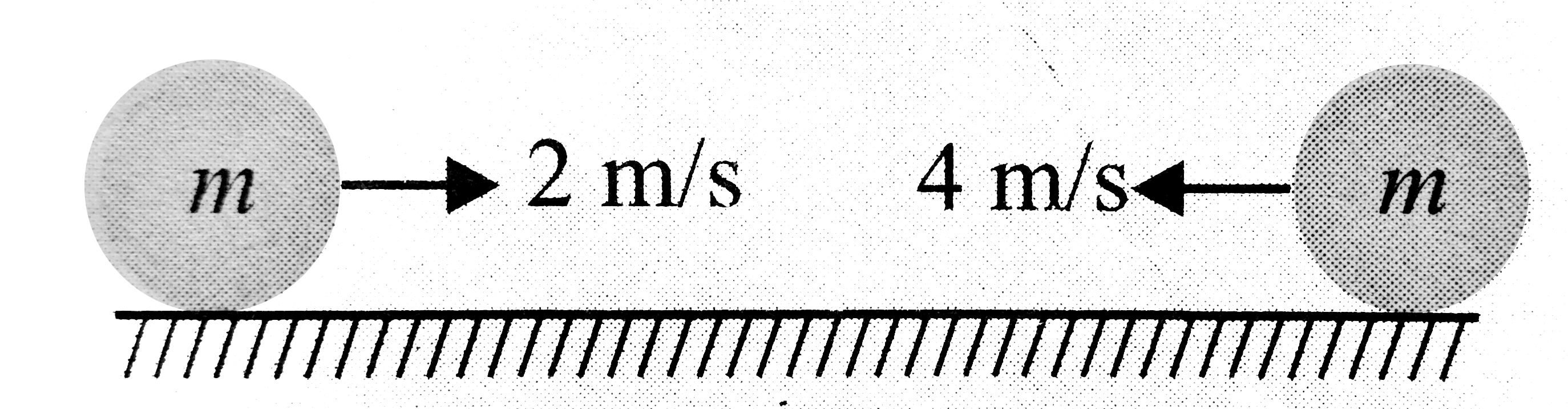
Two identical balls are approaching towards each other on a straight line with velocity 2m/s and 4m/s, respectiely. Find the final velocities after elastic collision between them.

Resolving the velocity before impact, velocity component along the plane =8sin60∘=4√3m/s and that normal to the plane =8cos60∘=4m/s.
If vm/s is the velocity after the impact and θ the angle made by the velocity with the normal to the plane, then velocity component along the plane =vsinθ and that normal to the plane =vcosθ.
As the velocity along the plane remains uchanged,
∴vsinθ=4√3.............i
Fom Newton's expereimental law,
cosθ=e(4) (in magnitude)
=2................ii
squaring and adding eqn i and ii
v2=52⇒v=2√13m/s
dividing eqn i by eqn ii we get
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CENTRE OF MASSBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:CENTRE OF MASSExercise:Subjective
Explore 23 Videos
- CENTRE OF MASSBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:CENTRE OF MASSExercise:Single Correct
Explore 141 Videos
- CENTRE OF MASSBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:CENTRE OF MASSExercise:Exercise 1.2
Explore 23 Videos
- CALORIMETRYBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:CALORIMETRYExercise:Solved Example
Explore 13 Videos
- DIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENTBook:CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISHChapter:DIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENTExercise:Integer
Explore 2 Videos
Similar Questions
Two identical smooth balls are projected from points O and A on the horizontal ground with same speed of projection. The angle of projection in each case is 30∘.The distance between O and A is 100m. The balls collide in mid-air and return to their respective points of projection. If the coefficient of restitution is 0.7, find the speed of projection of either ball (in m/s) correct to nearest integer. (Take g=10ms−2 and √3=1.7)
View SolutionAn object initially at rest explodes into three equal fragments A,B and C.The momentum of A is pˆi and that of B is √3pˆj
where p is a+ve number. The momentum of C will be
View SolutionA bomb, initially at rest, explodes into several pieces. (a) Is linear momentum of the system conserved? (b) Is kinetic energy of the system conserved? Explain.
View SolutionA colorimeter contains 400g of water at a temperature of 5∘C. Then, 200g of water at a temperature of +10∘C and 400g of ice at a temperature of −60∘C are added. What is the final temperature of the contents of calorimeter?
Specific heat capacity of water −1000 cal/kg/K
Specific latent heat of fusion of ice =80×1000 cal/kg
Relative specific heat of ice =0.5
View SolutionTo find the distance d over which a signal can be seen clearly in foggy conditions, a railways-engineer uses dimensions and assumes that the distance depends on the mass density ρ of the fog, intensity (power/area) S of the light from the signal and its frequency f. the engineer finds that d is proportional to S1/n. the value of n is
View SolutionA ball is moving with velocity 2m//s towards a heavy wall moving towards the ball with speed 1m//s as shown in figure. Assuming collision to be elastic, find the velocity of ball immediately after the collision.
View SolutionTwo identical balls are approaching towards each other on a straight line with velocity 2m/s and 4m/s, respectiely. Find the final velocities after elastic collision between them.

View SolutionTwo particles of masses m and 2m moving in opposite directions collide elastically with velocity 2v and v, respectiely. Find their velocities after collision.

View SolutionA 10kg ball and a 20kg ball approach each other with velocities 20m/s and 10m/s respectively. What are their velocities after collision, if the collision is perfectly elastic ?
View SolutionA ball strikes an identical ball with velocity 50 m/s and after the collision which is perfectly elastic it is found to move with velocity 30 m/s . Show that the two balls move at right angles to each other after collision .
View SolutionTwo balls are moving towards each other on a vertical line collides with each other as shown. Find their velocities just after collision.
View Solutionदो एकसमान गेंदें A तथा B के वेग क्रमश : 0.5 मी/से तथा - 0.3 मी/से हैं | वे एक रेखा में चलते हुए प्रत्यास्थ टक्कर करती हैं | टक्कर के पश्चात B तथा A के वेग क्रमश : होंगे :
View SolutionA 10kg ball and 20kg ball approach each other with velocities 20ms−1 and 10ms−1 respectively. What are their velocities after collision if the collision is perfectly elastic?
View SolutionA 10kg ball and 20kg ball approach each other with velocities 20ms−1 and 10ms−1 respectively. What are their velocities after collision if the collision is perfectly elastic?
View SolutionTwo particles of equal mass moving towards each other with velocities 20 m*s^(-1) and 30 m*s^(-1) collide. If the collision is elastic, find their velocities after the collision.
View SolutionA ball moving with speed u collides with an identical ball at rest. The velocities of two balls after collision are (If the collision is elastic):
View Solution
