Ph−CH(OH)CH3Specific rotation=+50∘SOCl2−−−→PhCH∣Cl−CH3
The reaction is carried out in the presence of pyridne, Which of the following mechanisms does it follow?
SN1
SN2
SNi
E2
The correct Answer is:b
To determine the mechanism of the reaction where an alcohol is converted into a benzylic halide in the presence of pyridine, we can follow these steps:
1. Identify the Reactants and Products:
- The reactant is an alcohol (Ph-CH(OH)CH₃) and the product is a benzylic halide (Ph-CHCl-CH₃).
- The reaction involves the substitution of the hydroxyl group (-OH) with a chlorine atom (Cl).
2. Understand the Role of Pyridine:
- Pyridine is a heterocyclic aromatic compound that acts as a base in this reaction.
- It is also a polar aprotic solvent, which means it does not donate protons (H⁺) but can stabilize ions.
3. Determine the Type of Reaction:
- The substitution of -OH with Cl can occur through two main mechanisms: SN1 and SN2.
- SN1 involves a two-step process where the leaving group departs first, forming a carbocation intermediate, followed by nucleophilic attack.
- SN2 involves a single concerted step where the nucleophile attacks the substrate as the leaving group departs.
4. Analyze the Solvent Effect:
- Since pyridine is a polar aprotic solvent, it favors the SN2 mechanism.
- Polar aprotic solvents stabilize the nucleophile but do not stabilize carbocations, making SN1 less favorable.
5. Conclusion:
- Given that the reaction occurs in a polar aprotic solvent (pyridine), and involves a direct nucleophilic substitution, the mechanism followed in this reaction is SN2.
Final Answer:
The mechanism followed in the reaction is SN2.
---
- The reactant is an alcohol (Ph-CH(OH)CH₃) and the product is a benzylic halide (Ph-CHCl-CH₃).
- The reaction involves the substitution of the hydroxyl group (-OH) with a chlorine atom (Cl).
- Pyridine is a heterocyclic aromatic compound that acts as a base in this reaction.
- It is also a polar aprotic solvent, which means it does not donate protons (H⁺) but can stabilize ions.
- The substitution of -OH with Cl can occur through two main mechanisms: SN1 and SN2.
- SN1 involves a two-step process where the leaving group departs first, forming a carbocation intermediate, followed by nucleophilic attack.
- SN2 involves a single concerted step where the nucleophile attacks the substrate as the leaving group departs.
- Since pyridine is a polar aprotic solvent, it favors the SN2 mechanism.
- Polar aprotic solvents stabilize the nucleophile but do not stabilize carbocations, making SN1 less favorable.
- Given that the reaction occurs in a polar aprotic solvent (pyridine), and involves a direct nucleophilic substitution, the mechanism followed in this reaction is SN2.
The mechanism followed in the reaction is SN2.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- AROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES Book:CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISHChapter:AROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES Exercise:Exercises Single Correct Answer Type
Explore 19 Videos
- AROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES Book:CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISHChapter:AROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES Exercise:Exercises Assertion-Resoning
Explore 11 Videos
- AROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES Book:CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISHChapter:AROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES Exercise:Exercises Multiple Correct Answers Type
Explore 8 Videos
- APPENDIX INORGANIC VOLUME 2Book:CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISHChapter:APPENDIX INORGANIC VOLUME 2Exercise:Short Answer Type
Explore 178 Videos
- BIOMOLECULESBook:CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISHChapter:BIOMOLECULESExercise:Exercises Archives (Analytical And Descriptive)
Explore 5 Videos
Similar Questions
The final product (C) in the follwing reactions is:
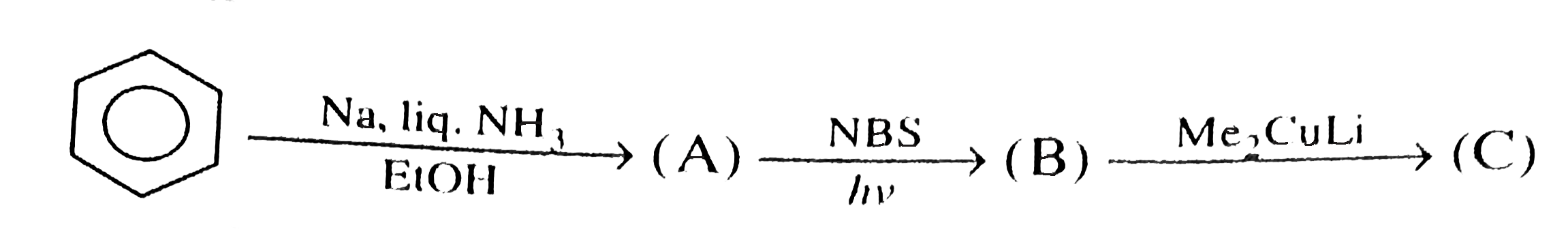
View SolutionAssertion (A): SN1 reaction is carried out in the presence of a plar protic solvent.
Reason (R): A polar protic solvent increases the stability of carbocation due to solvation.
View Solution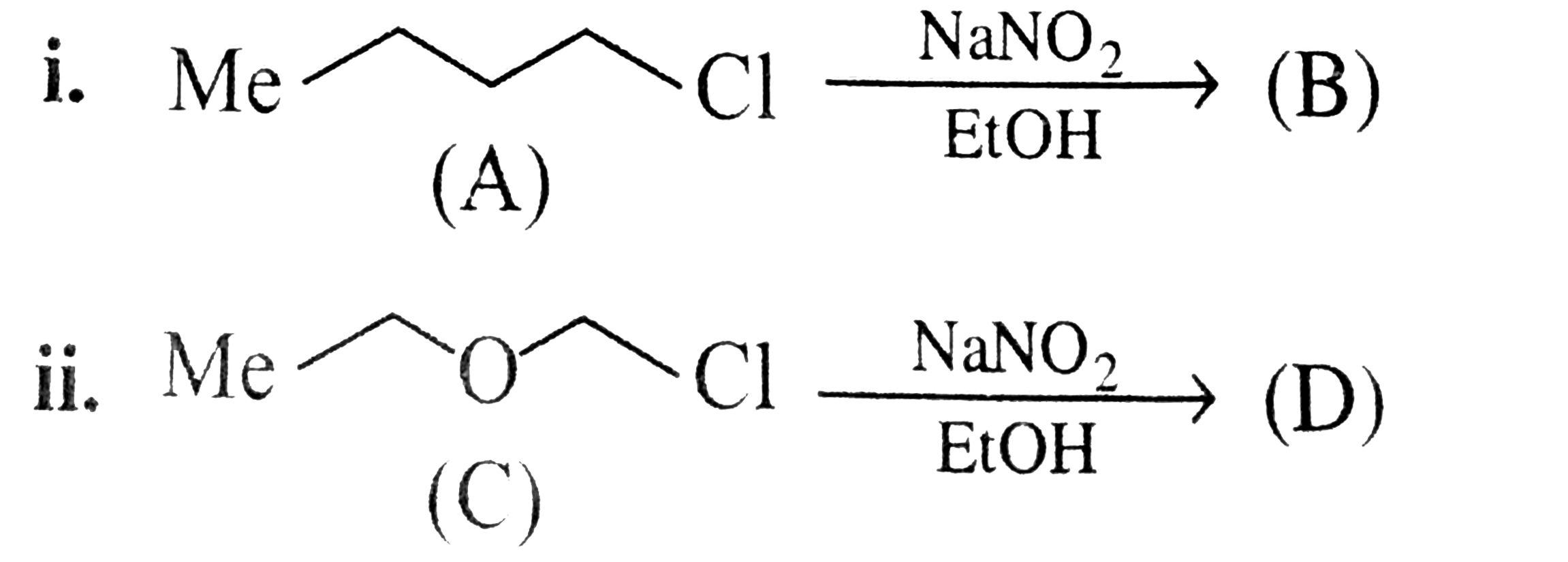
Which of the following statements is/are correct for the above reactions?
View SolutionWhich metals are generally extracted by the electrolytic processes ? What positions these metals generally occupy in the periodic table?
View SolutionAlanine, the amino acid the respective structure at pH = 2 and pH = 10 will be
View SolutionWrite the structures of monomers of the following polymers
(a) ⎡⎢ ⎢⎣−CH2−CH3∣C∣Ph−CH2−CH∣CN−⎤⎥ ⎥⎦n
(b) ⎡⎢ ⎢⎣−CH2−Cl∣C∣Cl−CH2−Cl∣C∣Cl−⎤⎥ ⎥⎦
( c) ⎡⎢ ⎢⎣−CH2−CH3∣C∣Ph−CH2−CH3∣C∣CN−⎤⎥ ⎥⎦.
View SolutionA racemic mixture of 2− Chloropropanoic acid is treated with excess of (+)−2− Butanol. The reaction can be represented as follows :
CH2−CH∣Cl(±)−COOH+CH3−CH∣OH (+) excess−CH2−CH3→CH3−CH∣Cl−COO− CH3∣CH−CH2−CH3+CH3−CH∣OH(+) (Left unreacted)−CH2−CH3
View SolutionThe releative rate or acid catalyssed dehydration of following alcohols would be:
(P) Ph−CH3∣C−CH∣OH−CH3
(Q) Ph−CH3∣C−CH2−CH2−OH
(R ) Ph−−CH3∣CH∣OH−CH2CH3
Ph−−CH3∣CH∣CH3−CH2OH
View SolutionThe IUPAC name of CH3−CH∣OH−CH∣CH3−CH∣OH− CH3∣C∣ CH3−CH3 is:
View SolutionThe releative rate or acid catalyssed dehydration of following alcohols would be: (P) Ph-overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(C)-underset(OH)underset(|)(CH)-CH_(3) (Q) Ph-overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(C)-CH_(2)-CH_(2)-OH (R ) Ph--underset(OH)underset(|)overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(CH)-CH_(2)CH_(3) Ph--underset(CH_(3))underset(|)overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(CH)-CH_(2)OH
View SolutionPh−CH(OH)CH3Specific rotation=+50∘SOCl2−−−→PhCH∣Cl−CH3
What si the specific rotation of the product?
View SolutionThe reaction shows which of the following mechanisms?
CH3−C∣CH3H−ClKOH(aq)−−−−−→CH3−CH∣CH3−OH+Cl−
View SolutionName the following compounds according to IUPAC system. (i) CH_(3) - CH_(2) - underset (CH_(2)Cl) underset(|)(CH) - overset (CH_(2)OH) overset(|) (CH) - underset (CH_(3)) underset (|) (CH) - CH_(3) CH_(3)- underset (CH_(3)) underset(|) (CH) -CH_(2) - underset(OH) underset(|) (CH) - overset (CH_(2)OH) overset(|) (CH) - CH_(2) (iii) (iv) H_(2)C = CH - underset (OH)underset (|) (CH) - CH_(2) - CH_(2) - CH_(3) (v) CH_(3) - underset (CH_(3)) underset ( |) C = underset (Br)underset(|) C - CH_(2)OH
View SolutionName the following compounds accoring to IUPAC system : (i) CH_(3)-CH_(2)- underset(CH_(2)Cl) underset(|)(CH)-overset(CH_(2)OH) overset(|)(CH)-underset(CH_(3)) underset(|)(CH)-CH_(3) (ii) CH_(3)-underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(CH)-CH_(2)-underset(OH) underset(|)(CH)-overset(CH_(2)OH) overset(|)(CH)-CH_(3) (iii) (iv) H_(2)C=CH-underset(OH)underset(|)(CH)-CH_(2)-CH_(2)-CH_(3) (v) CH_(3)- underset(CH_(3)) underset(|)(C)= underset(Br) underset(|)(C)-CH_(2)OH
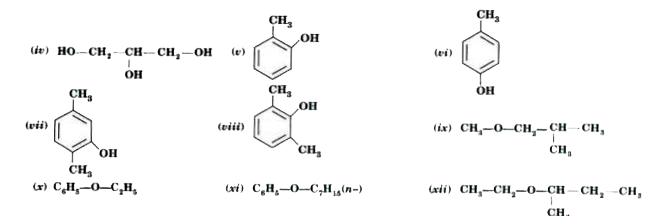
View SolutionWrite IUPAC names of the following compounds :
(i) CH3−CH∣CH3−CH2−CH∣OH−CH3∣C∣CH3−CH3 (ii) H3−C−CH∣OH−CH2−CH∣OH−CH∣C2H5−CH2−CH3
CH3−CH∣OH−CH∣OH−CH3
(iv) HO−CH2−CH∣OH−CH2−OH
View Solution
