What happens to the sound waves when they reach the round window through scala tympani ?
They die away
They increase in intensity
They are transmitted to the oval window
They remain unaffected
The correct Answer is:A
Step-by-Step Solution:
1. Understanding the Structure of the Ear:
- The ear consists of three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The inner ear contains the cochlea, which is divided into three sections: scala vestibuli, scala media, and scala tympani.
2. Identifying the Role of the Scala Tympani:
- The scala tympani is one of the chambers in the cochlea. It is filled with perilymph fluid and does not contain the organ of Corti, which is responsible for converting sound vibrations into neural signals.
3. Sound Wave Propagation:
- When sound waves travel through the cochlea, they enter the scala vestibuli first and then move into the scala media where the organ of Corti is located. The sound waves then continue into the scala tympani.
4. What Happens at the Round Window:
- The round window is a membrane-covered opening that allows for the movement of fluid within the cochlea. When sound waves reach the round window through the scala tympani, they do not cause any further stimulation of the organ of Corti.
5. Conclusion:
- As the sound waves reach the round window via the scala tympani, they effectively "die away" or dissipate. This is because the scala tympani does not contribute to the hearing process, and the sound waves do not increase in intensity, get transmitted to the oval window, or remain unaffected.
Final Answer:
When sound waves reach the round window through the scala tympani, they die away.
---
- The ear consists of three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The inner ear contains the cochlea, which is divided into three sections: scala vestibuli, scala media, and scala tympani.
- The scala tympani is one of the chambers in the cochlea. It is filled with perilymph fluid and does not contain the organ of Corti, which is responsible for converting sound vibrations into neural signals.
- When sound waves travel through the cochlea, they enter the scala vestibuli first and then move into the scala media where the organ of Corti is located. The sound waves then continue into the scala tympani.
- The round window is a membrane-covered opening that allows for the movement of fluid within the cochlea. When sound waves reach the round window through the scala tympani, they do not cause any further stimulation of the organ of Corti.
- As the sound waves reach the round window via the scala tympani, they effectively "die away" or dissipate. This is because the scala tympani does not contribute to the hearing process, and the sound waves do not increase in intensity, get transmitted to the oval window, or remain unaffected.
When sound waves reach the round window through the scala tympani, they die away.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION Book:AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHChapter:NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION Exercise:EXERCISE
Explore 50 Videos
- NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION Book:AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHChapter:NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION Exercise:Assignment SECTION - A (Objective Type Questions )
Explore 37 Videos
- NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION Book:AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHChapter:NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION Exercise:Assignment SECTION - D (Assertion-Reason Type Questions )
Explore 10 Videos
- MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTSBook:AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHChapter:MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTSExercise:TRY YOURSELF
Explore 38 Videos
- ORGANISMS AND POPULATIONS Book:AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHChapter:ORGANISMS AND POPULATIONS Exercise:ASSIGNMENT (SECTION-D) (Assertion-Reason Type Questions)
Explore 15 Videos
Similar Questions
What happens when:
View SolutionWhat happens when ?
(i)_E01_781_Q01.png)
View SolutionWhat happens when alcohol is taken?
View SolutionIn Fig. , A and B represent the displacement distance graphs for two sound waves when they pass through air.
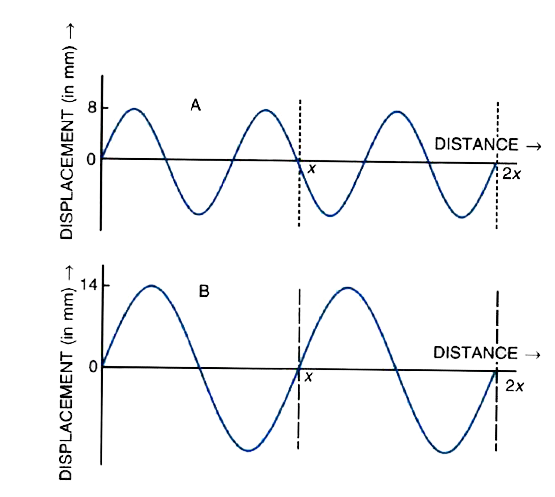
How do they differ in quality ?
View SolutionWhat happens when fluorine gas is passed through water?
View SolutionIn Fig. , A and B represent the displacement distance graphs for two sound waves when they pass through air.
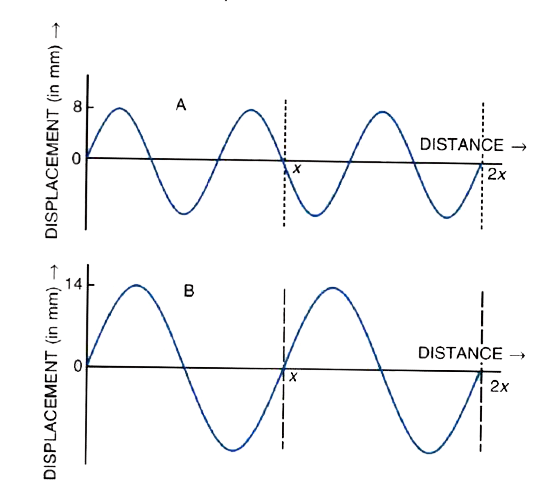
What is the relation between their
wavelengths
View SolutionIn Fig. , A and B represent the displacement distance graphs for two sound waves when they pass through air.
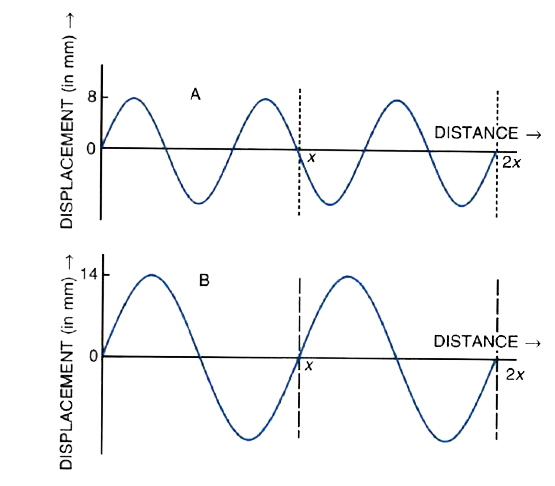
What is the relation between their
pitch
View SolutionIn Fig. , A and B represent the displacement distance graphs for two sound waves when they pass through air.
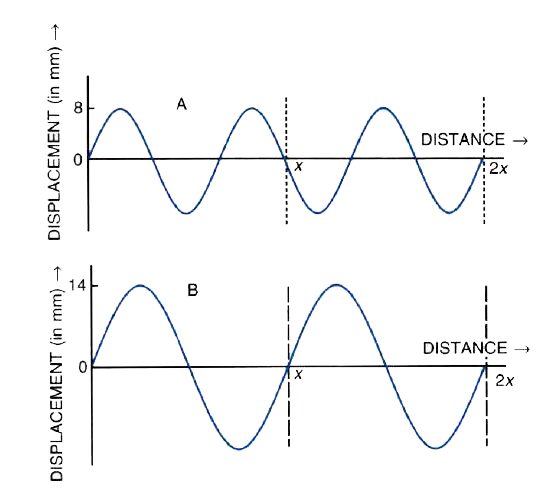
What is the relation between their
velocities
View SolutionIn Fig. , A and B represent the displacement distance graphs for two sound waves when they pass through air.
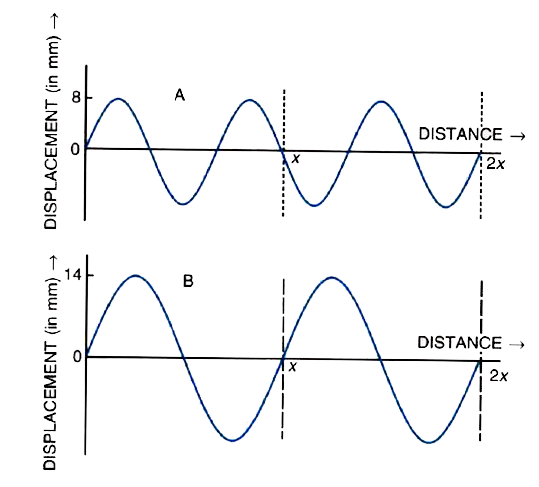
What is the relation between their
loudness
View SolutionWhat happens when cathode rays are passed through a gas?
View Solution
