Statement-1:An isolated and free electron cannot absorb a photon completely.
Statement-2 : All material particles behave wave like when in motion.
Statement-3: Light of intensity l , falls normally upon a plane mirror (perfectly reflecting surface ). The pressure exerted is 2lc
TFT
FFF
TTF
TTT
The correct Answer is:4
To analyze the statements provided in the question, we will evaluate each statement one by one and determine their validity.
Step 1: Evaluate Statement 1
Statement 1: An isolated and free electron cannot absorb a photon completely.
Analysis:
When a photon interacts with a free electron, the energy of the photon can be partially transferred to the electron. However, due to conservation of momentum, not all the energy can be absorbed by the electron. Part of the energy goes into increasing the kinetic energy of the electron, and the rest is used to maintain momentum conservation. Therefore, the statement is true.
Step 2: Evaluate Statement 2
Statement 2: All material particles behave wave-like when in motion.
Analysis:
This statement is based on de Broglie's hypothesis, which states that every moving particle or object has an associated wave. This wave-like behavior is significant at the quantum level, where particles such as electrons exhibit both particle and wave characteristics. Thus, this statement is also true.
Step 3: Evaluate Statement 3
Statement 3: Light of intensity I falls normally upon a plane mirror (perfectly reflecting surface). The pressure exerted is 2Ic.
Analysis:
When light strikes a perfectly reflecting surface, the momentum of the photons changes direction, effectively doubling the momentum change. The pressure exerted by the light can be calculated using the formula P=FA, where F is the force due to the change in momentum of the photons. The relationship between intensity (I), momentum, and pressure leads to the conclusion that the pressure exerted by the light is indeed 2Ic. Therefore, this statement is also true.
Conclusion
All three statements are true. Therefore, the correct option is option D.
---
Statement 1: An isolated and free electron cannot absorb a photon completely.
When a photon interacts with a free electron, the energy of the photon can be partially transferred to the electron. However, due to conservation of momentum, not all the energy can be absorbed by the electron. Part of the energy goes into increasing the kinetic energy of the electron, and the rest is used to maintain momentum conservation. Therefore, the statement is true.
Statement 2: All material particles behave wave-like when in motion.
This statement is based on de Broglie's hypothesis, which states that every moving particle or object has an associated wave. This wave-like behavior is significant at the quantum level, where particles such as electrons exhibit both particle and wave characteristics. Thus, this statement is also true.
Statement 3: Light of intensity I falls normally upon a plane mirror (perfectly reflecting surface). The pressure exerted is 2Ic.
When light strikes a perfectly reflecting surface, the momentum of the photons changes direction, effectively doubling the momentum change. The pressure exerted by the light can be calculated using the formula P=FA, where F is the force due to the change in momentum of the photons. The relationship between intensity (I), momentum, and pressure leads to the conclusion that the pressure exerted by the light is indeed 2Ic. Therefore, this statement is also true.
All three statements are true. Therefore, the correct option is option D.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Book:AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHChapter:DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Exercise:ASSIGNMENT SECTION I.Subjective
Explore 3 Videos
- DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Book:AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHChapter:DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Exercise:ASSIGNMENT SECTION J.Aakash Challengers
Explore 1 Video
- DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Book:AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHChapter:DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Exercise:ASSIGNMENT SECTION G. Integer
Explore 2 Videos
- CURRENT ELECTRICITYBook:AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHChapter:CURRENT ELECTRICITYExercise:ASSIGNMENT SECTION-J
Explore 4 Videos
- ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS Book:AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS Exercise:comprehension
Explore 3 Videos
Similar Questions
The heat of neutralization for a strong acid by a strong base is a constant
View SolutionThe intensity of the Sun's light in the vicinity of the earth is about 1000W/m2 .Imagine a spacecraft with a mirrored square sail of dimension 1.0 km. Estimate how much thrust (in newtons) this crafts will experience due to collisions with the Sun's photons
View SolutionThe photoelectric work function of potassium is 3.0 eV. If light having a wavelength of 2475 Å falls on potassium. Find the stopping potential in volts.
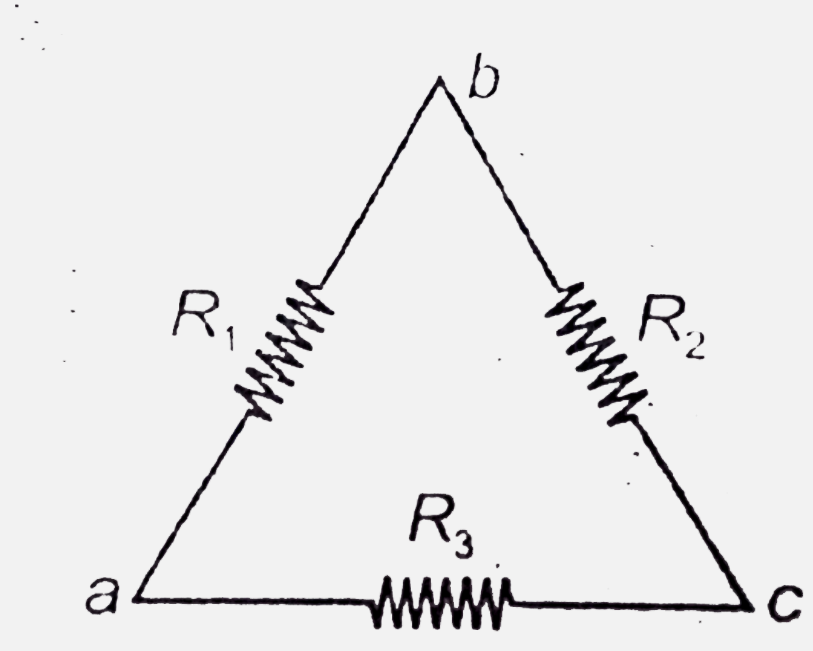
View SolutionConsider the circuit shown in the figure. Equivalent resistance between terminals ab,ac,c equals 30Ω,60Ω and 70Ω respectively. Find the respectively . Find the resistance R1,R2and R3
View SolutionA short electric dipole is placed at a distance x from centre O on the axis of a ring of radius R and charge Q is uniformly distributed over tis.

The net force acting on the dipole will be
View SolutionA plane light wave of intensity I=0.20Wcm−2 falls on a plane mirror surface with reflection coefficient ρ=0.8. The angle of incidence is 45∘. In terms of corpuscular theory, find the magnitude of the normal pressure exerted on that surface.
View SolutionStatement-1: In Photoelectric effect , electrons absorbing the photon can not be a free electron.
Statement -2: A free electron can't absorb a photon completely
View SolutionA plane electromagnetic wave is incident on a plane surface of area A, normally and is perfectly reflected. If energy E strikes the surface in time t then average pressure exerted on the surface is (c = speed of light)
View SolutionThe pressure exerted by an electromagnetic wave of intensity I (Wm^(-2)) on a non-reflecting surface is ( c is the velocity of light)
View SolutionStatement-1:An isolated and free electron cannot absorb a photon completely. Statement-2 : All material particles behave wave like when in motion. Statement-3: Light of intensity l , falls normally upon a plane mirror (perfectly reflecting surface ). The pressure exerted is "2l"/c
View Solutionl तीव्रता की वैद्युतचुम्बकीय तरंग एक पूर्ण परावर्तक तल पर अभिलम्बवत् आपतित होती है। तरंग द्वारा तल पर आरोपित दाब है (c = प्रकाश की चाल)
View SolutionI तीव्रता की वैद्युत-चुम्बकीय तरंग एक पूर्ण अवशोषक तल पर अभिलम्बवत् आपतित होती है। तरंग द्वारा तल पर आरोपित दाब है-
View Solution" of intensity "1.5kW/m^(2)" is incident normally on a perfectly absorbing surface.The pressure exerted by the light on the surface is "n times10^(-6)Pa" .Value of "n" is "
View Solutionकथन : एक कण, तरंग और कण दोनों तरह से व्यवहार कर सकता है परन्तु दी हुई स्थिति में यह या तो कण की तरह व्यवहार करेगा या फिर तरंग की सतह|
कारण : यदि एक फोटान एवं एक इलेक्ट्रान की तरंगदैर्ध्य समान हो तो फोटान का वेग इलेक्ट्रान के वेग से कम होगा|
View SolutionThe pressure exerted by an electromagnetic wave of intensity I(wm−2 on a non reflecting surface is: (C is the velocity of light)
View Solution
