A resistance R1 is connected to a source of constant voltage . On connecting a resistance R2 in series with R1
The total thermal power dissipated increases
Thermal power dissipated by R1 decreases
Thermal power dissipated by R1 increases
Total power dissipiated decreases
The correct Answer is:(2, 4)
To solve the problem step-by-step, let's analyze the situation where a resistance R1 is connected to a constant voltage source, and then a resistance R2 is added in series with R1.
Step 1: Understand the Circuit with Only R1
When only R1 is connected to the voltage source with an EMF E:
- The current I flowing through the circuit is given by Ohm's Law:
I=ER1
- The power P dissipated in R1 is given by the formula:
PR1=I2R1=(ER1)2R1=E2R1
Step 2: Analyze the Circuit with Both R1 and R2
Now, when R2 is connected in series with R1:
- The total resistance in the circuit becomes R1+R2.
- The new current I′ flowing through the circuit is:
I′=ER1+R2
- The total power Ptotal dissipated in the circuit is:
Ptotal=I′2(R1+R2)=(ER1+R2)2(R1+R2)=E2R1+R2
Step 3: Calculate the Power Across R1 with Both Resistors
The power dissipated across R1 when both resistors are connected is:
- Using the current I′:
PR1=I′2R1=(ER1+R2)2R1=E2R1(R1+R2)2
Step 4: Compare the Powers
1. Total Power Comparison:
- When only R1 is connected: Ptotal=E2R1
- When both R1 and R2 are connected: Ptotal=E2R1+R2
- Since R1+R2>R1, it follows that:
Ptotal<E2R1(Total power decreases)
2. Power Across R1 Comparison:
- When only R1 is connected: PR1=E2R1
- When both resistors are connected: PR1=E2R1(R1+R2)2
- We cannot definitively compare PR1 in both cases without knowing the relationship between R1 and R2.
Conclusion
- The total thermal power dissipated in the circuit decreases when R2 is added in series.
- We cannot determine whether the power across R1 increases or decreases without additional information about the values of R1 and R2.
Final Answer
- The total thermal power decreases when R2 is added in series with R1.
- We cannot comment on the power dissipated along R1.
When only R1 is connected to the voltage source with an EMF E:
- The current I flowing through the circuit is given by Ohm's Law:
I=ER1
- The power P dissipated in R1 is given by the formula:
PR1=I2R1=(ER1)2R1=E2R1
Now, when R2 is connected in series with R1:
- The total resistance in the circuit becomes R1+R2.
- The new current I′ flowing through the circuit is:
I′=ER1+R2
- The total power Ptotal dissipated in the circuit is:
Ptotal=I′2(R1+R2)=(ER1+R2)2(R1+R2)=E2R1+R2
The power dissipated across R1 when both resistors are connected is:
- Using the current I′:
PR1=I′2R1=(ER1+R2)2R1=E2R1(R1+R2)2
1. Total Power Comparison:
- When only R1 is connected: Ptotal=E2R1
- When both R1 and R2 are connected: Ptotal=E2R1+R2
- Since R1+R2>R1, it follows that:
Ptotal<E2R1(Total power decreases)
- When only R1 is connected: PR1=E2R1
- When both resistors are connected: PR1=E2R1(R1+R2)2
- We cannot definitively compare PR1 in both cases without knowing the relationship between R1 and R2.
- The total thermal power dissipated in the circuit decreases when R2 is added in series.
- We cannot determine whether the power across R1 increases or decreases without additional information about the values of R1 and R2.
- The total thermal power decreases when R2 is added in series with R1.
- We cannot comment on the power dissipated along R1.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CURRENT ELECTRICITYBOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHCHAPTER - CURRENT ELECTRICITYEXERCISE - ASSIGNMENT SECTION-D( LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE QUESTIONS)
3 Videos
- CURRENT ELECTRICITYBOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHCHAPTER - CURRENT ELECTRICITYEXERCISE - ASSIGNMENT SECTION-D( LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE QUESTIONS) Comprehension - II
5 Videos
- CURRENT ELECTRICITYBOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHCHAPTER - CURRENT ELECTRICITYEXERCISE - ASSIGNMENT SECTION-B(OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTION ))
44 Videos
- COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS BOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHCHAPTER - COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS EXERCISE - ASSIGNMENT SECTION D (Assertion-Reason)
10 Videos
- DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER BOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISHCHAPTER - DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER EXERCISE - ASSIGNMENT (SECTION-D)
10 Videos
Similar Questions
A galvanmeter of resistance G is converted into a voltmeter of range 0 -1V by connecting resistance R1 in series with it. The additional resistance that should be connected in series with R1 to increase the range of the voltmeter to 0-2 V will be :
View SolutionA resistance R draws power P when connected to an AC source. If an inductance is now placed in series with the resistance, such that the impedence of the circuit becomes Z, the power drawn will be
View Solution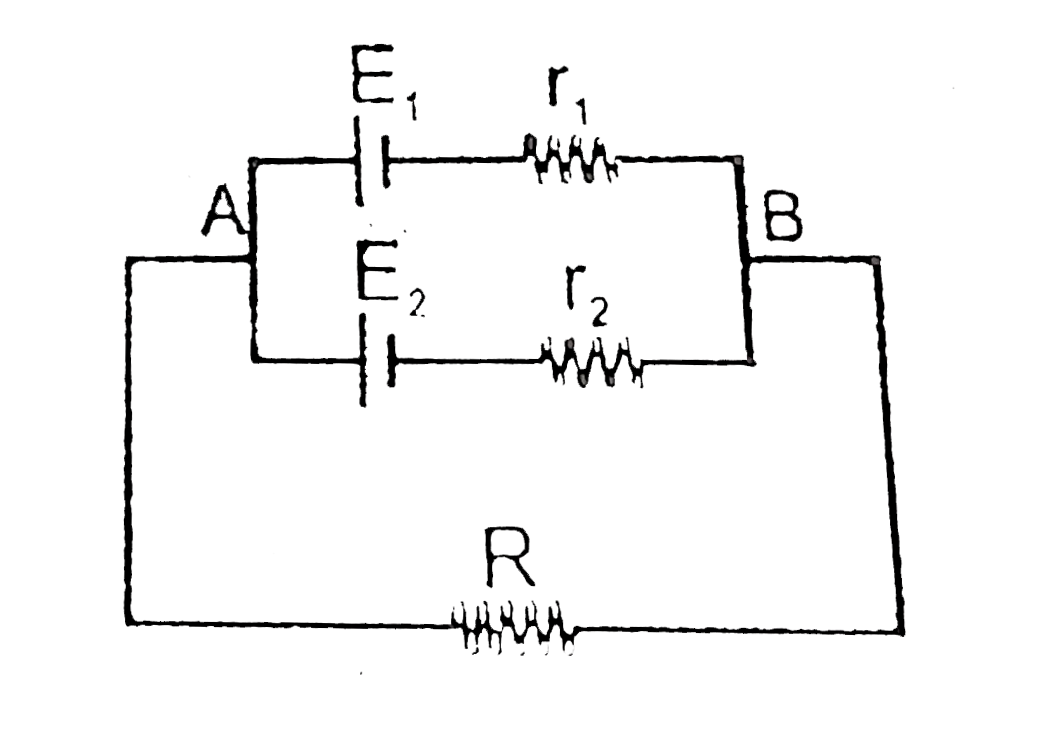
Two batteries of E1 internal resistance r1 & emf E2 internal resistance r2 are connected in parallel and makes a battery system. An external resistance R is connected across this system as shown in the figure.
View SolutionWhen a celll is connected to an external resistance R1, current through it is i1. When the same cell is connected to an external resistance R2, current through it is i2. Calculate the emf and internal resisance of the cell.
View SolutionA voltmeter of resistance R1 and an ammeter of resistance R2 are connected in series across a battery oif negligible internal resistance. When as resistance R is connected in parallel to voltmeter reading of ammeter increases three times white that of voltmeter reduces to one third. Find the ratio of R1 and R2.
View SolutionThe ratio of distance of two satellites from the centre of earth is 1 : 4. The ratio of their time periods of rotation will be :
View SolutionTwo cells of equal e.m.f. E b ut of difference internal resistance r1 and r2 are connected in parallel and the combination is connected with an external resistance R to obtain maximum power in R. find the value of R

View SolutionAn unknown resistance R1 is connected is series with a resistance of 10Ω. This combination is connected to one gap of a meter bridge, while other gap is connected to another resistance R2. The balance point is at 50cm Now , when the 10Ω resistance is removed, the balanced point shifts to 40cm Then the value of R1 is.
View SolutionAn unknown resistance R1 is connected is series with a resistance of 10Ω. This combination is connected to one gap of a meter bridge, while other gap is connected to another resistance R2. The balance point is at 50cm Now , when the 10Ω resistance is removed, the balanced point shifts to 40cm Then the value of R1 is.
View SolutionA cell of e.m.f. 2V and negligible internal resistance is connected to resistor R1 and R2 as shown in the figure. The resistance of the Voltmeter R1 and R2 are 80Ω,40Ω and 80Ω respectively. The reading of the voltmeter is:-
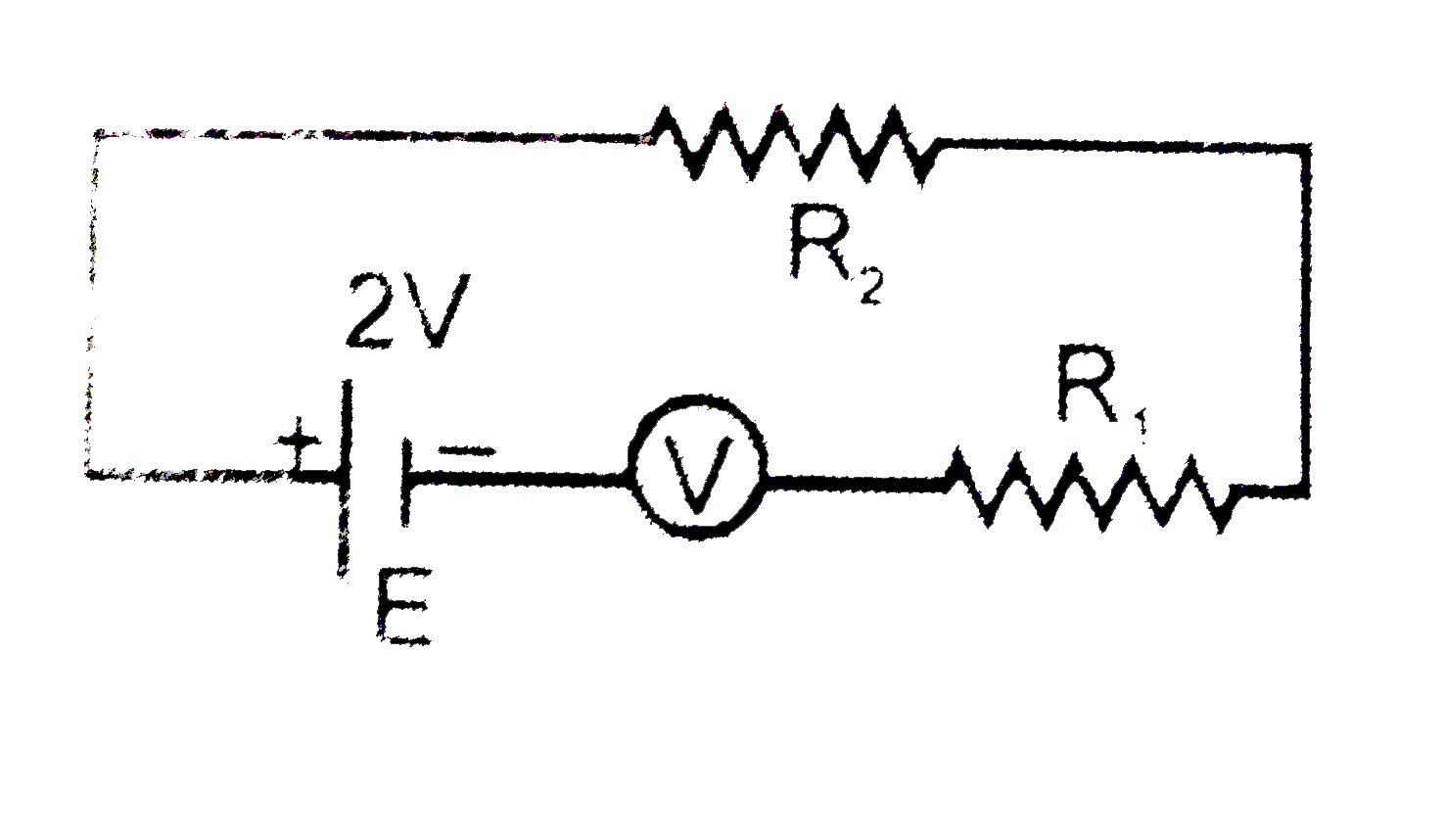
View Solution

