The curve drawn between velocity and frequency of a photon in vacuum will be
straight line parallel to frequency axis
straight line parallel to velocity axis.
straight line passing through oritgin and making an angle of 45∘ with frequency axis
hyperbola.
The correct Answer is:A
To solve the question about the relationship between the velocity and frequency of a photon in a vacuum, we can follow these steps:
1. Understand the Properties of Photons:
- Photons are particles of light that travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, denoted as c.
- The speed of light in a vacuum is a constant value, approximately 3×108 m/s.
2. Relationship Between Velocity and Frequency:
- The velocity v of a photon is related to its frequency f and wavelength λ by the equation:
v=f⋅λ
- In a vacuum, the velocity v of a photon is always equal to c, regardless of its frequency.
3. Analyze the Graph:
- Since the velocity v is constant and equal to c, it does not change with frequency f.
- This means that if we plot a graph with frequency on the x-axis and velocity on the y-axis, the velocity will remain constant at c for all values of frequency.
4. Determine the Shape of the Curve:
- A constant value of velocity means that the graph will be a horizontal line.
- Specifically, this line will be parallel to the frequency axis (x-axis) because the velocity does not depend on frequency.
5. Conclusion:
- Therefore, the correct answer is that the curve drawn between velocity and frequency of a photon in vacuum will be a straight line parallel to the frequency axis.
Final Answer:
The curve drawn between velocity and frequency of a photon in vacuum will be a straight line parallel to the frequency axis.
---
- Photons are particles of light that travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, denoted as c.
- The speed of light in a vacuum is a constant value, approximately 3×108 m/s.
- The velocity v of a photon is related to its frequency f and wavelength λ by the equation:
v=f⋅λ
- In a vacuum, the velocity v of a photon is always equal to c, regardless of its frequency.
- Since the velocity v is constant and equal to c, it does not change with frequency f.
- This means that if we plot a graph with frequency on the x-axis and velocity on the y-axis, the velocity will remain constant at c for all values of frequency.
- A constant value of velocity means that the graph will be a horizontal line.
- Specifically, this line will be parallel to the frequency axis (x-axis) because the velocity does not depend on frequency.
- Therefore, the correct answer is that the curve drawn between velocity and frequency of a photon in vacuum will be a straight line parallel to the frequency axis.
The curve drawn between velocity and frequency of a photon in vacuum will be a straight line parallel to the frequency axis.
टॉपर्स ने हल किए ये सवाल
- ELECTRO MAGNETIC WAVESBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTRO MAGNETIC WAVESExercise:Exercise 2
Explore 6 Videos
- DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMExercise:DPP.No.71
Explore 1 Video
- ELECTRODYNAMICSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTRODYNAMICSExercise:Advanced level problems
Explore 29 Videos
समान प्रश्न
Assertion : Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature
Reason : The electric and magnetic fields in electromagnetic waves are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation.
View SolutionConsider a uniform wire of length l. Cross-sectional area A, Young's modulus of the material of the wave is Y. Some information related to the wire is given in column-1 and dependence of the result is given in column-2. Then match the approprite choice between the columns and match the list given in options
Column-I Column-II(A) Let us suspend wire vertically from a (p) Young'sModulusrigud support and attach a mass m atits lower end. If the mass is slightly pulleddown and released, it executes S.H.Mof a time period which will depend on(B) Work done in stretching the wire up to length (q) elongation (x)l+xwill depend on(C) If the given is fixed between two rigid (r) length (l)supports and its temperature is decreasedthermal stress that develops in the wirewill depend on(D) If the wire is pulled at its ends equal and (s) area of cross-section (A) opposite forces of magnitude F so that itundergoes an elongation x, according toHook's law, F=kx, where k is the forceconstant.Force constant (k) of the wirewill depend on
View SolutionCalculate the magnetic moment (in Am2 ) of a thin wire with a current I = 8A, wound tightly on half a torus (see figure). The diameter of the cross section of the torus is equal to d = 5 cm, and the number of turns is N = 500.

View SolutionThe curve drawn between velocity and frequency of a photon in vacuum will be
View SolutionThe velocity of photon is proportional to (where v is frequency)
View SolutionFrequency curve is a simple form of ________ which is drawn by freehand smoothed curves. (frequency polygon / histogram )
View Solutionनिर्वात में फोटॉन के वेग और आवृत्ति में खींचा गया वक्र होगा :
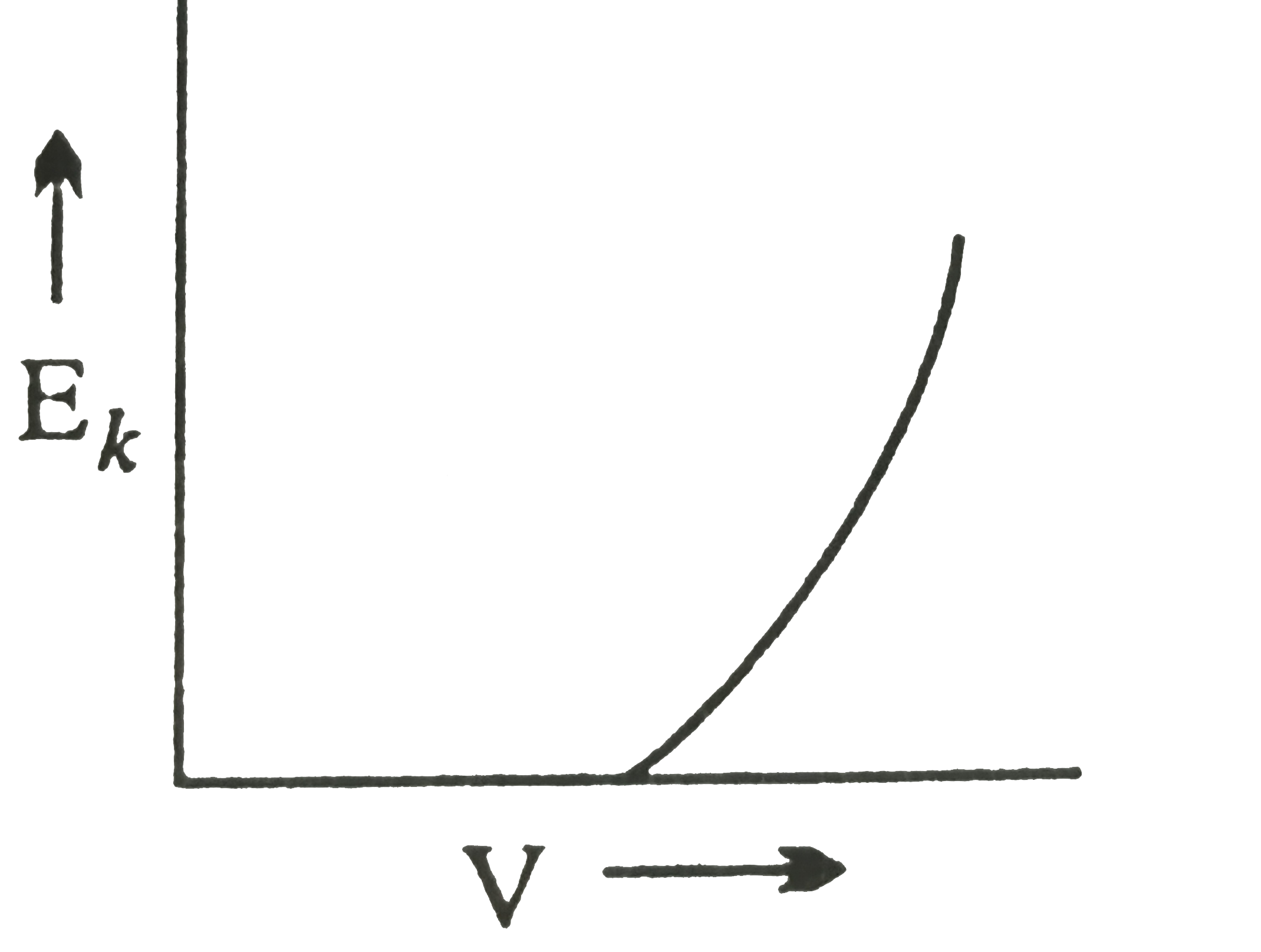
View Solutionप्रकाश-विद्युत प्रभाव के लिए उत्सर्जित फोटो इलेक्ट्रॉनों की अधिकतम गतिज ऊर्जा EK तथा आपतित फोटॉनों की आवृत्ति υe के मध्य खींचा गया वक्र चित्र में दर्शाया गया है। इस वक्र का ढाल दर्शाता है-
View Solutionfor an electron in H-atom the frequency of photon for transition between levels 1 and 2 is v. The photon frequency for transition between levels 2 and 3 is closet to
View SolutionWhat will be the frequency of photon of wavelength 1.215Å travelling in vacuum?
View SolutionA photon of frequency v has momentum associated with it equal to (c is velocity of photon):
View Solutionकण की गति के लिये वेग तथा समय के मध्य बनाये गये ग्राफ में वक्र तथा समय अन्तराल t1और t2 के बीच का क्षेत्रफल है
View SolutionOgive curve can be drawn for which type of frequency?
View SolutionThe de Broglie wavelength of an electron moving with a velocity c/2 (c=velocity of light in vacuum) is equal to the wavelength of a photon. The ratio of the kinetic energies of electron and photon is
View SolutionThe de Broglie wavelength of an electron moving with a velocity c/2 (c =velocity of light in vacuum) is equal to the wavelength of a photon. The ratio of the kinetic energies of electron and photon is
View Solution
