A radioactive nucleus (initial mass number A and atomic number Z) emits 3 α-paticles and 2 positrons. The ratio of number of neutrons to that of protons in the final nucleus will be
A−Z−8Z−4
A−Z−4Z−8
A−Z−12Z−4
A−Z−4Z−2
The correct Answer is:B
.ZXA→32He4+Z−8YA−12+2+1e0+2υ
number of proton =Z−8
number of neutron
=(A−12)−(Z−8)=A−Z−4
ratio is A−Z−4Z−8.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMExercise:DPP No.28
Explore 9 Videos
- DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMExercise:DPP No.29
Explore 20 Videos
- DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMExercise:DPP No.26
Explore 8 Videos
- CURRENT ELECTRICITYBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:CURRENT ELECTRICITYExercise:High Level Problems (HIP)
Explore 19 Videos
- ELECTRO MAGNETIC WAVESBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTRO MAGNETIC WAVESExercise:Exercise 3
Explore 27 Videos
Similar Questions
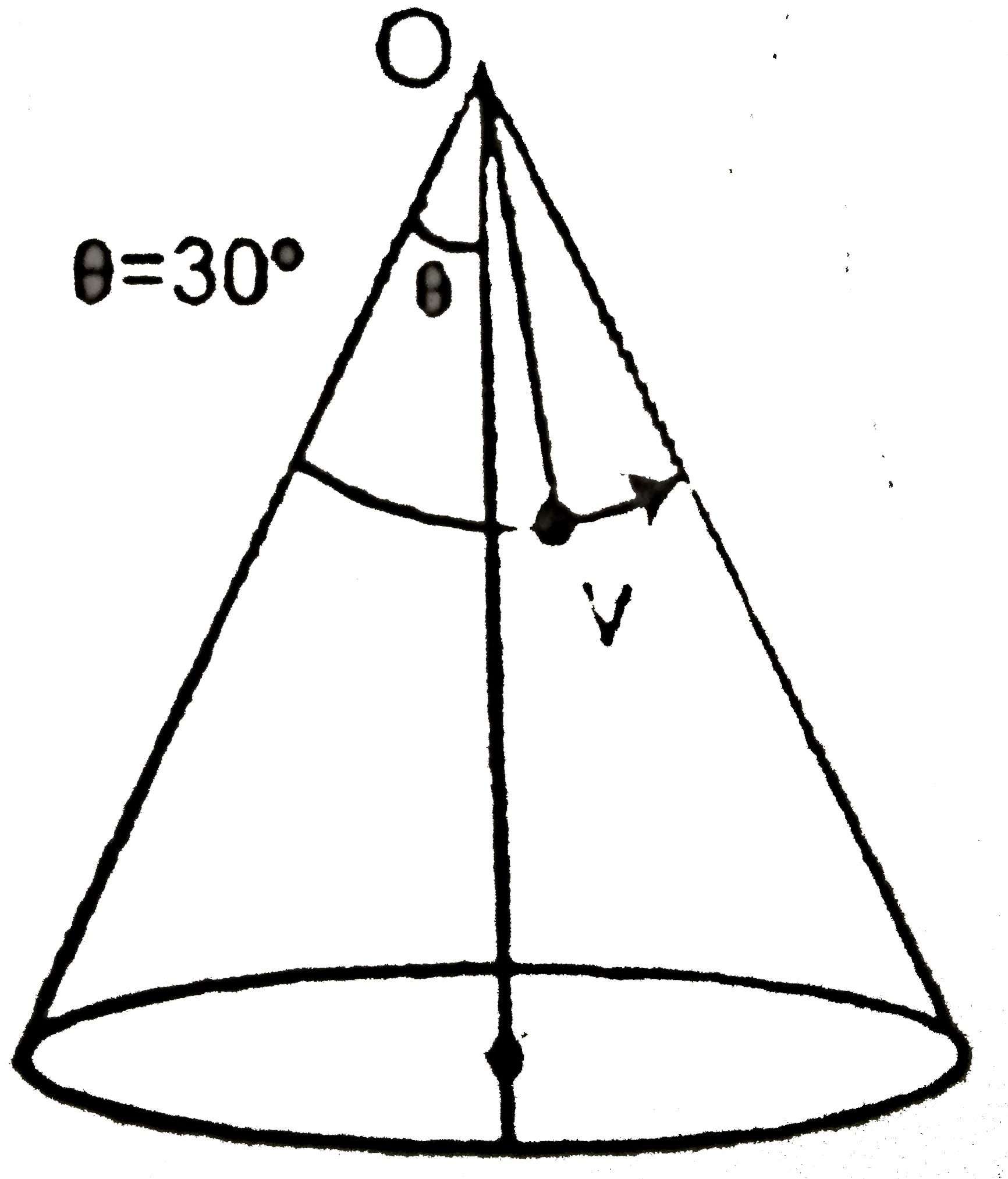
A bob of mass 2kg is suspended from point O of a core with an inextensible string strinng of length √3m. It is moving in horizontal circle over the surface of cone as shown in the figure. Then :(g=10m/s2)
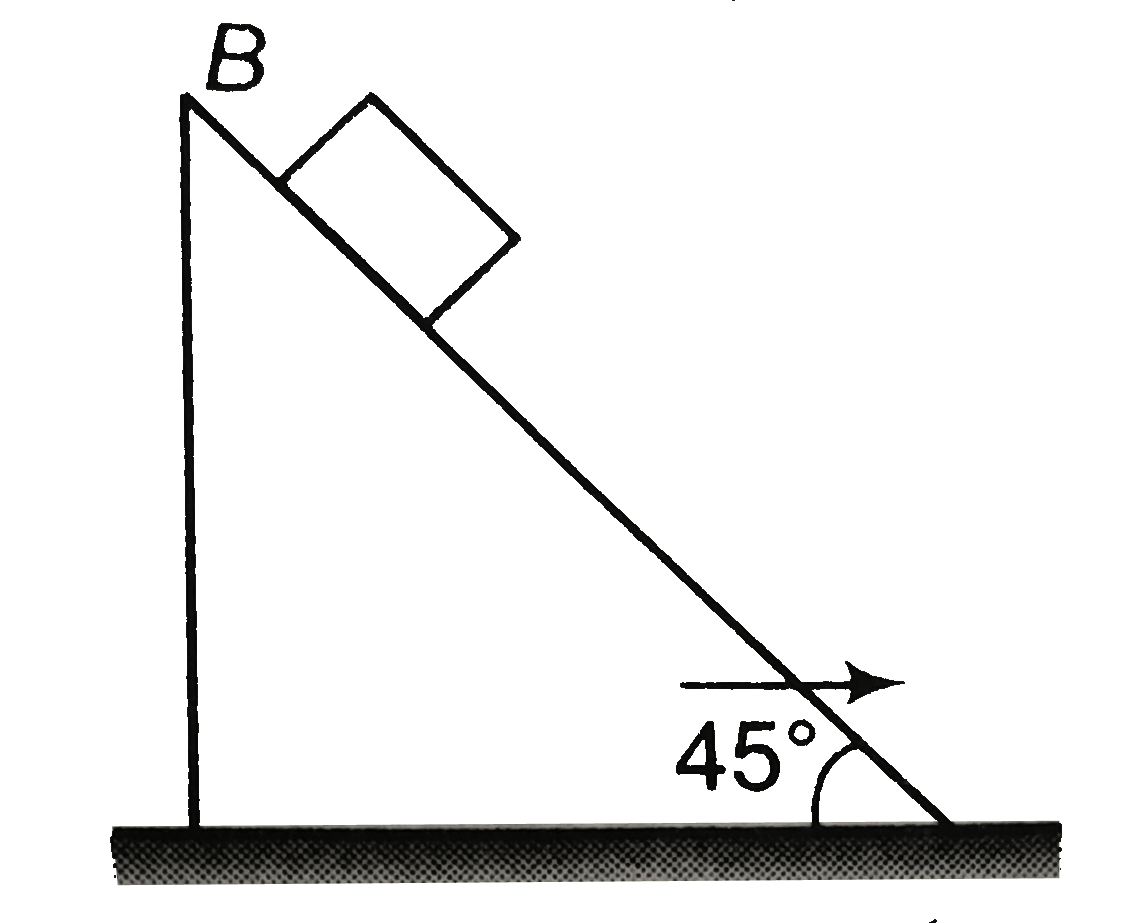
View SolutionIf the coefficient of friction between A and B is μ, the maximum acceleration of the wedge A for which B will remain at rest with respect to the wedge is
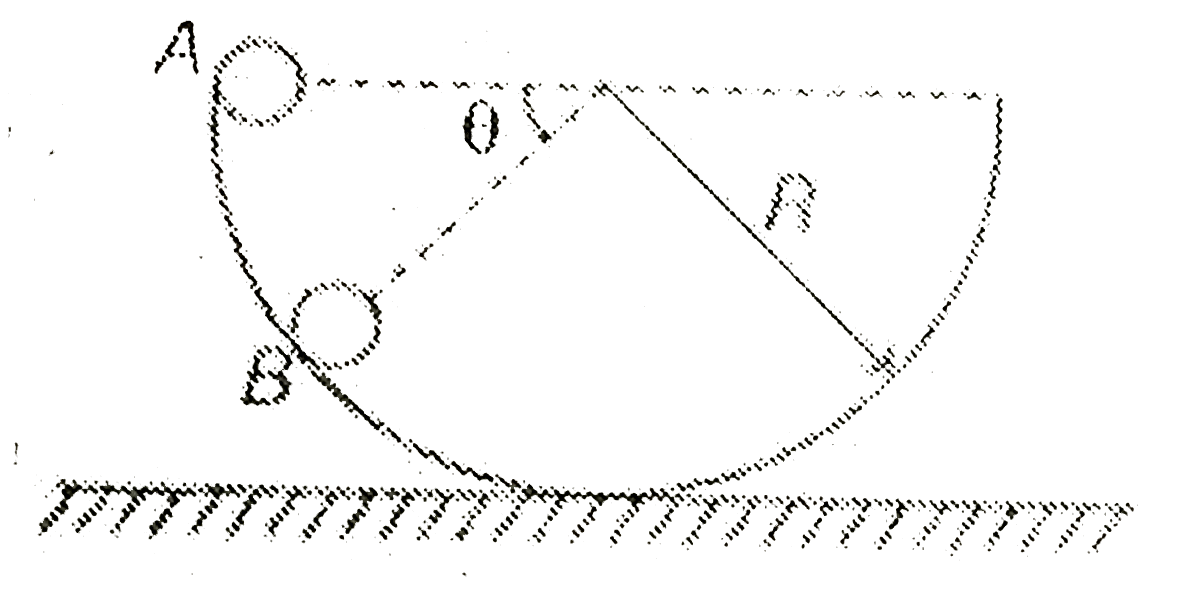
View SolutionA small particle of mass m is released from rest from point A inside a smooth hemishperical bowl as shown in figure. The ratio (X) of magnitude of centripetal force and normal reaction on the particle at any point B varies with θ as
View SolutionA galvanometer having 30 divisions has a current sensitivity of 20μA/ division. It has a resistance of 5Ω How will you convert it into an ammeter measuring upto 1A ?
View SolutionAn electromagnetic wave of frequency υ=3 MHz passes from vacuum into a dielectric medium with permittivity ε=4. Then
View SolutionA radiaoactive nucleus (initial mass number A and atomic number Z emits 3 a- particles and 2 positrons The ratio of number of neutrons to that of proton in the final nucleus will be
View Solutionएक रेडियोऐक्टिव नाभिक (प्रारंभिक द्रव्यमान संख्या A तथा परमाणु क्रमांक Z) 3 अल्फा कण तथा 2 पाजिट्रॉन उत्सर्जित करता है | अंतिम नाभिक में न्यूट्रॉनों और प्रोटॉनों का अनुपात होगा -
View Solutionएक नाभिक, पोजिट्रॉन तथा γ विकिरण उत्सर्जित करता है | यदि प्रारम्भिक नाभिक के परमाणु क्रमांक व द्रव्यमान संख्या Z व A हैं तो अन्तिम नाभिक के परमाणु क्रमांक व द्रव्यमान संख्या होगी :
View Solutionएक नाभिक AZX, एक α-कण उत्सर्जित करता है और परिणामी नाभिक एक पोजिट्रॉन उत्सर्जित करता है | अन्तिम नाभिक का परमाणु क्रमांक व द्रव्यमान संख्या क्रमश: होगी:
View Solutionएक रेडियोऐक्टिव नाभिक (द्रव्यमान संख्या A तथा परमाणु संख्या Z) तीन α-कण तथा दो पोजिट्रॉन उत्सर्जित करता है | अन्तिम नाभिक मैं न्यूट्रॉनों तथा प्रोटॉनों की संख्या का अनुपात होगा :
View SolutionA radioactive nucleus (initial mass number A and atomic number Z) emits 3α-particles and 2 positrons. The ratio of number of neutrons to that of protons in the final nucleus will be
View SolutionA radioactive nucleus ._(Z) X^(A) emite 3 alpha- particles and 5 beta - particles . The ratio of number of neutrons to that of protons in the producet nucleus will be :
View SolutionA radioactive nucleus (initial mass number A and atomic number Z) emits 2α and 2 positrons. The ratio of number of neutrons to that of proton in the final nucleus will be
View SolutionA radioactive nucleus (initial mass number A and atomic number Z) emits 2α and 2 positrons. The ratio of number of neutrons to that of proton in the final nucleus will be
View SolutionA radioactive nucleus (initial mass number A and atomic number Z) emits 2α and 2 positrons. The ratio of number of neutrons to that of proton in the final nucleus will be
View SolutionA radioactive nucleus (initial mass number A and atomic number Z) emits 3 α -particles and 2 positrons. The ratio of number of neutrons to that of protons in the final nucleus will be:
View Solution
