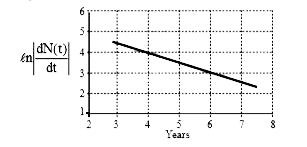
To determine the half life of a radioactive element , a student plot a graph of in ∣∣∣dN(t)dt∣∣∣ versus t , Here ∣∣∣dN(t)dt∣∣∣ is the rate of radiation decay at time t , if the number of radioactive nuclei of this element decreases by a factor of p after 4.16year the value of p is
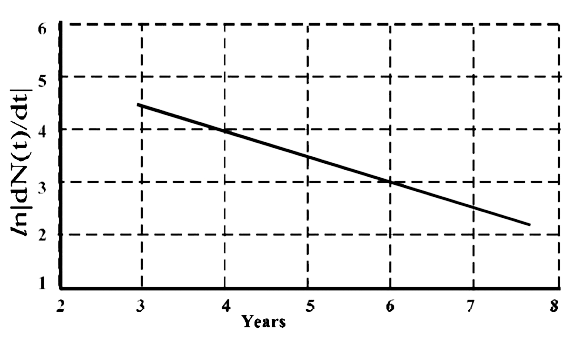
The correct Answer is:8
−dNdt=λN
=dNdt=λN0e−λt
ln∣∣∣dNdt∣∣∣=−λt+ln(λN0)
y=mx+c
m=−λ
λ=12 [slope by graph =12]
T=ln2λ
=2×0.693=4.16n
n=3=no. of half life.
p=z3=8.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- NUCLEAR PHYSICSBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - NUCLEAR PHYSICSEXERCISE - Exercise-3 Part-II JEE (MAIN)
19 Videos
- NUCLEAR PHYSICSBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - NUCLEAR PHYSICSEXERCISE - Exercise -3 Part-III CBSE PROBLEMS (LAST 10 YEARS)
34 Videos
- NUCLEAR PHYSICSBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - NUCLEAR PHYSICSEXERCISE - Exercise-2 Part-4 Comprehension
6 Videos
- GRAVITATIONBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - GRAVITATIONEXERCISE - HIGH LEVEL PROBLEMS
16 Videos
- REVISION DPPBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - REVISION DPPEXERCISE - All Questions
463 Videos
Similar Questions
Starting with a sample of pure 66Cu,78 of it decays into Zn in 15 min. The corresponding half-life is
View SolutionWhen a deuteron of mass 2.0141 a.m.u and negligible K.E. is absorbed by a Lithium (.3Li6) nucleus of mass 6.0155 a.m.u. the compound nucleus disintegration spontaneously into two alpha particles, each of mass 4.0026 a.m.u. Calculate the energy carried by each α particle.
View SolutionThe radionuclide .56Mn is being produced in a cyclontron at a constant rate P by bombarding a manganese target with deutrons. .56Mn has a half-life of 2.5h and the target contains large numbers of only the stable manganese isotopes .56Mn. The reaction that produces .56Mn is
.56Mn+d→.56Mn+p
After being bombarded for a long time, the activity of .56Mn becomes constant, equal to 13.86×1010s−1. (Use 1n2=0.693, Avagardo number =6×102, atomic weight of .56Mn=56gmol−1).
At what constant rate P, .56Mn nuclei are being produced in the cyclontron during the bombardment?
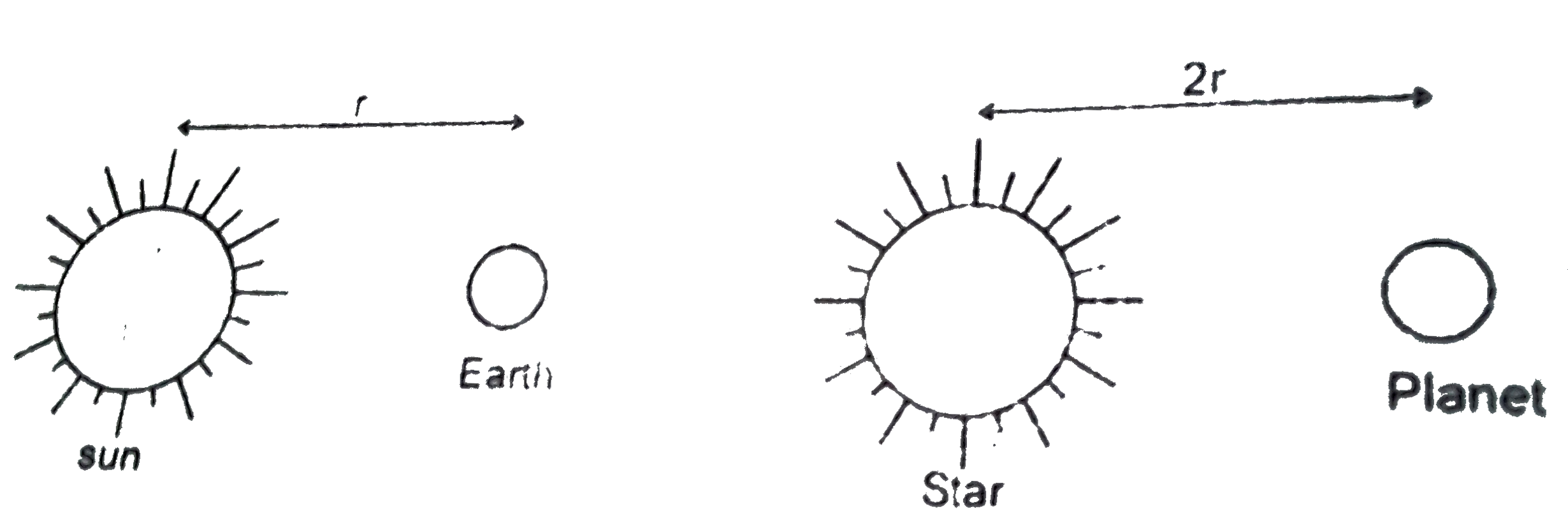
View SolutionLet a star be much brighter than our sun but its mass is same as that of sun If our earth has average lift span of man as 70years In the earth like planet of this star system having double the distance from our star find the average lift span of a man on this planet in terms of our year
 .
.
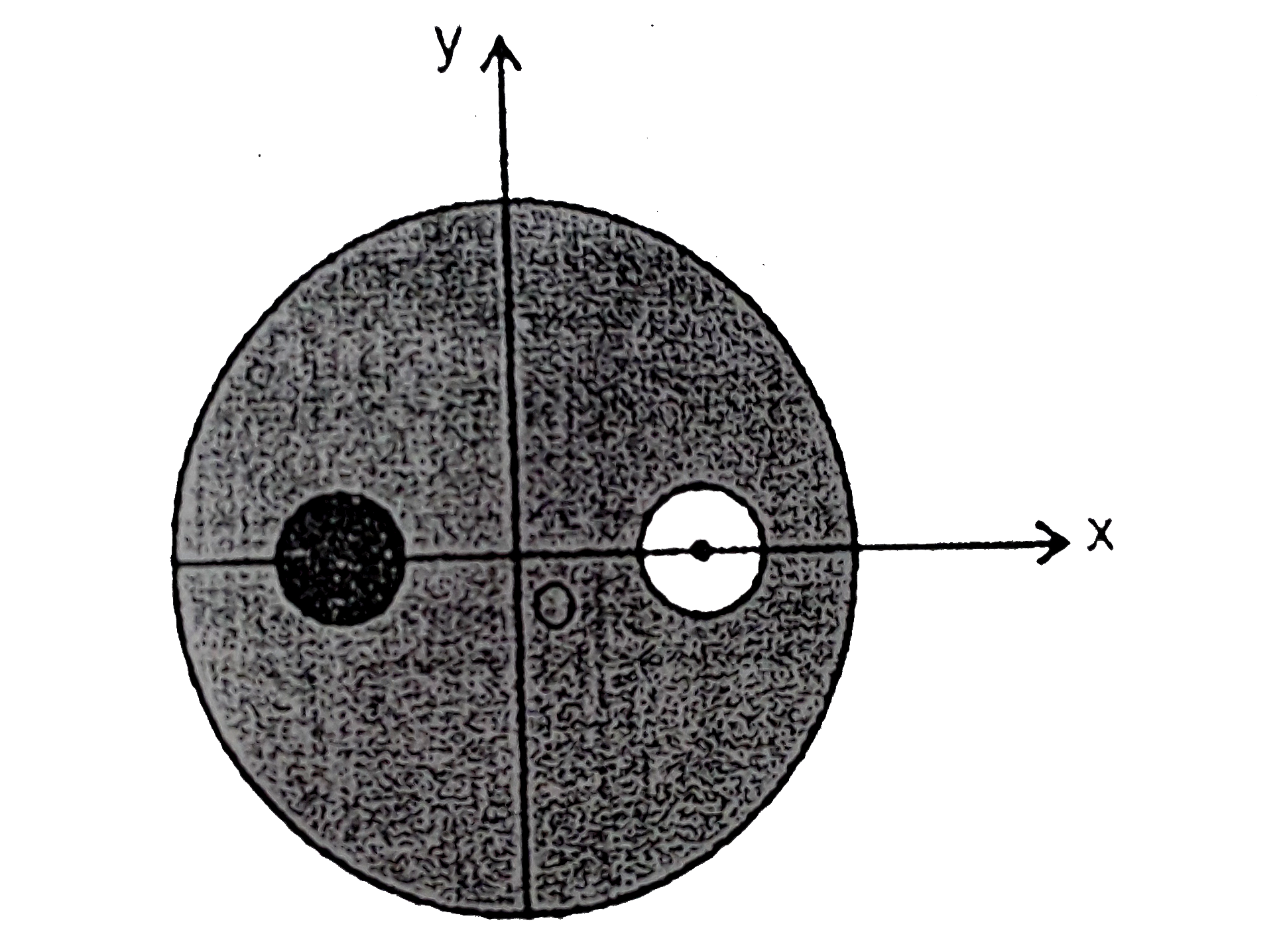
View SolutionConsider a solid sphere of density ρ and radius 4R. Centre of the sphere is at origin. Two spherical cavities centred at (2R,0) and (−2R,0) are created in sphere. Radii of both cavities is R. In left cavity material of density 2ρ is filled while second cavity is kept empty. What is gravitational field at origin.
View SolutionTo determine the half life of a radioactive element , a student plot a graph of in ∣∣∣dN(t)dt∣∣∣ versus t , Here ∣∣∣dN(t)dt∣∣∣ is the rate of radiation decay at time t , if the number of radioactive nuclei of this element decreases by a factor of p after 4.16year the value of p is

View SolutionNuclei of radioactive element A are produced at rate 't^(2') (where t is time) at any time t . The element A has decay constant lambda . Let N be the number of nuclei of element A at any time t . At time t=t_(0), dN//dt is minimum. The number of nuclei of element A at time t=t_(0) is
View SolutionFor a radioactive material, its activity A and rate of change of its activity of R are defined as A=−dNdt and R=−dAdt, where N(t) is the number of nuclei at time t. Two radioactive source P (mean life τ) and Q (mean life 2τ) have the same activity at t=0. Their rates of activities at t=2τ are Rp and RQ, respectively. If RPRQ=ne, then the value of n is:
View SolutionIf −(dNdt)o is the initial activity and −(dNdt) is the activity at time t in a radioactive disintegration then :
View SolutionRadioactive element decays to form a stable nuclide, then the rate of decay of reactant ((dN)/(dt)) will vary with time (t) as shown in figure
View SolutionTo determine the half life of a radioactive element, a student plots a graph of In ∣∣∣dN(t)dt∣∣∣ versus t. Here dN(t)dt is the rate of radioactive decay at time t.
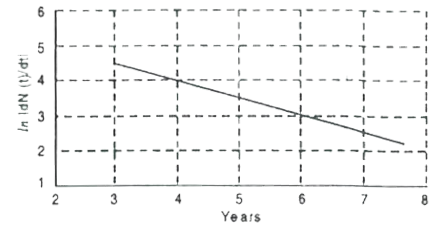
If the number of radioactive nuclei of this element decreases by a factor of p after 4.16 years. the value of p is...........
View Solutionकिसी रेडियोसक्रिय तत्व की अर्ध - आयु निकालने के लिए एक छात्र ln|dN(t)/dt| का एक t साथ ग्राफ़ बनता है [चित्र] यहाँ dN(t)/dt,t समय पर रेडियोसक्रिय क्षय की दर है। यदि इस तत्व के रेडियोसक्रिय नाभिकों की संख्या , 4.16 वर्षों के बाद p के घटक से कम हो जाती हो , तो p का मान है।
View SolutionDraw a graph showing the variation of decay rate (−dNdt) with number (N) of radioactive nuclei.
View SolutionA radioactive sample decays to form a stable nuclide. A graph showing variation of rate of disintegration (dNdt) of radioactive sample with time (t) is
View Solutionरेडियोधर्मी तत्व की अर्द्धआयु ज्ञात करने के लिये एक छात्र ln∣∣∣dN(t)dt∣∣∣ का t के साथ ग्राफ बनाता है। यहाँ dN(t)dt रेडियोधर्मी क्षय की। समय पर दर है। यदि 4.16 सालों के बाद इस रेडियोधर्मी पदार्थ के नाभिकों की संख्या p घटक से कम हो जाती है. p का मान बताइये।
View SolutionTo determine the half life of a radioactive element , a student plote a graph of in ∣∣∣dN(t)dt∣∣∣versust,Here∣∣∣dN(t)dt∣∣∣ is the rate of radioatuion decay at time t , if the number of radoactive nuclei of this element decreases by a factor of p after 4.16 year the value of p is

View Solution

