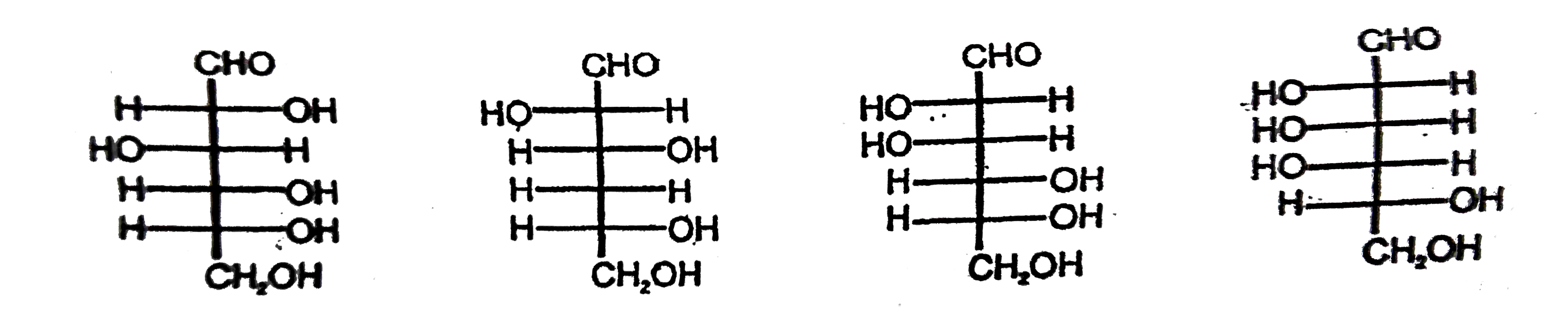
Draw fisher projections for the two D-aldoheptose whose stereorientation at C2,C3,C4,C5 is same as that of D−glucose
at C2,C3,C4 and C5.
The correct Answer is:(##RESORGCHMV02XIIC04E01253_A01##)
To solve the problem of drawing Fischer projections for the two D-aldoheptoses whose stereochemistry at C2, C3, C4, and C5 is the same as that of D-glucose, we will follow these steps:
Step 1: Draw the Fischer projection of D-glucose
1. Start by drawing the aldehyde group (CHO) at the top.
2. Below the aldehyde, draw the carbon chain with 7 carbons in total (C1 to C7).
3. For each of the stereocenters (C2, C3, C4, C5), place the hydroxyl (OH) groups according to the configuration of D-glucose:
- C2: OH on the right
- C3: OH on the right
- C4: OH on the left
- C5: OH on the right
4. The last carbon (C7) will have a CH2OH group.
Fischer Projection of D-glucose:
CHO|C1|C2−OH|C3−OH|C4−H|C5−OH|C6−H∣C7−CH2OH
Step 2: Draw the first D-aldoheptose
1. The first D-aldoheptose will have the same configuration at C2, C3, C4, and C5 as D-glucose.
2. Start with the aldehyde group (CHO) at the top.
3. For the carbon chain, keep the same stereochemistry:
- C2: OH on the right
- C3: OH on the right
- C4: OH on the left
- C5: OH on the right
4. At C6, we will place an OH group on the left side (this is the variation).
5. The last carbon (C7) will still have a CH2OH group.
Fischer Projection of the first D-aldoheptose:
CHO|C1|C2−OH|C3−OH|C4−H|C5−OH|C6−OH∣C7−CH2OH
Step 3: Draw the second D-aldoheptose
1. Start with the aldehyde group (CHO) at the top.
2. For the carbon chain, keep the same stereochemistry:
- C2: OH on the right
- C3: OH on the right
- C4: OH on the left
- C5: OH on the right
3. At C6, we will place an OH group on the right side (this is the variation).
4. The last carbon (C7) will still have a CH2OH group.
Fischer Projection of the second D-aldoheptose:
CHO|C1|C2−OH|C3−OH|C4−H|C5−OH|C6−H∣C7−CH2OH
Summary of the Fischer Projections:
- The first D-aldoheptose has the OH group on the left at C6.
- The second D-aldoheptose has the OH group on the right at C6.
1. Start by drawing the aldehyde group (CHO) at the top.
2. Below the aldehyde, draw the carbon chain with 7 carbons in total (C1 to C7).
3. For each of the stereocenters (C2, C3, C4, C5), place the hydroxyl (OH) groups according to the configuration of D-glucose:
- C2: OH on the right
- C3: OH on the right
- C4: OH on the left
- C5: OH on the right
4. The last carbon (C7) will have a CH2OH group.
CHO|C1|C2−OH|C3−OH|C4−H|C5−OH|C6−H∣C7−CH2OH
1. The first D-aldoheptose will have the same configuration at C2, C3, C4, and C5 as D-glucose.
2. Start with the aldehyde group (CHO) at the top.
3. For the carbon chain, keep the same stereochemistry:
- C2: OH on the right
- C3: OH on the right
- C4: OH on the left
- C5: OH on the right
4. At C6, we will place an OH group on the left side (this is the variation).
5. The last carbon (C7) will still have a CH2OH group.
CHO|C1|C2−OH|C3−OH|C4−H|C5−OH|C6−OH∣C7−CH2OH
1. Start with the aldehyde group (CHO) at the top.
2. For the carbon chain, keep the same stereochemistry:
- C2: OH on the right
- C3: OH on the right
- C4: OH on the left
- C5: OH on the right
3. At C6, we will place an OH group on the right side (this is the variation).
4. The last carbon (C7) will still have a CH2OH group.
CHO|C1|C2−OH|C3−OH|C4−H|C5−OH|C6−H∣C7−CH2OH
- The first D-aldoheptose has the OH group on the left at C6.
- The second D-aldoheptose has the OH group on the right at C6.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- BIOMOLECULESBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:BIOMOLECULESExercise:Advanced Level(Part I)
Explore 20 Videos
- BASIC CONCEPTSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:BASIC CONCEPTSExercise:ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(BASIC CONCEPTS)
Explore 27 Videos
- BIOMOLECULES & POLYMERBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:BIOMOLECULES & POLYMERExercise:ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Biomolecules & Polymer)
Explore 34 Videos
Similar Questions
Carbohydrates contain?
View SolutionThe kinetic energy of an electron accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 3V will be:
View SolutionWhich two of the following aldohexoses give the same osazone derivative ?
View Solution[(^nC0+nC3+)1/2(^nC1+nC2+nC4+nC5]2+3/4(^nC1−nC2+nC4−nC5+)2= 3 b. 4 c. 2 d. 1
View SolutionThe order of the differential equation,whose general solution is y=C_(1)e^(x)+C_(2)e^(2x)+C_(3)e^(3x)+C_(4)e^(x-c_(5)) where C_(1),C_(2),C_(3),C_(4),C_(5) are arbitrary constants,is
View SolutionC0C2+C1C3+C2C4+c3C5+...+Cn−2Cn
View Solution(C_(0)-C_(2)+C_(4)-C_(6)......)^(2)+(C_(1)-C_(3)+C_(5)-C_(7).........)^(2)=2^(n)
View SolutionDraw fisher projections for the two D -aldoheptose whose stereorientation at C_(2),C_(3),C_(4),C_(5) is same as that of D- glucose at C_(2),C_(3),C_(4) and C_(5) .
View SolutionFind the sum of the following
C0.C3+C1.C4+C2.C5+…+Cn−3.Cn.
View Solution.5C0+.5C1+.5C2+.5C3+.5C4+.5C5=……………
View Solutionसिद्ध कीजिए कि .5C1+5C2+5C3+5C4+5C5=31
View Solution15C0⋅5C5+15C1⋅5C4+15C2⋅5C3+15C3⋅5C2+15C4⋅5C1 is equal to :
View SolutionIf c_(1) ,c_(2),c_(3),c_(4),c_(5) And c_6 Is a constant, then the order of the differential equation whose comprehensive solution y=c_(1) cos(x +c_(2))+c_(3)sin(x+c_(4))+c_(5)e^(x)+c_(6) is.
View SolutionThe order of the differential equation whose solution is given by y=(c1+c2)cos(x+c3)−c4ex+c5wherec_(1), c_(2), c_(3), c_(4), c_(5)are arotrary constant -
View SolutionFind the differential equation whose general solution is given by y=(c1+c2)cos(x+c3)−c4ex+c5, where c1,c2,c3,c4,c5 are arbitary constants.
View Solution
