What is the expected value of van't Hoff factor for K3[Fe(CN)6] in dilute solution?
i=4 because
K3[Fe(CN)6])→3K++[Fe(CN)6]3−
Topper's Solved these Questions
- SOLUTIONSBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - SOLUTIONSEXERCISE - EXERCISE-1(PART-1)
33 Videos
- SOLUTIONSBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - SOLUTIONSEXERCISE - EXERCISE-1(PART-2)
40 Videos
- SOLUTIONSBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - SOLUTIONSEXERCISE - (MSPs)
7 Videos
- SOLUTION AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIESBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - SOLUTION AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIESEXERCISE - PHYSICAL CHEMITRY (SOLUTION & COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES)
51 Videos
- STEREOISOMERISMBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - STEREOISOMERISMEXERCISE - EXERCISE (PART III : PRACTICE TEST-2 (IIT-JEE (ADVANCED PATTERN))
23 Videos
Similar Questions
Calculate the normality of NaOH when 2g is present in 800mL solution.
View SolutionPersons are medically considered to have lead poisoning if they
have a concentration greater than 10 micrograms of lead per decilitre
of blood. What is the concentration in parts per billion?
View SolutionA 6.90M solution of KOH contains 30% by weight of KOH. Calculate the density of the solution.
View SolutionA system of greater disorder of molecules is more probable. The disorder of molecules is reflected by the entropy of the system. A liquid vapourizes to form a more disordered gas. When a solute is present, there is additional contribution to the entropy of the liquid due to increased randomness. As the entropy of solution is higher than that of pure liquid, there is weaker tendency to form the gas. Thus, a solute (non-volatile) lowers the vapour pressure of a liquid, and hence a higher boiling point of the solution.
Similarly, the greater randomness of the solution opposes the tendercy to freeze. In consequence, a lower temperature must be reached for achieving the equilibrium between the solid (frozen solvent) and the solution. The elevation in boiling point (ΔTb) and depression in freezing point (ΔTf) of a solution are the colligative properties which depend only on the concentration of particles of the solute and not their identity. For dilute solutions, (ΔTb) and (ΔTf) are proportional to the molarity of the solute in the solution.
To aqueous solution of Nal, increasing amounts of solid Hgl2 is added. The vapour pressure of the solution
View Solution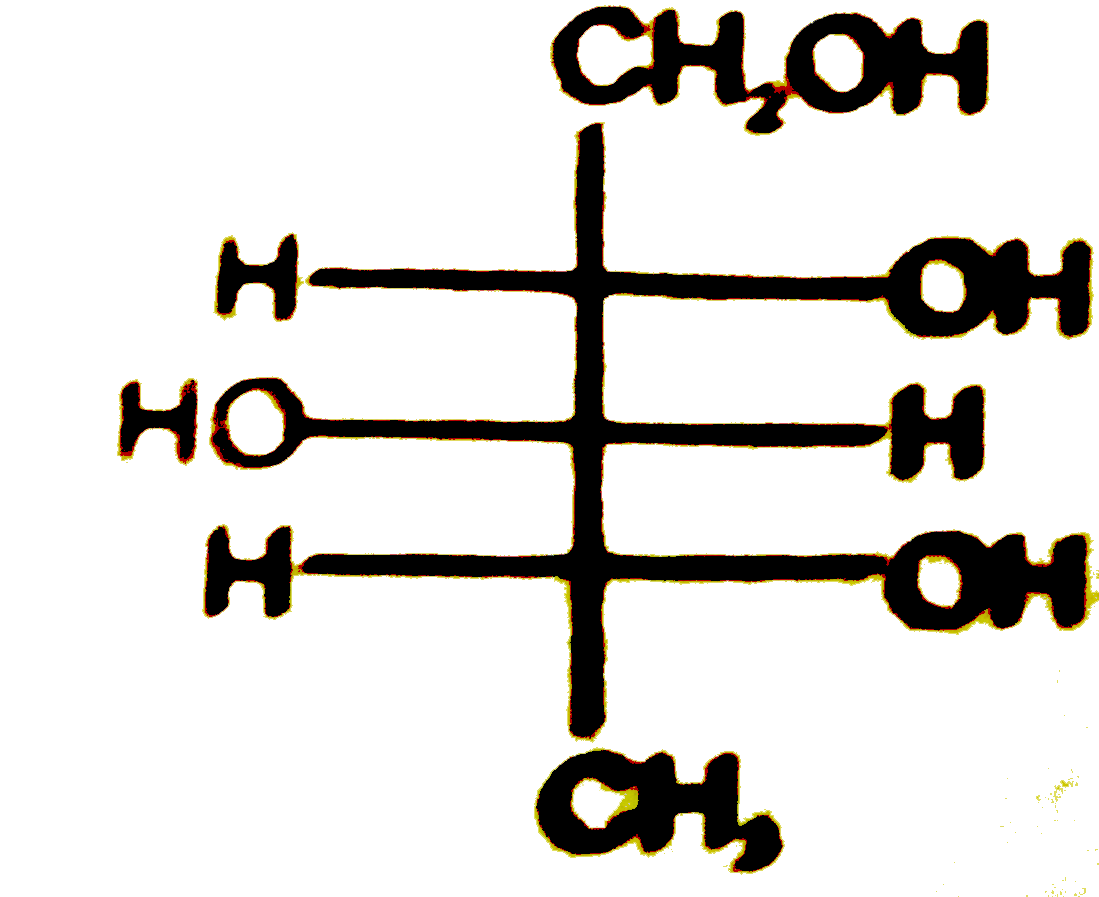 is a Fischer projection of one of_______ stereoisomers ?
is a Fischer projection of one of_______ stereoisomers ?
View SolutionWhich one of the following salts will have the same value of van't hoff factor (i) as that of K_(4)[Fe(CN)_(6)] ?
View SolutionWhat is expected value of van't Hoff factor for K3[Fe(CN)6] in the dilute solution?
View SolutionWhich one of the following salts would have the same value of the van't Hoff factor as that of K3Fe(CN)6 ?
View SolutionWhat is the expected value of Van't Hoff factor for K_(4)[Fe(CN)_(6)] when it completley dissociates in water ?
View SolutionVan't Hoff factor of a centinormal solution solution of K3[Fe(CN)6] is 3.333. The precentage dissociation of K3[Fe(Cn6)6] is :
View SolutionThe Van't Hoff factor (i) for a dilute solution of K_(3)[Fe(CN)_(6)] is
View SolutionThe van't Hoff factor for a dilute solution of K_(3)[Fe(CN)_(6)] is likely to be
View SolutionWhich of the salts has the same value of van't Hoff factor 'i' as K3[Fe(CN)6]?
View SolutionVan't Hoff factor of centimolal solution of K3[Fe(CN)6] is 3.333 . Calculate the percent dissociation of K3[Fe(CN)6]
View SolutionWhich onc of the following salts will have the same value of van't Hoff factor (i) as that of K4[Fe(CN)6].
View SolutionK3[Fe(CN)6] के लिए वान्ट हॉफ कारक का मान बताओं।
View Solution

