An organic liquid, A is immiscible with water. When boiled together with water, the boiling point is 90∘C which the partial vapour pressure of water is 256mmHg. The superincumbent (atmospheric) pressure is 736mmHg. The weight ratio of the liqid water collected 2.5:1. What is the molecular weight of the liquid.
The correct Answer is:mL=112.7
To solve the problem, we will use the relation between the weights of the liquid and water collected, their molecular weights, and their partial vapor pressures.
1. Identify Given Data:
- Boiling point of the mixture = 90∘C
- Partial vapor pressure of water (Pw) = 256mm Hg
- Atmospheric pressure (Patm) = 736mm Hg
- Weight ratio of liquid to water = 2.5:1
2. Calculate the Partial Vapor Pressure of the Liquid:
The partial vapor pressure of the liquid (PA) can be calculated using the formula:
PA=Patm−Pw
Substituting the values:
PA=736mm Hg−256mm Hg=480mm Hg
3. Set Up the Weight Ratio Equation:
The weight ratio of the liquid (w1) to water (w2) is given as:
w1w2=2.51
Therefore, we can express w1 in terms of w2:
w1=2.5w2
4. Use the Formula Relating Weights and Partial Pressures:
The relation between the weights of the liquid and water, their molecular weights (MA for the liquid and Mw for water), and their partial pressures is given by:
w1w2=MA⋅PAMw⋅Pw
Substituting w1 and w2:
2.5w2w2=MA⋅48018⋅256
This simplifies to:
2.5=MA⋅48018⋅256
5. Solve for the Molecular Weight of the Liquid:
Rearranging the equation to solve for MA:
MA=2.5⋅18⋅256480
Now, calculate MA:
MA=2.5⋅18⋅256480=11520480=24g/mol
Final Answer:
The molecular weight of the liquid A is 24g/mol.
- Boiling point of the mixture = 90∘C
- Partial vapor pressure of water (Pw) = 256mm Hg
- Atmospheric pressure (Patm) = 736mm Hg
- Weight ratio of liquid to water = 2.5:1
The partial vapor pressure of the liquid (PA) can be calculated using the formula:
PA=Patm−Pw
Substituting the values:
PA=736mm Hg−256mm Hg=480mm Hg
The weight ratio of the liquid (w1) to water (w2) is given as:
w1w2=2.51
Therefore, we can express w1 in terms of w2:
w1=2.5w2
The relation between the weights of the liquid and water, their molecular weights (MA for the liquid and Mw for water), and their partial pressures is given by:
w1w2=MA⋅PAMw⋅Pw
Substituting w1 and w2:
2.5w2w2=MA⋅48018⋅256
This simplifies to:
2.5=MA⋅48018⋅256
Rearranging the equation to solve for MA:
MA=2.5⋅18⋅256480
Now, calculate MA:
MA=2.5⋅18⋅256480=11520480=24g/mol
The molecular weight of the liquid A is 24g/mol.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- SOLUTIONSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:SOLUTIONSExercise:EXERCISE-2(PART-2)
Explore 37 Videos
- SOLUTIONSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:SOLUTIONSExercise:EXERCISE-2(PART-4)
Explore 4 Videos
- SOLUTIONSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:SOLUTIONSExercise:EXERCISE-1(PART-3)
Explore 3 Videos
- SOLUTION AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIESBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:SOLUTION AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIESExercise:PHYSICAL CHEMITRY (SOLUTION & COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES)
Explore 51 Videos
- STEREOISOMERISMBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:STEREOISOMERISMExercise:EXERCISE (PART III : PRACTICE TEST-2 (IIT-JEE (ADVANCED PATTERN))
Explore 23 Videos
Similar Questions
An organic liquid, A is immiscible with water. When boiled together with water, the boiling point is 90∘C which the partial vapour pressure of water is 652mmHg. The superincumbent (atmospheric) pressure is 736mmHg. The weight ratio of the liqid water collected 2.5:1. What is the molecular weight of the liquid.
View SolutionAn organic liquid, A is immiscible with water. When boiled together with water, the boiling point is 90∘C which the partial vapour pressure of water is 345mmHg. The superincumbent (atmospheric) pressure is 736mmHg. The weight ratio of the liqid water collected 2.5:1. What is the molecular weight of the liquid.
View SolutionBoiling point of a mixture of water and nitrobenzene is 99∘C, the vapour pressure of water is 733mm of Hg and the atmospheric pressure is 760nn if Hg. The molecular weight of nitrobenzene is 123. Find the ratio weights of the components of the distillate.
View SolutionAt 25∘C, the vapour pressure of pure water is 25.0mmHg. And that of an aqueous dilute solution of urea is 20mmHg. Calculate the molality of the solution.
View SolutionIn the steam distillation of an organic oil (immiscible with water), the mixture of oil and water boils at 372 K under 1 atm pressure. The vapour pressure of water is 595 mm of Hg at this temperature. The collected condensate contains 50% by weight of the oil. Calculate the molecular weight of the oil.
View SolutionThe vapour pressure of water at 20∘Cis17.54mm. When 20g of non - ionic substance is dissolved in 100g of water, the vapour pressure is lowered by 0.30mm. What is the molecular mass of the substance ?
View SolutionVapour pressure of pure water at 298 k is 23.8 mm Hg. Calculate the lowering of vapour pressure caused by adding 5g of sucrose in 50 g of water.
View SolutionThe variation of vapour pressure of different liquids with temperature is shown in figure
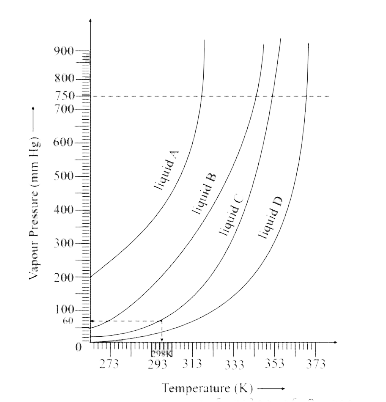
At high altitude, atmospheric pressure is low (say 60 mm Hg). At what temperature liquid D boils?
View SolutionThe vapour pressure of water at 293K is 17.535mmHg. Calculate the vapour pressure of water at 293K when 25g of glucose is dissolved in 450g of water.
View SolutionThe vapour pressure of water at room temperature is 23.8 mm Hg. The vapour pressure of an aqueous solution of sucrose with mole fraction 0.1 is equal to
View Solution
