The relationship between osmotic pressure (P) at 273 K when 10g glucose (P1) 10g urea (P2) and 10g sucrose (P3) are dissolved in 250 ml of water is
P_(1)gtP_(2)gtP_(3)~
P3>P1>P3
P2>P1>P3
P_(2)gtP_(3)gtP_(1)
P=CRT order of conc is urea > glucose > sucrose
Topper's Solved these Questions
- SOLUTIONSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:SOLUTIONSExercise:Advabced Level Problems (PART-2)
Explore 35 Videos
- SOLUTIONSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:SOLUTIONSExercise:EXERCISE-3(PART-3)
Explore 30 Videos
- SOLUTION AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIESBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:SOLUTION AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIESExercise:PHYSICAL CHEMITRY (SOLUTION & COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES)
Explore 51 Videos
- STEREOISOMERISMBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:STEREOISOMERISMExercise:EXERCISE (PART III : PRACTICE TEST-2 (IIT-JEE (ADVANCED PATTERN))
Explore 23 Videos
Similar Questions
The osmotic pressure of 6% solution of urea at 300 K is
View SolutionThe solubility of Ba(OH)2. 8H2O in water at 288K is 5.6g per 100g of water. What is the molality hydroxide ions in saturated solution of Ba(OH)2. 8H2O at 288K ? [At. Mass of Ba=137,O=16,H=1)
View SolutionA system of greater disorder of molecules is more probable. The disorder of molecules is reflected by the entropy of the system. A liquid vapourizes to form a more disordered gas. When a solute is present, there is additional contribution to the entropy of the liquid due to increased randomness. As the entropy of solution is higher than that of pure liquid, there is weaker tendency to form the gas. Thus, a solute (non-volatile) lowers the vapour pressure of a liquid, and hence a higher boiling point of the solution.
Similarly, the greater randomness of the solution opposes the tendercy to freeze. In consequence, a lower temperature must be reached for achieving the equilibrium between the solid (frozen solvent) and the solution. The elevation in boiling point (ΔTb) and depression in freezing point (ΔTf) of a solution are the colligative properties which depend only on the concentration of particles of the solute and not their identity. For dilute solutions, (ΔTb) and (ΔTf) are proportional to the molarity of the solute in the solution.
To aqueous solution of Nal, increasing amounts of solid Hgl2 is added. The vapour pressure of the solution
View Solution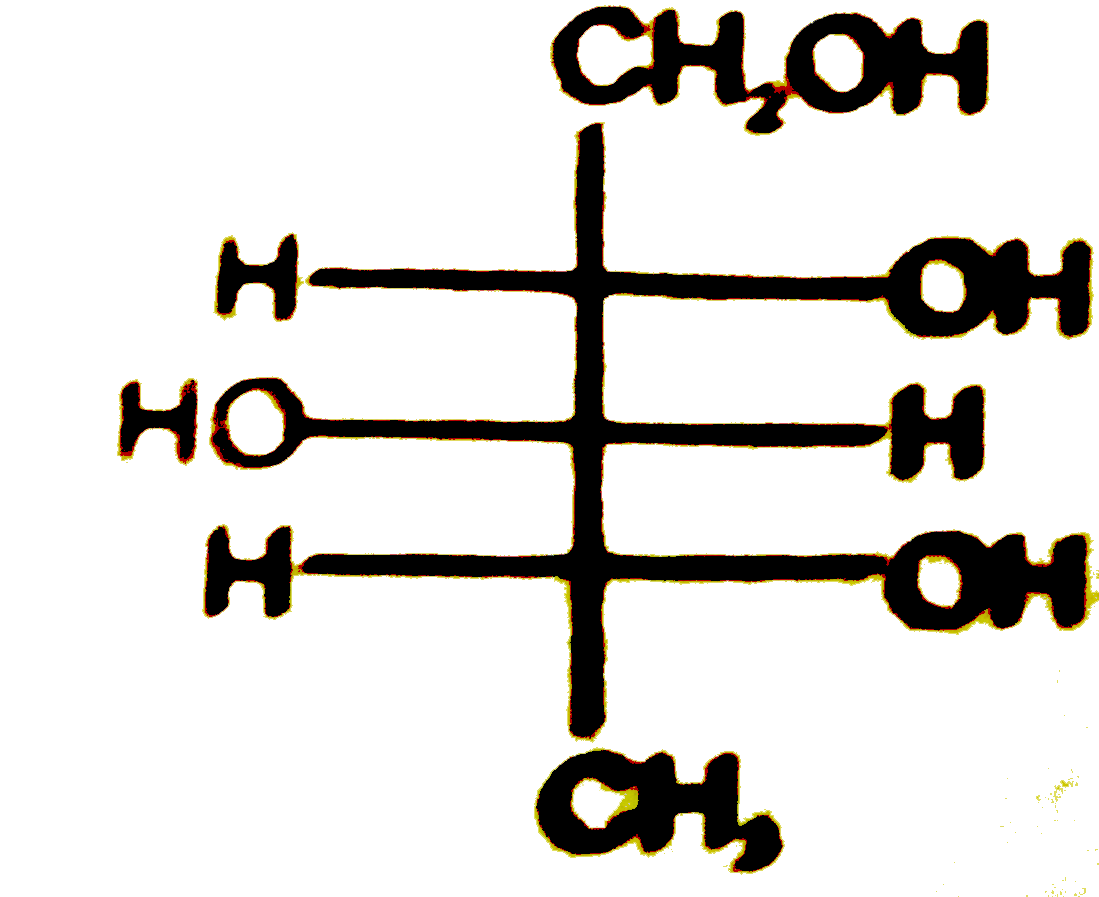 is a Fischer projection of one of_______ stereoisomers ?
is a Fischer projection of one of_______ stereoisomers ?
View Solution10.0g of glucose (π1), 10.0g of (urea(π2), and 10.0g of sucrose (π3) are dissolved in 250.0mL of water at 273K(π=osmotic pressure of a solution). The relationship between the osmotic pressure pressure of the solutions is
View SolutionThe relationship between osmotic pressure at 273 K when 10 g glucose (P_(1)), 10 g urea (P_(2)) and 10 g sucrose (P_(3)) are dissolved in 250 mL of water is:
View SolutionRelationship between osmotic pressure at 273 K when 1% glucose (pi_(1)),1% urea (pi_(2)),81 % sucrose (pi_(3)) are dissolved in 1 litre of water :
View SolutionWhat is the relation in the osmotic pressure at 273 K when 10 g of glucose (π1), 10 g of urea (π2) and 10 g of sucrose (π3) are dissolved in 250 mL of water ?
View SolutionCalculate the molality of 10g of glucose in 90g of water.
View Solutionএকই আয়তনের দুটি জলীয় দ্রবণের একটি তে 10g ইউরিয়া (আনবিক গুরুত্ব =60) এবং অপরটিতে 10g গ্লুকোজ (আনবিক গুরুত্ব =180) দ্রবীভুত আছে। একই উশ্নতায় ঐ দ্রবন্দ্বয়ের অভিস্রবন চাপ কি সমান হবে? কারন দর্শাও।
View Solution273 केल्विन पर, 250 मिली जल में 10 ग्राम ग्लूकोस (p1),10 ग्राम यूरिया (p2) तथा 10 ग्राम सुक्रोस (p3) के परासरण दाब में सम्बन्ध है
View SolutionAt 273 K temperature, if 10 gm glucose (p_(1)) , 10 gm urea (p_(2)) and 10 gm sucrose (p_(3)) is dissolved in 250 mL of water, then what is the correct relation of osmotic pressure for them ?
View SolutionThe relationship between osmotic pressure at 273 K when 10 g glucose ( P_1 ), 10 g urea ( P_2 ) and 10 g sucorse ( P_3 ) are dissoved in 250 ml of water is
View SolutionThe relationship between osmmotic pressure at 273 k when 10 g glucose (P_(1)) , 10 g urea (P_(2)) and 10g sucorse P_(3)) are dissoved in 250 ml of water is
View SolutionThe relationship between osmotic pressure at 273 K when 10 g glucose (P_1) , 10 g urea (P_2) and 10 g sucrose (P_3) are dissolved in 250 ml of water is:
View SolutionThe relationship between osmotic pressure at 273 K when 10 g glucose (P_1) , 10 g urea (P_2) and 10 g sucrose (P_3) are dissolved in 250 ml of water is:
View Solution
