If a ball of steel density (ρ=7.8gcm−3) attains a terminal velocity of 10cms−2 when falling in a tank of water (coefficient of viscoity ηwater=8.5×10−4Pa.s) then its terminal velocity in glycerine (ρ=12gcm−3,η=13.2Pa.a) would be nearly.
6.25×10−4cms−1
6.45×10−4cms−1
1.5×10−5cm/s
1.6×10−5cms−1
The correct Answer is:A
Vρg=6πηrv+vρlg
Vg(ρ−ρl)=6πηrv
Vg(ρ−ρl)=6πη'rv'
V'η'=(ρ−ρl')(ρ−ρl)×vηη'
=(7.8×1.2)(7.8−1)×10×8.5×10−413.2
v'=6.25×10−4cm/s.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ELASTICITY AND VISCOCITYBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - ELASTICITY AND VISCOCITYEXERCISE - Advanced Level Problems
9 Videos
- ELASTICITY AND VISCOCITYBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - ELASTICITY AND VISCOCITYEXERCISE - Exercise- 3 PART - I
7 Videos
- DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMSBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMSEXERCISE - dpp 92 illustration
2 Videos
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONEXERCISE - Exercise
43 Videos
Similar Questions
A wire loaded by a weight of density 7.8g/cc is found to be of length 100cm. On immersing the weight in water. The length decrease by 0.20 cm find the original length of the wire.
View SolutionA small sphere falls from rest in a viscous liquid. Due to friction, heat is produced. Find the relation between the rate of production of heat and the radius of the sphere at terminal velocity.
View SolutionA spherical ball is moving with terminal velocity inside a liquid. Determine the relationship of rate of heat loss with the radius of ball.
View SolutionAs shown in the figure, the key K is closed, the direction of the induced current in the coil B will be -

A. clockwise and instantaneous
B. anti-clockwise and instantaneous
C. clockwise and continuous
D. anti-clockwise and continuous
View SolutionA steel ball of mass m falls in a viscous liquid with terminal velocity v, then the steel ball of mass 8m will fall in the same liquid with terminal velocity
View Solutionif a ball of steel (density rho=7.8 g//cm^(3) ) attains a terminal velocity of 10 cm//s when falling in a tank of water (coefficient of viscosity, eta_(water) =8.5xx10^(-4) Ps s), then its terminal velocity in glycerine (rho =1.2 g//cm^(2), eta =13.2 Pa s) would be nearly
View Solution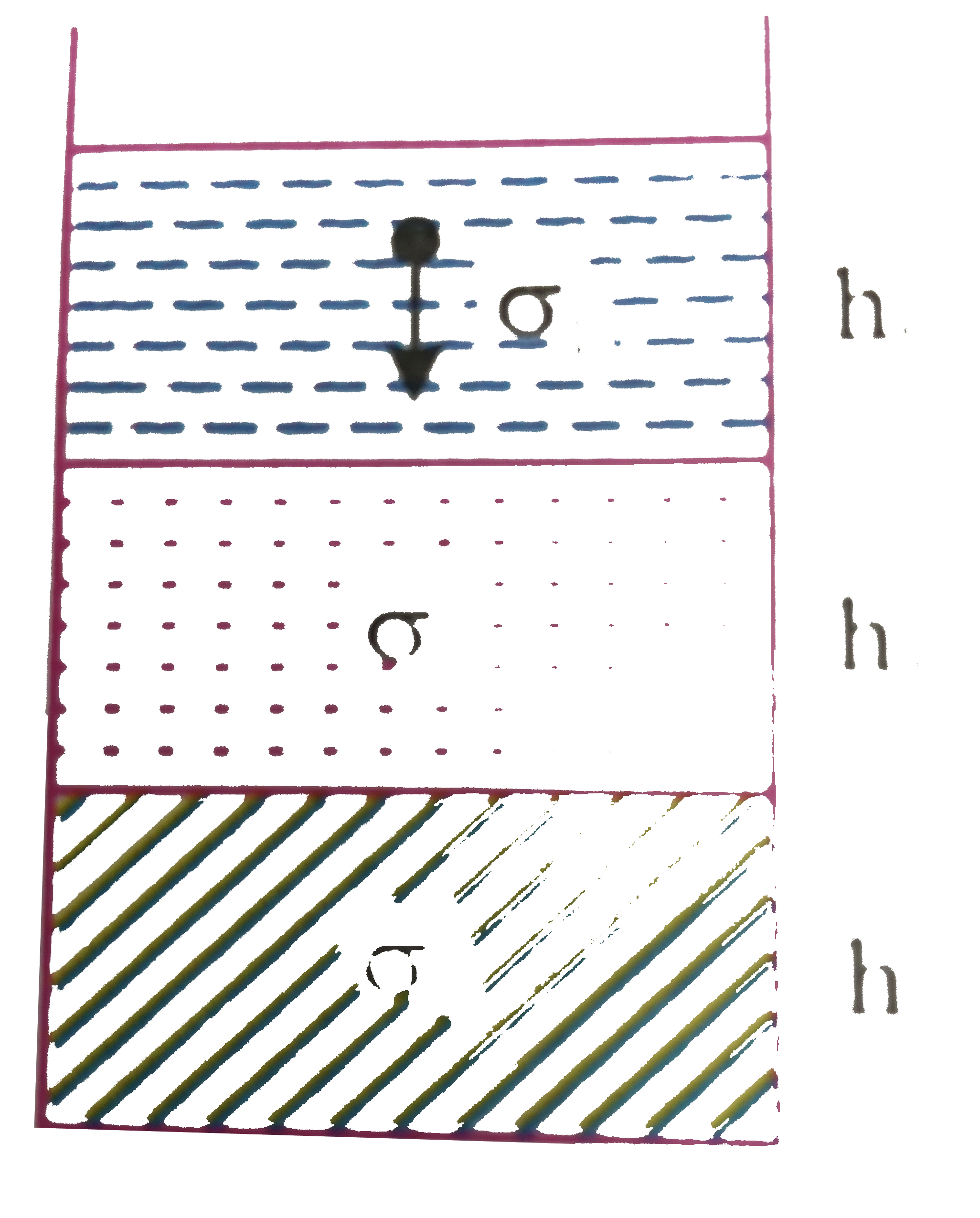
A ball moves successively through three liquids, at rest as shown, of densities σ1,σ2 and σ3 and viscosity coefficient η1,η2 and η3 and respectively with the same terminal velocity then
View Solutionfind the terminal velocity of a steel ball 2mm in diameter falling through glycerine. Relative density of steel =8, relative density of glycerine =1.3 and viscosity of glycerine=8.3 poise.
View SolutionIf a ball of steel (density p = 7.8 g cm^(-3) ) attains a terminal velocity of 10cm s^(-1) when falling in a tank of water (coefficient of viscosity) water = 8.5 xx 10^(-4) pa s. What will the terminal velocity in glycerine (P = 1.2 g cm^(-3), eta = 13.2 rho a. s) be ?
View Solutionयदि जल (η=8.5×10−4 पास्कल सेकण्ड ) से भरे टैंक में स्टील ( घनत्व ρ=7.8 ग्राम/सेमी3) की गेंद गिरने पर 10 सेमी/सेकण्ड के अन्त्य वेग से चलती है तो ग्लिसरीन ( घनत्व σ=1.2 ग्राम/सेमी3,η=13.2 पास्कल सेकण्ड ) में इसका अन्त्य वेग लगभग होगा :
View Solutionयदि पानी (श्यानता गुणांक ηपानी =8.5×10−4 पास्कल सेकंड ) से भरे टैंक में एक स्टील ( घनत्व = 7.8 ग्राम/सेमी3 ) की गेंद सीमांत चाल 10 सेमी / सेकंड से गिरती हो तो ग्लिसरीन (ρ=12 ग्राम/सेमी3, eta =13.2 पास्कल सेकंड ) में इसका सीमांत वेग लगभग होगा -
View SolutionA spherical ball of steel of radius 2 mm is falling down through glycerine. Determine the terminal velocity of the ball. Specific gravities of steel and glycerine are 8 and 1.3 respectively . Coefficient of viscosity of glycerine, eta=8.3 poise.
View SolutionIf a ball of steel ( density p = 7.8 g cm^(-3) ) attains terminal velocity of 10 cm s^(-1) when falling in a water ( coefficient of viscosity eta_("water") = 8.5 xx 10^(-4) Pa.s) then its terminal velocity in glycerine (p = 1.2 g cm^(-3) , eta = 13.2 Pa.s) would be, nearly :
View SolutionFind the terminal velocity of a steel ball 2 mm in diameter falling through glycerine. Relative density of steel is 8, relative density of glycerine is 1.3 and viscosity of glycerine is 8.3 poise.
View SolutionDefine terminal velocity. Show that the terminal velocity υ of a sphere of radius r, density ρ falling vertically through a viscous fluid of density σ and coefficient of viscosity η is given by υ=29(ρ−σ)r2gη Use this formula to explain the observed rise of air bubbles in a liquid.
View SolutionIf rho is density of falling body and sigma is the density of fluid then the terminal velocity of the falling body is proportional to
View Solution

