How many of the following quantities show increase in their value of increasing temperature?
a. Extent of physisorption of gases on solids.
b. Electrical conductivity of an electrolyte solution.
c. Electrical conductivity of an electrolyte solution.
d. Ionic product of water.
e. Vapour pressure of a pure and liquid.
f. Vapour pressure of an ideal solution which follows Rault's law, (keeping composition same)
g. Solubility of gases in liquids.
h. Reducing power of carbon monoxide for extraction of metals
Correct answer:
5
4
6
3
The correct Answer is:B
To determine how many of the given quantities show an increase in their value with increasing temperature, we will analyze each option step by step.
1. Extent of physisorption of gases on solids:
- As temperature increases, the kinetic energy of gas molecules increases, leading to a greater tendency for them to escape from the surface of the solid. Therefore, the extent of physisorption decreases with increasing temperature.
- Conclusion: Does not increase.
2. Electrical conductivity of an electrolyte solution:
- With an increase in temperature, the degree of dissociation of the electrolyte increases, leading to more ions in solution. The mobility of these ions also increases, resulting in higher electrical conductivity.
- Conclusion: Increases.
3. Electrical conductivity of an electrolyte solution (duplicate):
- This is the same as the previous point, so the conclusion remains the same.
- Conclusion: Increases.
4. Ionic product of water:
- The ionic product of water increases with temperature because more water molecules dissociate into H⁺ and OH⁻ ions at higher temperatures.
- Conclusion: Increases.
5. Vapor pressure of a pure liquid:
- As temperature increases, more liquid molecules gain enough energy to escape into the vapor phase, resulting in an increase in vapor pressure.
- Conclusion: Increases.
6. Vapor pressure of an ideal solution which follows Raoult's law (keeping composition same):
- Raoult's law states that the vapor pressure of a solvent in a solution is dependent on the temperature. However, if the composition is kept the same, the vapor pressure does not inherently increase just because of temperature alone; it is dependent on the mole fraction. Thus, it does not show a direct increase in value with temperature.
- Conclusion: Does not increase.
7. Solubility of gases in liquids:
- Generally, the solubility of gases in liquids decreases with increasing temperature due to decreased gas solubility at higher temperatures.
- Conclusion: Does not increase.
8. Reducing power of carbon monoxide for extraction of metals:
- The reducing power of carbon monoxide decreases with increasing temperature because higher temperatures favor the oxidation of CO, making it a weaker reducing agent.
- Conclusion: Does not increase.
Summary of Results:
- Increases:
- Electrical conductivity of an electrolyte solution (2 instances)
- Ionic product of water
- Vapor pressure of a pure liquid
- Does not increase:
- Extent of physisorption of gases on solids
- Vapor pressure of an ideal solution (Raoult's law)
- Solubility of gases in liquids
- Reducing power of carbon monoxide
Total Count of Quantities that Increase:
- Total = 4 (Electrical conductivity (2), Ionic product of water, Vapor pressure of a pure liquid)
Final Answer:
The correct answer is 4 quantities show an increase in their value with increasing temperature.
---
- As temperature increases, the kinetic energy of gas molecules increases, leading to a greater tendency for them to escape from the surface of the solid. Therefore, the extent of physisorption decreases with increasing temperature.
- Conclusion: Does not increase.
- With an increase in temperature, the degree of dissociation of the electrolyte increases, leading to more ions in solution. The mobility of these ions also increases, resulting in higher electrical conductivity.
- Conclusion: Increases.
- This is the same as the previous point, so the conclusion remains the same.
- Conclusion: Increases.
- The ionic product of water increases with temperature because more water molecules dissociate into H⁺ and OH⁻ ions at higher temperatures.
- Conclusion: Increases.
- As temperature increases, more liquid molecules gain enough energy to escape into the vapor phase, resulting in an increase in vapor pressure.
- Conclusion: Increases.
- Raoult's law states that the vapor pressure of a solvent in a solution is dependent on the temperature. However, if the composition is kept the same, the vapor pressure does not inherently increase just because of temperature alone; it is dependent on the mole fraction. Thus, it does not show a direct increase in value with temperature.
- Conclusion: Does not increase.
- Generally, the solubility of gases in liquids decreases with increasing temperature due to decreased gas solubility at higher temperatures.
- Conclusion: Does not increase.
- The reducing power of carbon monoxide decreases with increasing temperature because higher temperatures favor the oxidation of CO, making it a weaker reducing agent.
- Conclusion: Does not increase.
- Increases:
- Electrical conductivity of an electrolyte solution (2 instances)
- Ionic product of water
- Vapor pressure of a pure liquid
- Extent of physisorption of gases on solids
- Vapor pressure of an ideal solution (Raoult's law)
- Solubility of gases in liquids
- Reducing power of carbon monoxide
- Total = 4 (Electrical conductivity (2), Ionic product of water, Vapor pressure of a pure liquid)
The correct answer is 4 quantities show an increase in their value with increasing temperature.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- TEST PAPERSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:TEST PAPERSExercise:PART - III CHEMISTRY SEC - 1
Explore 12 Videos
- TEST PAPERSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:TEST PAPERSExercise:PART - III CHEMISTRY SEC - 2
Explore 18 Videos
- SURFACE CHEMISTRYBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:SURFACE CHEMISTRYExercise:Section - 5
Explore 1 Video
- TEST SERIESBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:TEST SERIESExercise:CHEMISTRY
Explore 50 Videos
Similar Questions
10dm3 of N2 gas and 10dm3 of gas X contain the same number of molecules at the same temperature, the gas (X) may be
View SolutionWhat is power (in watt) of a light source emitting 3.125×1018 photons per second, while the wavelength of light is 620nm ? (use hc=12400eVÅ)
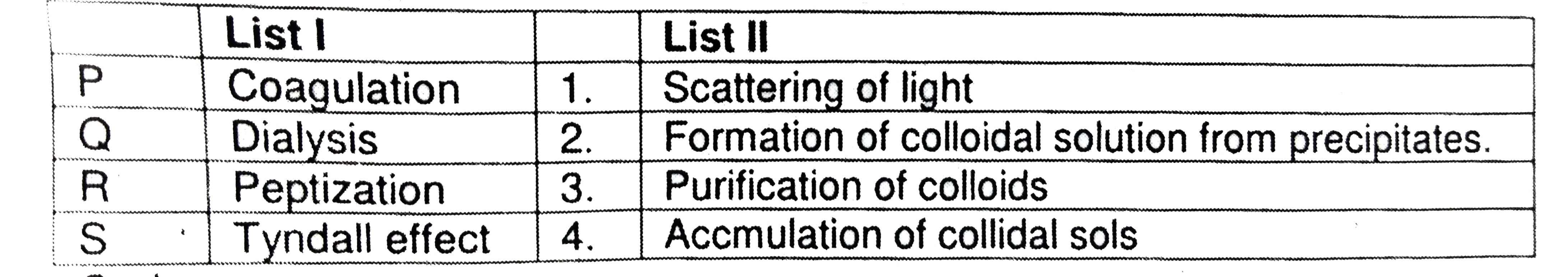
View SolutionMatch list I with list II and select the correct answer :
View Solutionwhich of the following plots will obtained for a conductometric titration of strong acid against a weak base?
View SolutionThe conductance of electrolyte solution increases wih temperature.
View SolutionHow many of the following quantities show increase in their value of increasing temperature? a. Extent of physisorption of gases on solids. b. Electrical conductivity of an electrolyte solution. c. Electrical conductivity of an electrolyte solution. d. Ionic product of water. e. Vapour pressure of a pure and liquid. f. Vapour pressure of an ideal solution which follows Rault's law, (keeping composition same) g. Solubility of gases in liquids. h. Reducing power of carbon monoxide for extraction of metals Correct answer:
View SolutionThe vapour pressure of a solution of 5g of non-electrolyte in 100g of water at a particular temperature is 2985 N m^(-2) . The vapour pressure of pure water at that temperature is 3000 N m^(-2) . The molecular weight of the solute is
View SolutionThe vapour pressure of solution containing 5 g of non-electrolyte in 90g of water at a particular temperature is 2985 Nm–2. The vapour pressure of pure water at that temperature is 3000 Nm–2. The molecular weight of the solute is –
View SolutionTwo liquids A and B form an ideal solution. At 300 K, the vapour pressure of a solution containing 1 mole of A and 3 moles of B is 550 mm of Hg. At the same temperature, if one mole of B is added to this solution, the vapour pressure of the solution increases by 10 mm of Hg. Determine the vapour pressure of A and B in their pure states
View SolutionThe vapour pressure of a solution cont.aning 10 g of a non-electrolyte in 200 g of water at a particular temperature is 2985 Pa. The vapour pressure of pure water at that temperature is 3000 Pa. Calculate the molecular mass of the solute.
View SolutionAssertion: The conductivity of electrolytic solutions increases with the increase of heat. Rationale: The electrical conductivity decreases with the increase of heat.
View SolutionThe vapour pressure of a solution of 5g of a non-electrolyte in 100g water at a particular temperature is 2950Pa and that of pure water at the same temperature is 3000Pa. The molar mass of the solute is
View SolutionThe vapour pressure of a pure liquid A is 70 torr at 27^(@)C It forms and ideal solution with another liquid B. The mole fraction of B is 0.2 and the total vapour pressure of the solution is 84 torr at 27^@ C .the vapour pressure of pure liquid B at . the vapur pressure of pure liquid B at 27^(@)C is _____.
View Solutionतापमान में वृद्धि के साथ, एक विद्युत अपघट्य के विलयन की चालकता सामान्यतः
View SolutionTwo liquids A and B form ideal solution. At 300K, the vapour pressure of a solution containing 1 mole of A and 3 moles of B is 550mm of Hg. At the same temperature, if one more mole of B is added to this solution, the vapour pressure of the solution increases by 10mm of Hg. Determine the vapour pressure of a and B in their pure states.
View Solution
