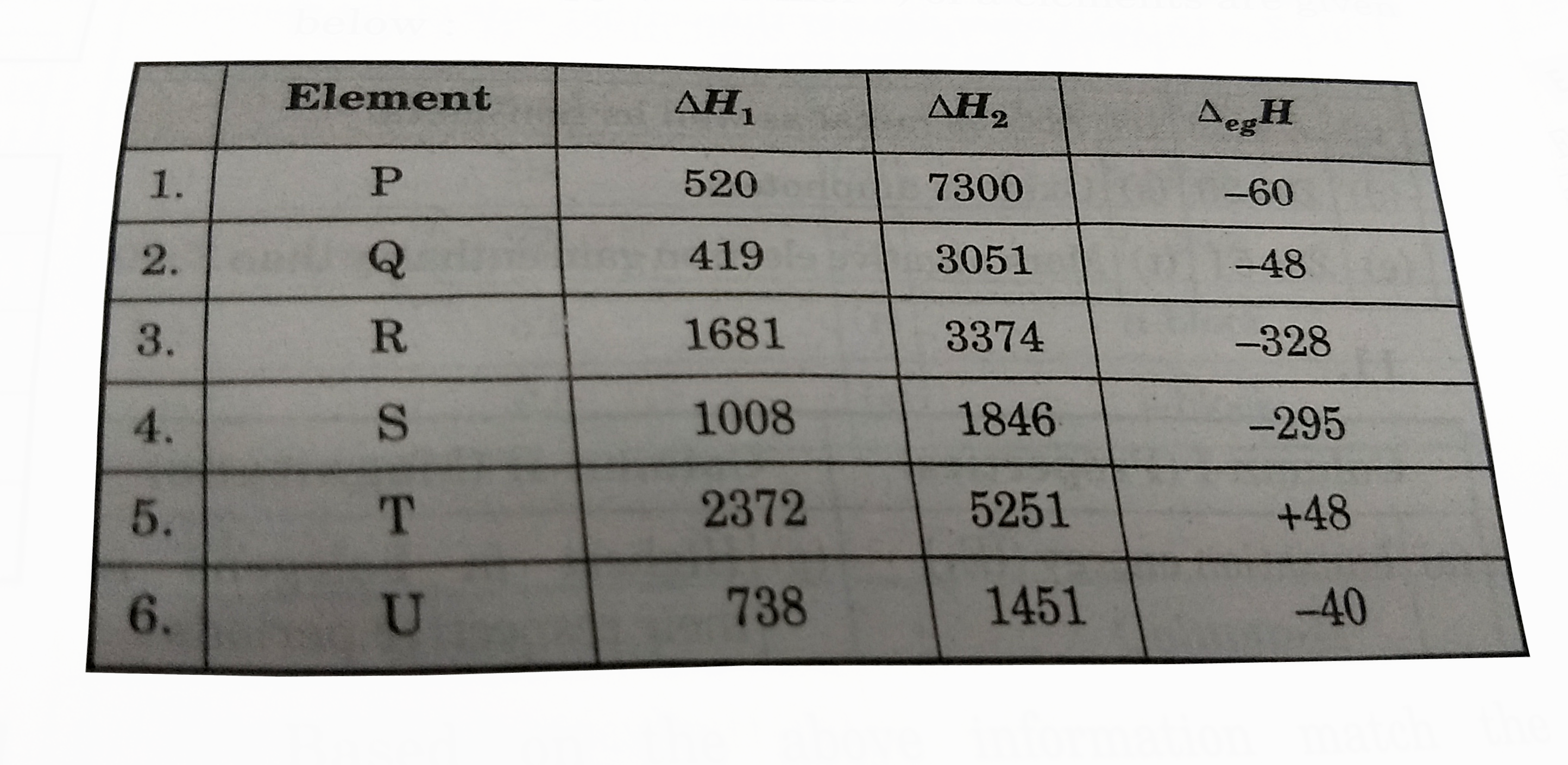
The first (ΔiH1) and the second (ΔiH2) ionization enthalpies (in kJ mol−1) and the (ΔegH) electron gain enthalpy (in kJ mol−1) of a few elements are given below:
ElementsΔH1ΔH2ΔegHI5207300–60II4193051–48III16813374–328IV10081846–295V23725251+48VI7381451–40
Which of the above elements is likely to be :
(a) the least reactive element.
(b) the most reactive metal.
(c) the most reactive non-metal.
(d) the least reactive non-metal.
(e) the metal which can form a stable binary halide of the formula MX2(X=halogen).
(f) the metal which can form a predominantly stable covalent halide of the formula MX (X=halogen)?
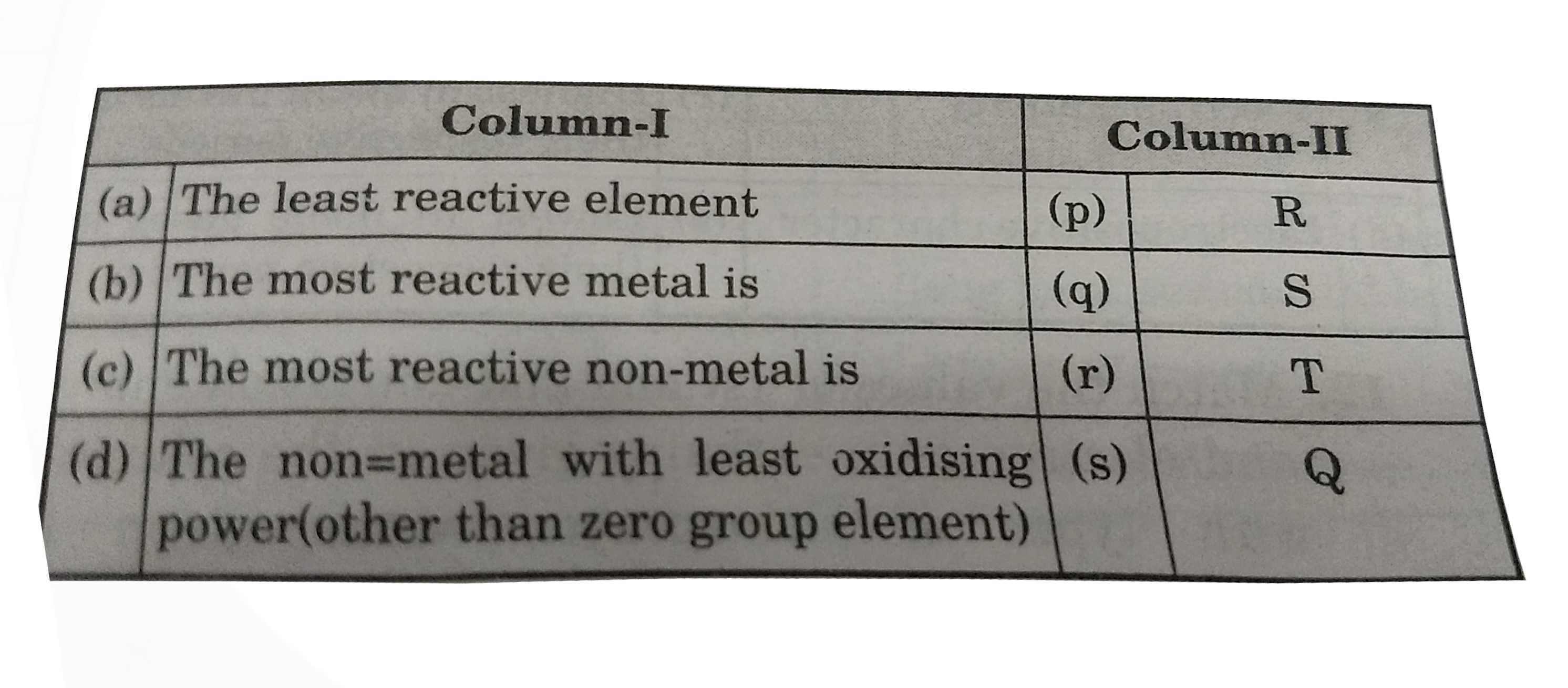
R
S
P
U
The correct Answer is:A
Non-metal having higher negative value of electron gain enthalpy corresponds to halogen.Hence R is more reactive non-metal (easily forms anion)
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
A red solide is insoluble in water. However it becomes soluble if some KI is added to water. On heating the red solid in a test tube, there is liberation of some violet coloured fumes and droplets of a metal appear on the cooler parts of the test tube. The red solid is :
View SolutionSodium (Na =23) crystallizen in bcc arrangement with the interfacial separation between the atoms at the edge 53.6pm. The density of sodium crystal is:
View SolutionThe first (Delta_(i)H_(1)) and second (Delta_(i)H_(2)) ionisation enthalpies ("in" kJ mol^(-1)) and the (Delta_(eg)H^(ө)) electron gain enthalpy ("in" kJ mol^(-1)) of a few elements are given below: {:("Elements",(Delta_(i)H_(1)),(Delta_(i)H_(2)),Delta_(eg)H^(ө)),(I,520,7300,-60),(II,419,3051,-48),(III,1681,3374,-328),(IV,1008,1846,-295),(V,2372,5251,+48),(VI,738,1451,-40):} Which of the above elements is likely to be a. the least reactive element. b. the most reactive metal. c. the most reactive non-metal. d. the least reactive non-metal. e. the metal which can form a stable binary halide of the formula MX (X=halogen). f. the metal which can form a predominantly stable covalent halide of the formula MX(X=halogen).
View SolutionThe first (ΔH1) and second (ΔH2) ionisation enthalpies (in kJmol−1) and the (ΔHeg) electron gain enthalpy (in kJmol−1) of a elements are given below:
Based on the above information match the following columns.
View SolutionThe first (ΔIH1) and second (ΔIH2) ionisation enthalpies (in kJ mol−1) and the (ΔegH) electron gain enthalpy (in kJ mol−1) of a few elements are given below:
The least reactive element is :
View SolutionMatch the values of ionization energy and electron gain enthalpy listed in column I with characteristic(s) of elements listed in column II. {:("Column-I","Column-II"),((A)"2372 5251 +48",(p)"Element which acts as a strong reducing agent"),((B)"419 3051 -48",(q)"Element which exists as a monoatomic molecule"),((C )"1681 3374 -333",(r)"Least reactive non-metal"),((D)"1008 1846 -295",(s)"Element which acts as a strong oxidising agent"),(,(t)"Element which oxides is a stronger basic in nature"):}
View SolutionThe first (Delta_(i)H_(1) and second (Delta_(i)H_(2) ionization enthalpies (in kJ/mol) and electron gain enthalpy (in kJ/mol) of few elements are given below: {:("Elements",Delta_(i)H_(1),Delta_(i)H_(2),Delta_(eg)H),(I,520,7300,-60),(II,1681,3374,-328),(III,899,1757,+48),(IV,2372,5251,+48):} Which of the above is likely to be He:
View SolutionThe first (Delta_(i)H_(1) and second (Delta_(i)H_(2) ionization enthalpies (in kJ/mol) and electron gain enthalpy (in kJ/mol) of few elements are given below: {:("Elements",Delta_(i)H_(1),Delta_(i)H_(2),Delta_(eg)H),(I,520,7300,-60),(II,1681,3374,-328),(III,899,1757,+48),(IV,2372,5251,+48):} Which of the following is likely to be an alkali metal?
View SolutionThe first (Delta_(i)H_(1)) and the (Delta_(i)H_(2)) ionization enthalpy (in kJ mol^(-1) ) and the (Delta_(eg) H) electron gas enthalpy (in kJ mol^(-1) ) of a few elements are given below : {:("Element",,Delta_(i)H_(1),,Delta_(i)H_(2),,Delta_(eg)H),(I,,520,,7300,,-60),(II,,419,,3051,,-48),(III,,1681,,3374,,-328),(IV,,1008,,1846,,-295),(V,,2372,,5251,,+48),(VI,,738,,1451,,-40):} Which of the above element is likely to be : (a) the least reactive element ( b) the most reactive metal (c ) the most reactive non- metal ( d ) the least reactive non- metal ( e) metal which can form a stable binary halide of the formula MX_(2) ( x= halogen ) ? (f ) the metal which can form predominantly stable covalent halide of the formula MX ( X= halogen ) ?
View SolutionMatch the correct ionisation enthalpies and electron gain enthalpies of the following elements {:(,,"Elements",,,,DeltaH_(1),,DeltaH_(2),,Delta_(eg)H),((i),,"Most reactive non metal",,A.,,419,,3051,,-48),((ii),,"Most reactive metal",,B.,,1681,,3374,,-328),((iii),,"Least reactive element ",,C.,,738,,1451,,-40),((iv),,"Metal forming binary halide " ,,D.,,2372,,5251,,+48):}
View SolutionThe first and second ionization enthalpies and electron gain enthalpy of some elements are as given below: Which of the elements given above is the least reactive?
View SolutionThe first (IE1) and the second (IE2) ionization enthalpies (kJ mol−1) of a few elements designated by Roman numerals are shown below:
ElementIE1IE2I23725251II5207300III9001760III9001760IV16803380
Which of the above elements is likely to be a,
reactive non metal
View SolutionThe first (Delta_(i)H_(1)) and second (Delta_(i)H_(2)) ionization enthalpies ("in kJ mol"^(-1)) and the electron gain enthalpy (Delta_(eg)H)("in kJ mol"^(-1)) of the elements I, II, III, IV and V are given below the least reactive non - metal and the most reactive metal of these are respectively
View SolutionThe first (ΔiH1) and second (ΔiH2) ionisation enthalpies (inkJmol−1) and the (ΔegHө) electron gain enthalpy (inkJmol−1) of a few elements are given below:
Elements(ΔiH1)(ΔiH2)ΔegHөI5207300−60II4193051−48III16813374−328IV10081846−295V23725251+48VI7381451−40
Which of the above elements is likely to be
a. the least reactive element.
b. the most reactive metal.
c. the most reactive non-metal.
d. the least reactive non-metal.
e. the metal which can form a stable binary halide of the formula MX2 (X=halogen).
f. the metal which can form a predominantly stable covalent halide of the formula MX(X=halogen).
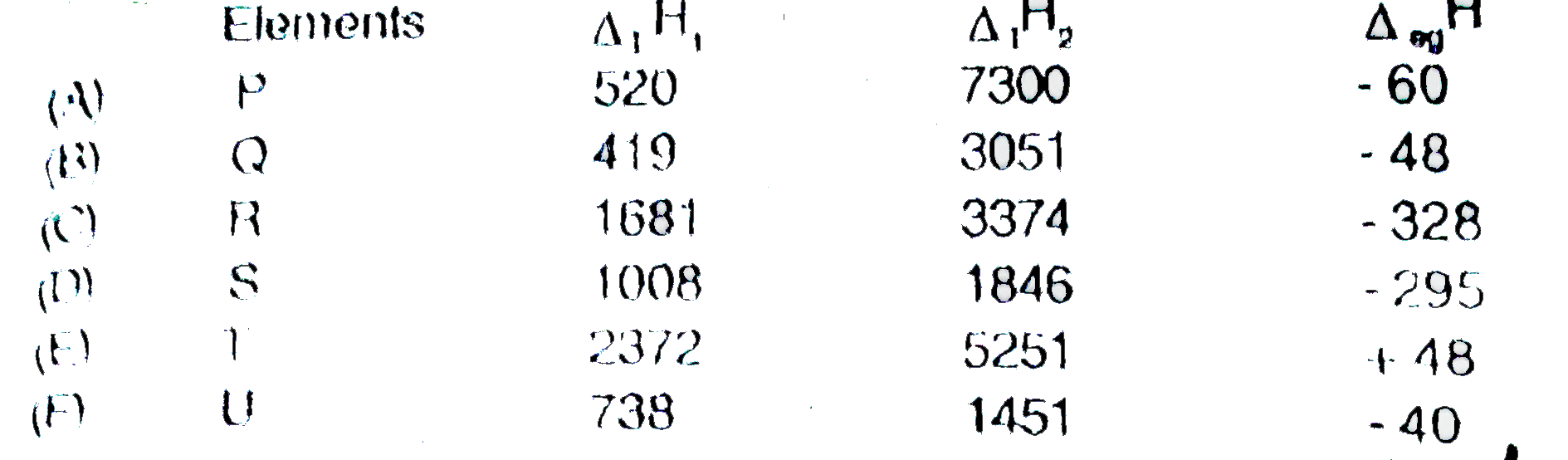
View SolutionThe first (Delta_iH_1) and the second (Delta_iH_2) ionisation enthalpies in "kJmol"^(-1) and the electron gain enthalpy (Delta_(eg)H) in "kJmol"^(-1) of a few elements are given below: {:("Elements",Delta_iH_1,Delta_iH_2,Delta_(eg)H),("(P)",520,7300,-60),("(Q)",419,3051,-48),("(R)",1681,3374,-328),("(S)",1008,1846,-295),("(T)",2372,5251,+48),("(U)",738,1451,-40):} Which one of the above elements is least reactive?
View SolutionThe first (ΔiH1) and the second (ΔiH2) ionisation enthalpies in kJmol−1 and the electron gain enthalpy (ΔegH) in kJmol−1 of a few elements are given below:
ElementsΔiH1ΔiH2ΔegH(P)5207300−60(Q)4193051−48(R)16813374−328(S)10081846−295(T)23725251+48(U)7381451−40
Which one of the above elements is least reactive?
View Solution

