Which carbonyl group is protonated most readily in acidic solution, but gives nucleophilic addition by NH4NH−Ph least readily ?
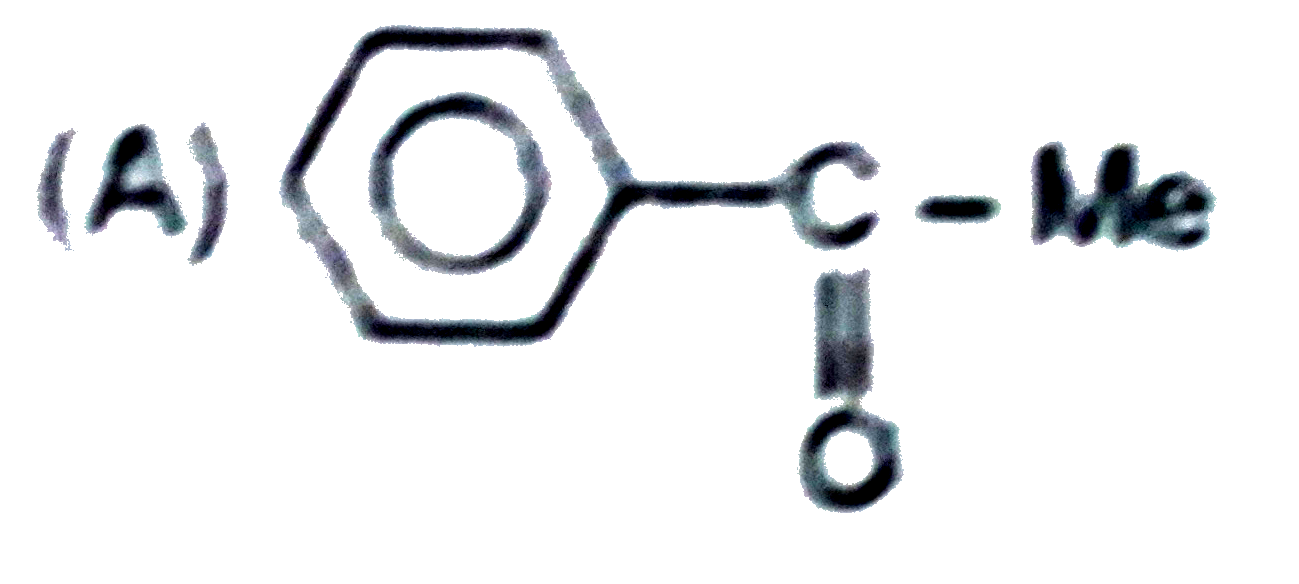
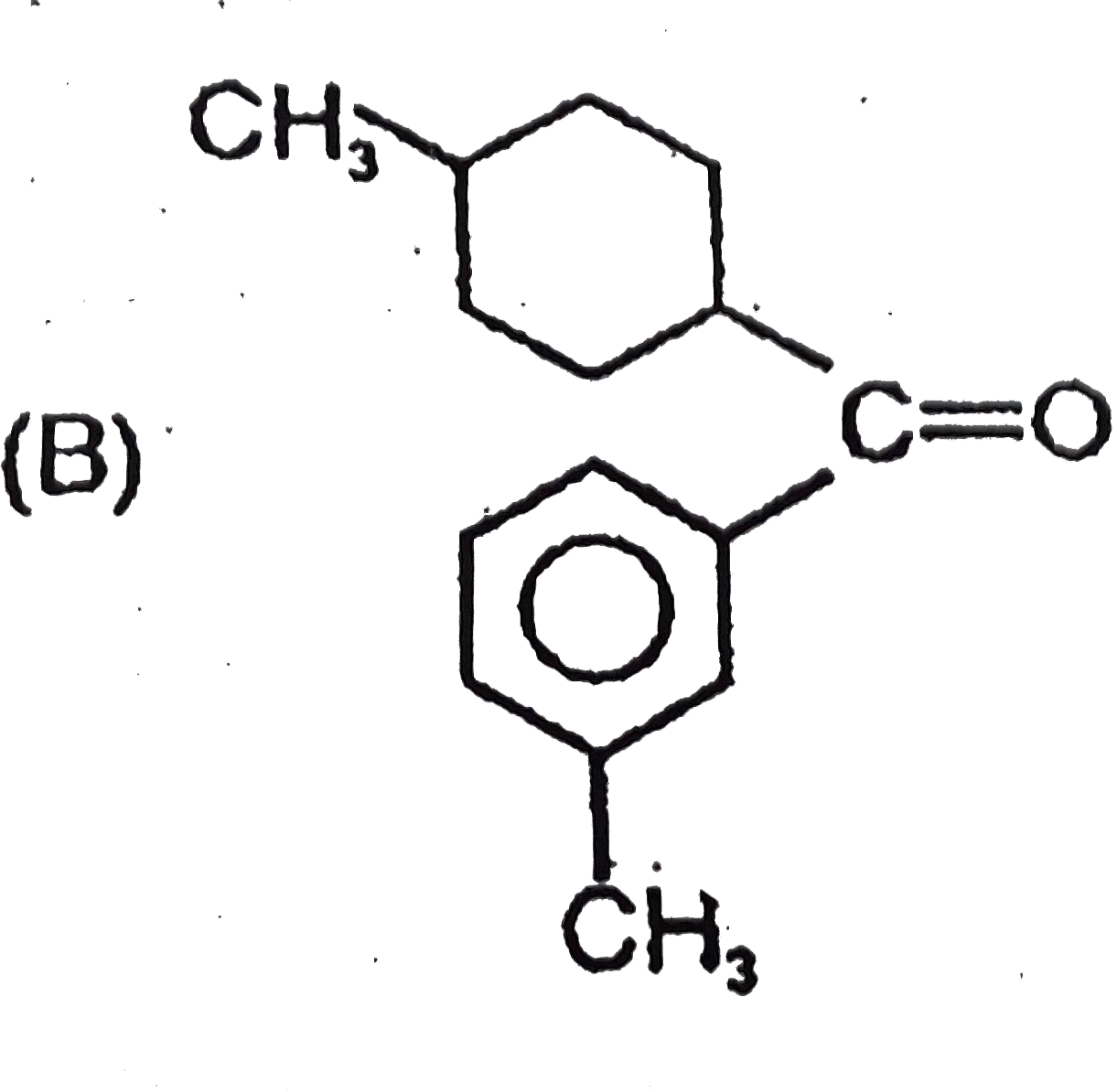
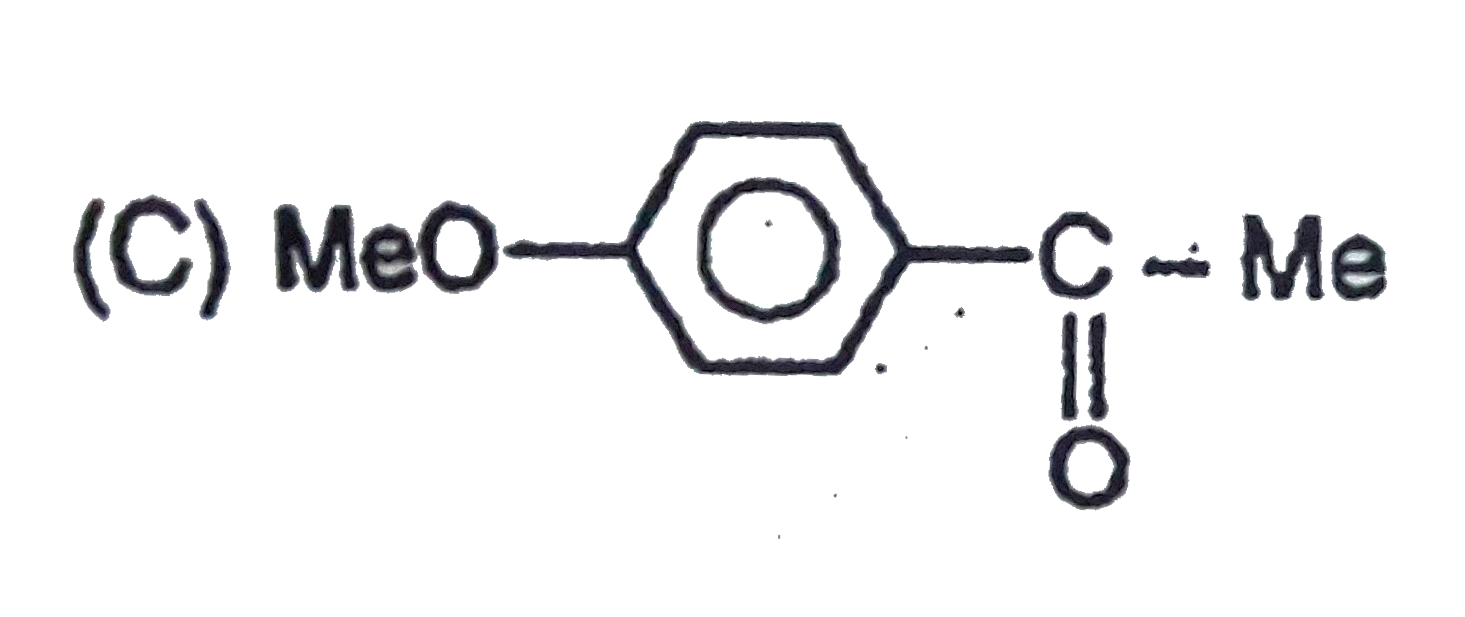
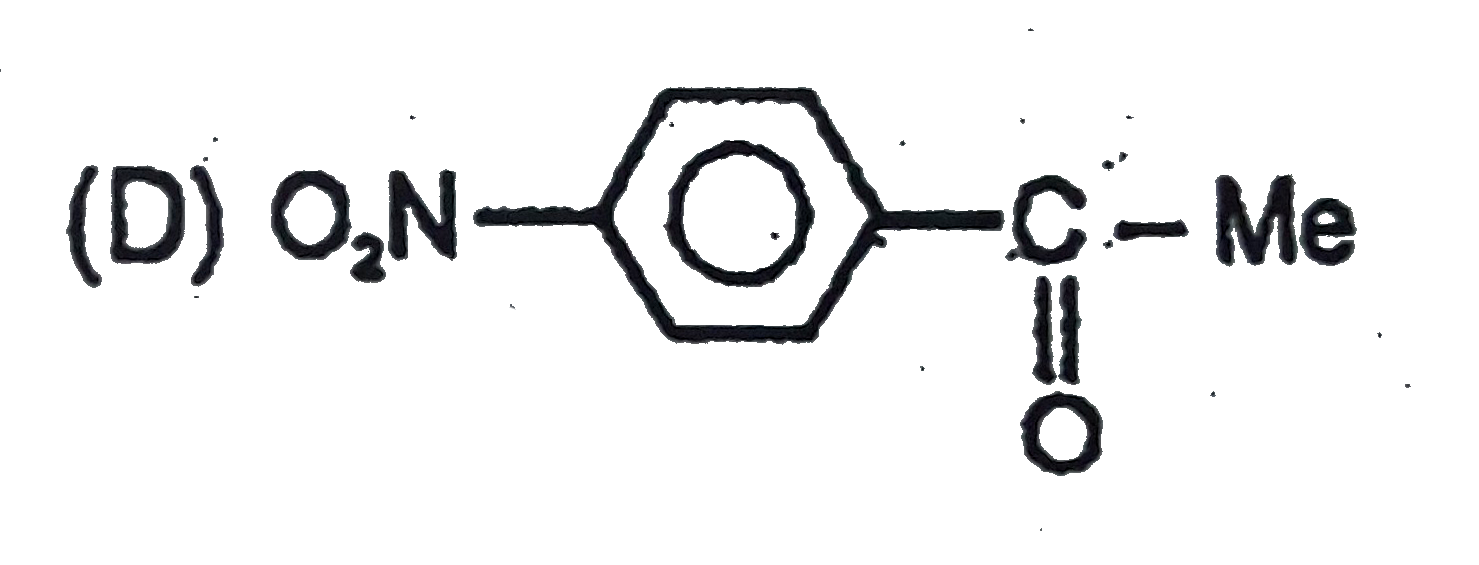
The correct Answer is:3
To solve the question, we need to analyze the stability of the carbocation formed upon protonation of different carbonyl groups and their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition by phenylhydrazine (NH4-NHPh).
1. Identify the Carbonyl Groups:
We need to consider the different carbonyl groups presented in the options. Let's denote them as A, B, C, and D for simplicity.
2. Protonation of Carbonyl Groups:
When a carbonyl group (C=O) is protonated in an acidic solution, it forms a more electrophilic species. The stability of the resulting carbocation (formed after protonation) is crucial for determining which carbonyl group is protonated most readily.
3. Evaluate Carbocation Stability:
- Option A: Contains a benzene ring. The carbocation formed here is moderately stable due to resonance.
- Option B: Contains a methyl group (CH3). The +I effect from the methyl group stabilizes the carbocation, making it more stable than Option A.
- Option C: Contains an O-Me (methoxy) group. The +M effect from the lone pair on the oxygen significantly stabilizes the carbocation, making it the most stable among the options.
- Option D: Contains a nitro group (NO2). The -M effect from the nitro group destabilizes the carbocation, making it the least stable.
4. Conclusion on Protonation:
Based on the stability of the carbocations formed, Option C (with the O-Me group) is protonated most readily due to the high stability of the carbocation formed.
5. Nucleophilic Addition Reaction:
Now, we need to consider the nucleophilic addition of NH4-NHPh to these carbonyl groups. The more electron-dense the carbonyl carbon is, the less readily it will undergo nucleophilic attack.
- In Option C, the presence of the O-Me group increases electron density at the carbonyl carbon due to the +M effect, making it less susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
6. Final Answer:
Therefore, the carbonyl group that is protonated most readily (Option C) also gives nucleophilic addition by NH4-NHPh the least readily.
Final Answer:
Option C is the carbonyl group that is protonated most readily in acidic solution but gives nucleophilic addition by NH4-NHPh least readily.
We need to consider the different carbonyl groups presented in the options. Let's denote them as A, B, C, and D for simplicity.
When a carbonyl group (C=O) is protonated in an acidic solution, it forms a more electrophilic species. The stability of the resulting carbocation (formed after protonation) is crucial for determining which carbonyl group is protonated most readily.
- Option A: Contains a benzene ring. The carbocation formed here is moderately stable due to resonance.
- Option B: Contains a methyl group (CH3). The +I effect from the methyl group stabilizes the carbocation, making it more stable than Option A.
- Option C: Contains an O-Me (methoxy) group. The +M effect from the lone pair on the oxygen significantly stabilizes the carbocation, making it the most stable among the options.
- Option D: Contains a nitro group (NO2). The -M effect from the nitro group destabilizes the carbocation, making it the least stable.
Based on the stability of the carbocations formed, Option C (with the O-Me group) is protonated most readily due to the high stability of the carbocation formed.
Now, we need to consider the nucleophilic addition of NH4-NHPh to these carbonyl groups. The more electron-dense the carbonyl carbon is, the less readily it will undergo nucleophilic attack.
- In Option C, the presence of the O-Me group increases electron density at the carbonyl carbon due to the +M effect, making it less susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
Therefore, the carbonyl group that is protonated most readily (Option C) also gives nucleophilic addition by NH4-NHPh the least readily.
Option C is the carbonyl group that is protonated most readily in acidic solution but gives nucleophilic addition by NH4-NHPh least readily.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Which carbonyl group of the given compound is most reactive for nucleophilic addition reaction?
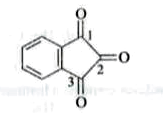 A1B2C3DAll have equal reactivity
A1B2C3DAll have equal reactivityWhich among the following is most reactive to give nucleophilic addition?
AFCH2CHOBClCH2CHOCBrCH2CHODICH2CHO
Aldehyde, ketone, acid and acid derivatives contain >C=O group. Aldehyde and ketones gives nucleop addition reactions where as acid and acid derivatives gives nucleophilic addition followed by ellmination reaction Nucleophilic addition reactions followed by ellimination of acid derivatives is known as acyl substitution reacts This subsitution reaction takes places by formation of tertrahedral intermediate.
Which one of the following is least reactive compound for nucleophilic acyl substitution.
View SolutionAldehyde, ketone, acid and acid derivatives contain >C=O group. Aldehyde and ketones gives nucleop addition reactions where as acid and acid derivatives gives nucleophilic addition followed by ellmination reaction Nucleophilic addition reactions followed by ellimination of acid derivatives is known as acyl substitution reacts This subsitution reaction takes places by formation of tertrahedral intermediate.
Which of the following compounds has very poor leaving group?
View SolutionAldehyde, ketone, acid and acid derivatives contain >C=O group. Aldehyde and ketones gives nucleop addition reactions where as acid and acid derivatives gives nucleophilic addition followed by ellmination reaction Nucleophilic addition reactions followed by ellimination of acid derivatives is known as acyl substitution reacts This subsitution reaction takes places by formation of tertrahedral intermediate. For the given reaction
_E01_571_Q01.png)
which of these is correct?
View SolutionAldehydes and ketones are amphoteric. Thus they can act both as acids and bases. Under acidic conditions, the carbon of the protonated canbonyl group is much more electrophilic, reacting even with weak nucleopphilie. Carbonyl compound gives nucleophilic addition reaction. In this reaction the nucleophilic attack proceeds the elecrophilic attack.
Carbonyl compounds gives nucleophilic addition with
View SolutionAldehydes and ketones are amphoteric. Thus they can act both as acids and bases. Under acidic conditions, the carbon of the protonated canbonyl group is much more electrophilic, reacting even with weak nucleopphilie. Carbonyl compound gives nucleophilic addition reaction. In this reaction the nucleophilic attack proceeds the elecrophilic attack.
Which of these statements are correct?
View SolutionAldehydes and ketones are amphoteric. Thus they can act both as acids and bases. Under acidic conditions, the carbon of the protonated canbonyl group is much more electrophilic, reacting even with weak nucleopphilie. Carbonyl compound gives nucleophilic addition reaction. In this reaction the nucleophilic attack proceeds the elecrophilic attack.
Which of the statements are//is correct?
View Solution

