Geometrical isomerism is shown by ?
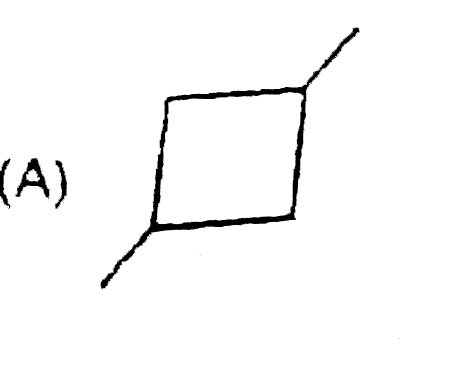
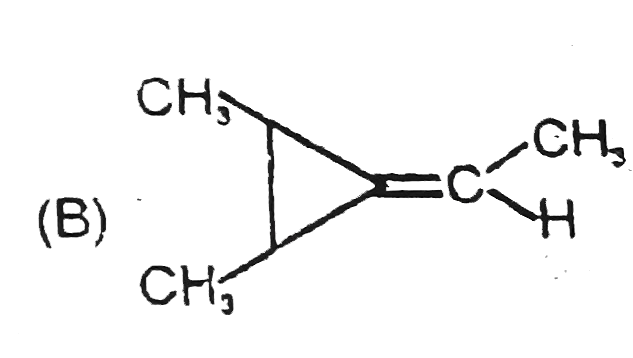
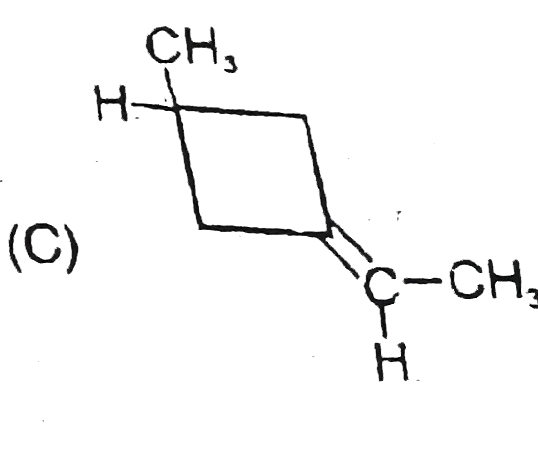
Ph−CH=CH−CH3
The correct Answer is:A,B,D
To determine which compounds exhibit geometrical isomerism, we need to analyze the presence of double bonds and the arrangement of groups around those double bonds. Here’s a step-by-step solution:
Step 1: Understand Geometrical Isomerism
Geometrical isomerism occurs due to the restricted rotation around a double bond (C=C) or within a ring structure. For geometrical isomers to exist, there must be two different groups attached to each carbon of the double bond.
Hint: Look for double bonds or rings in the compounds, as these are necessary for geometrical isomerism.
Step 2: Analyze Each Option
- Option A: Check for double bonds. If there are only single bonds, geometrical isomerism cannot occur.
Hint: Single bonds allow free rotation, which prevents isomerism.
- Option B: Identify if there is a double bond and if the carbons have different groups attached. If both carbons of the double bond have the same groups, geometrical isomerism cannot occur.
Hint: Ensure both carbons in the double bond have different substituents for isomerism to be possible.
- Option C: Similar to option B, check the groups attached to the double bond. If they are the same on one side, geometrical isomerism is not possible.
Hint: Look for unique groups on both sides of the double bond.
- Option D: Examine the structure carefully. If both carbons of the double bond have different groups, then geometrical isomerism can occur.
Hint: Identify if there are two different groups on each carbon of the double bond.
Step 3: Conclusion
After analyzing all options:
- Option A does not show geometrical isomerism due to the absence of double bonds.
- Option B does not show geometrical isomerism because the groups are not different on one side of the double bond.
- Option C also fails to show geometrical isomerism for similar reasons.
- Option D shows geometrical isomerism because both carbons in the double bond have different groups attached.
Final Answer: Option D shows geometrical isomerism.
Geometrical isomerism occurs due to the restricted rotation around a double bond (C=C) or within a ring structure. For geometrical isomers to exist, there must be two different groups attached to each carbon of the double bond.
- Option A: Check for double bonds. If there are only single bonds, geometrical isomerism cannot occur.
Hint: Single bonds allow free rotation, which prevents isomerism.
After analyzing all options:
- Option A does not show geometrical isomerism due to the absence of double bonds.
- Option B does not show geometrical isomerism because the groups are not different on one side of the double bond.
- Option C also fails to show geometrical isomerism for similar reasons.
- Option D shows geometrical isomerism because both carbons in the double bond have different groups attached.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
A red solide is insoluble in water. However it becomes soluble if some KI is added to water. On heating the red solid in a test tube, there is liberation of some violet coloured fumes and droplets of a metal appear on the cooler parts of the test tube. The red solid is :
View SolutionSodium (Na =23) crystallizen in bcc arrangement with the interfacial separation between the atoms at the edge 53.6pm. The density of sodium crystal is:
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is shown by
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is shown by
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is not shown by
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is shown by
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is shown by
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is shown by ?
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is shown by
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is shown by
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is shown by
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is shown by :
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is shown by
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is shown by
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is shown by
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is not shown by
View Solution
