Electrical resistance of certain materials, known as superconductors, changes abruptly from a non-zero value to zero as their temperature is lowered below a critical temperature TC(0). An interesting property of superconductors is that their critical temperature becomes smaller than TC(0) if they are placed in a magnetic field i.e., the critical temperature TC(B) is a function of the magnetic field strength B. The dependence of on B is shown in the figure.

A superconductor has TC(0)=100K. When a magnetic field of 7.5 T is applied its TC decreases to 75 K. For this material one can definitely say that when (Note T-Tesla)

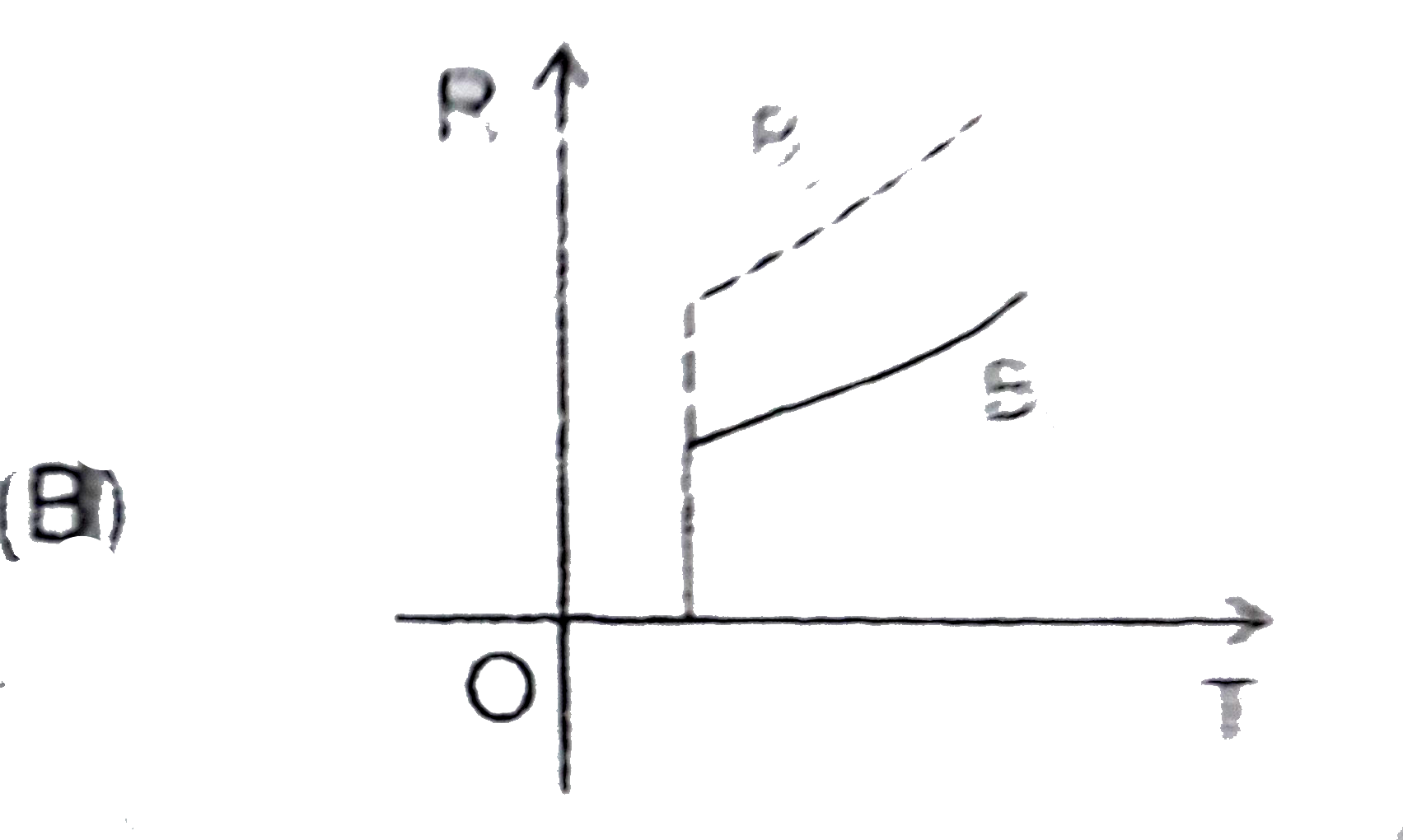
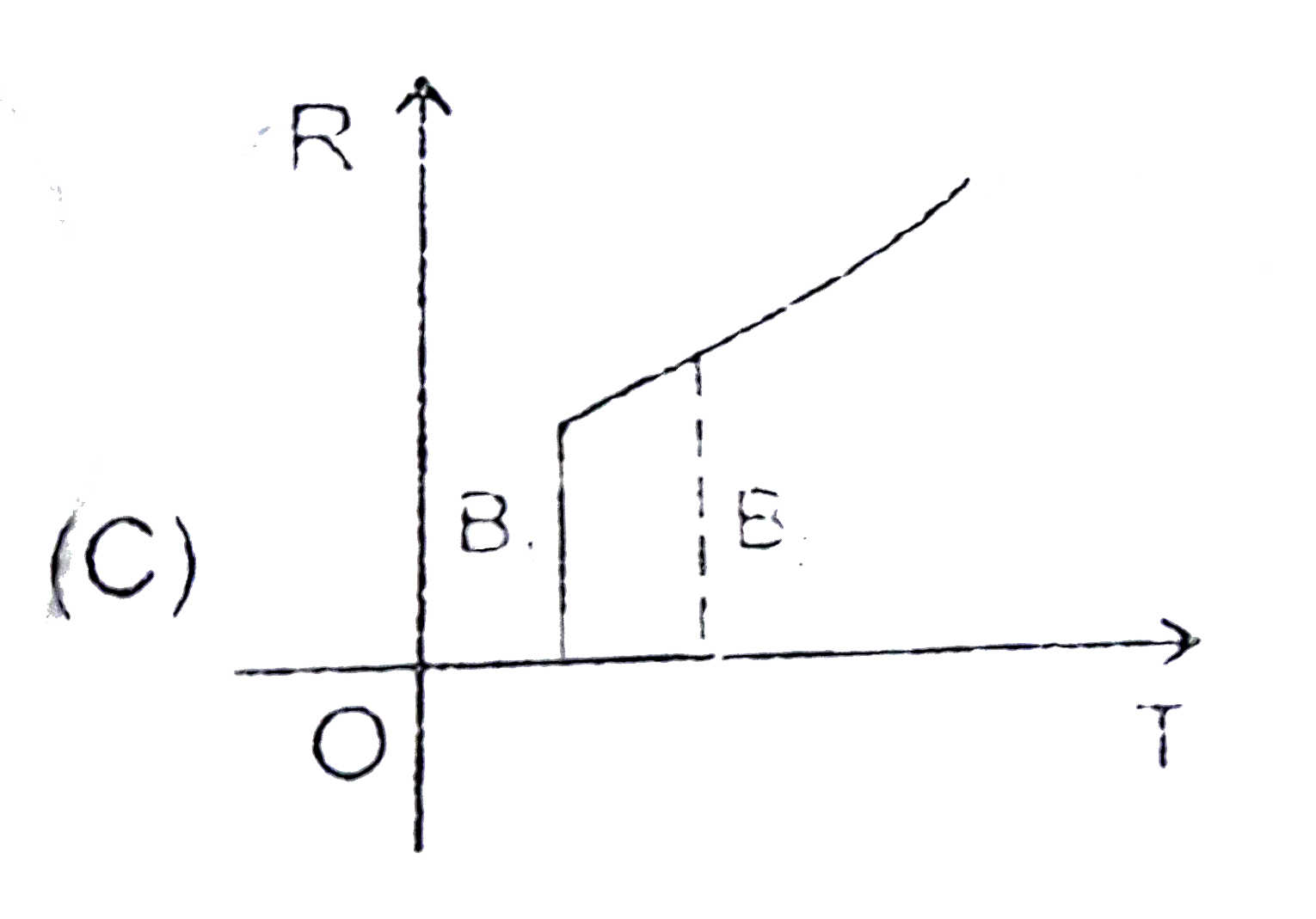
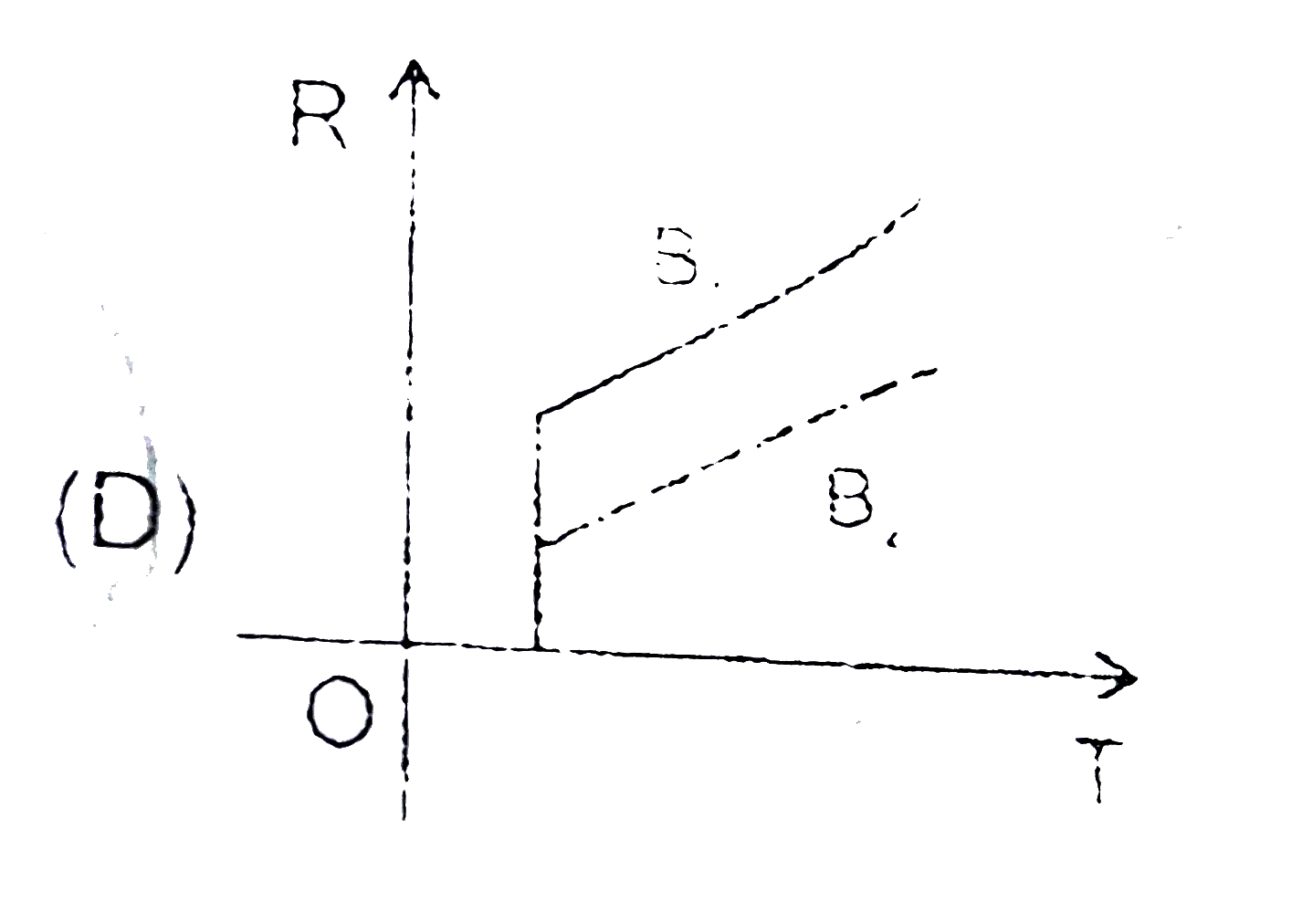
The correct Answer is:A
As the magnetic field is greater, the critical temperature is lower and as B2 is larger than B1.Graph A is correct.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONExercise:Exercis-3 PART 2
Explore 16 Videos
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONExercise:Exercis-3 PART 3
Explore 16 Videos
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONExercise:Exercis-2 PART 4
Explore 6 Videos
- ELECTRODYNAMICSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTRODYNAMICSExercise:Advanced level problems
Explore 29 Videos
- ELECTROSTATICSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROSTATICSExercise:HLP
Explore 38 Videos
Similar Questions
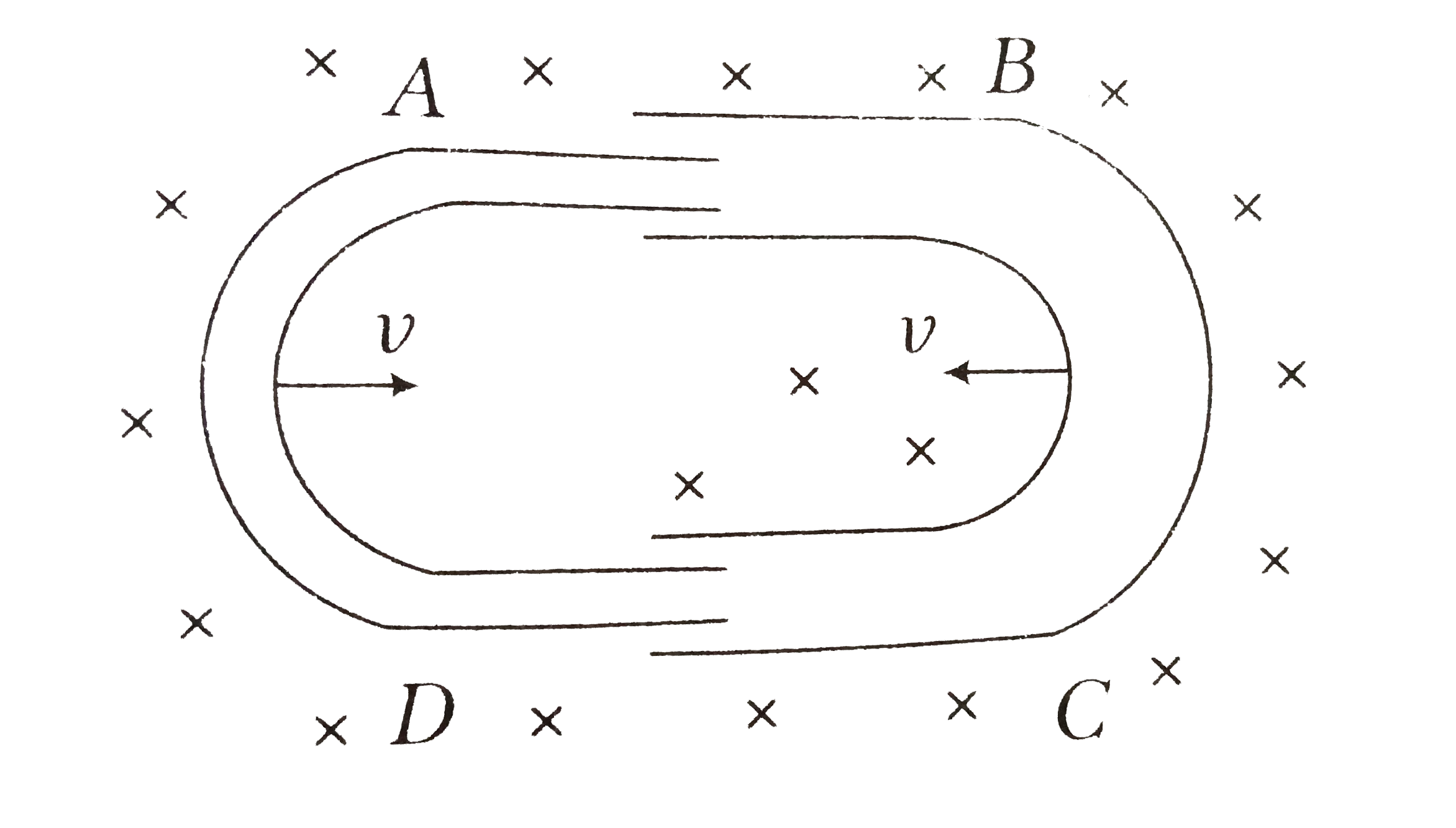
One conducting U-tube can slide inside another as shown in figure, maintaining electrical contacts between the tubes. The magnetic field B is perpendicular to the plane of the figure. If each tube moves towards the other at a constant speed u, then the emf induced in the circuit in terms of B, l and v, where l is the width of each tube, will be
View SolutionA mercury drop of radius 1 cm is sprayed into 106 droplets of equal size. Calculate the energy expended if surface tension of mercury is 35×10−3N/m .
View SolutionFigure shows a conducting rod of negligible resistance that can slide on smooth U-shaped rail made of wire of resistance 1Ω/m. Position of the conducting rod at t=0 is shown. A time dependent magnetic field B=2t tesla is switched on at t=0
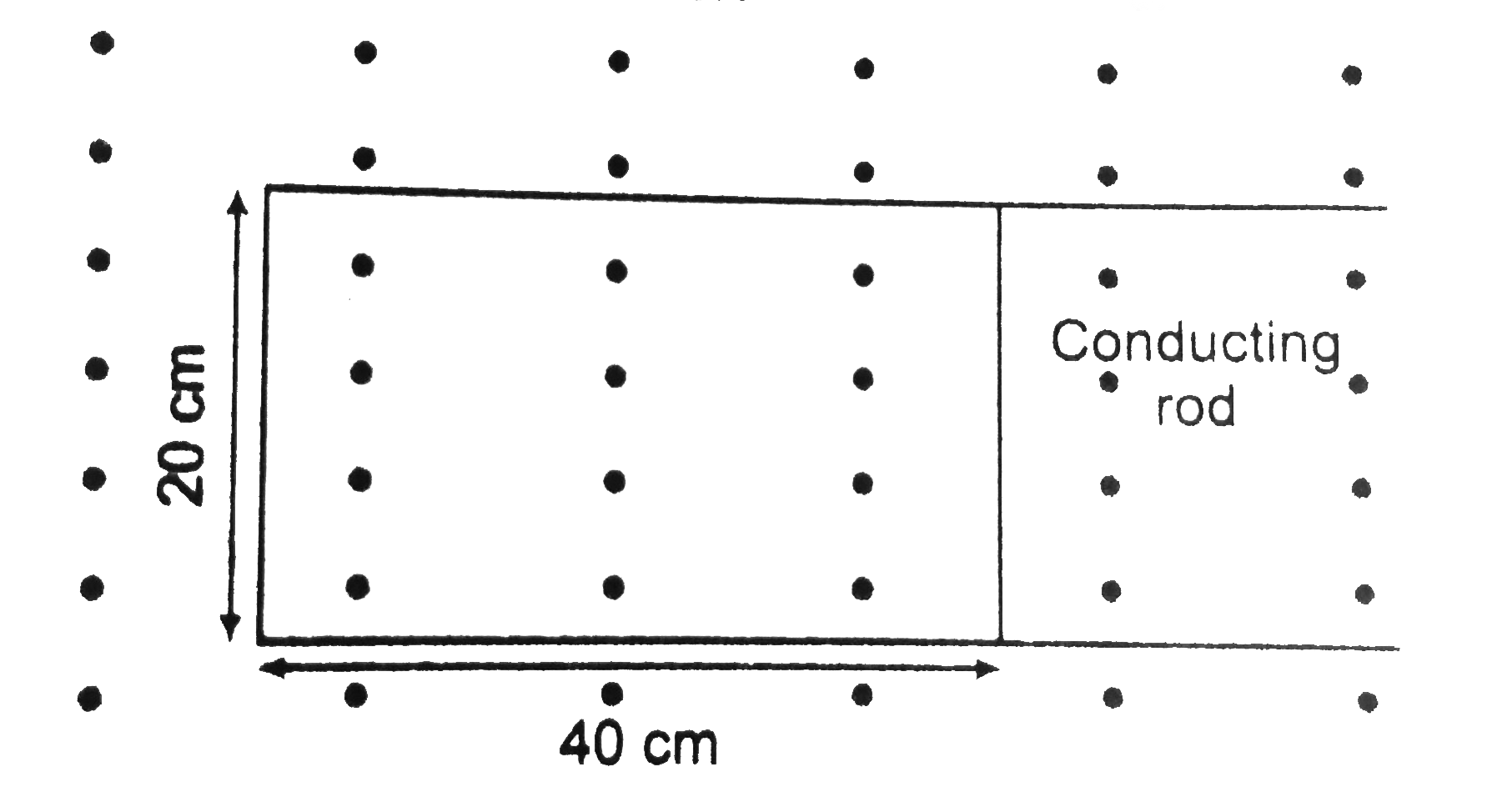
The current in the loop at t=0 due to induced emf is
View SolutionCalculate the magnetic moment (in Am2 ) of a thin wire with a current I = 8A, wound tightly on half a torus (see figure). The diameter of the cross section of the torus is equal to d = 5 cm, and the number of turns is N = 500.

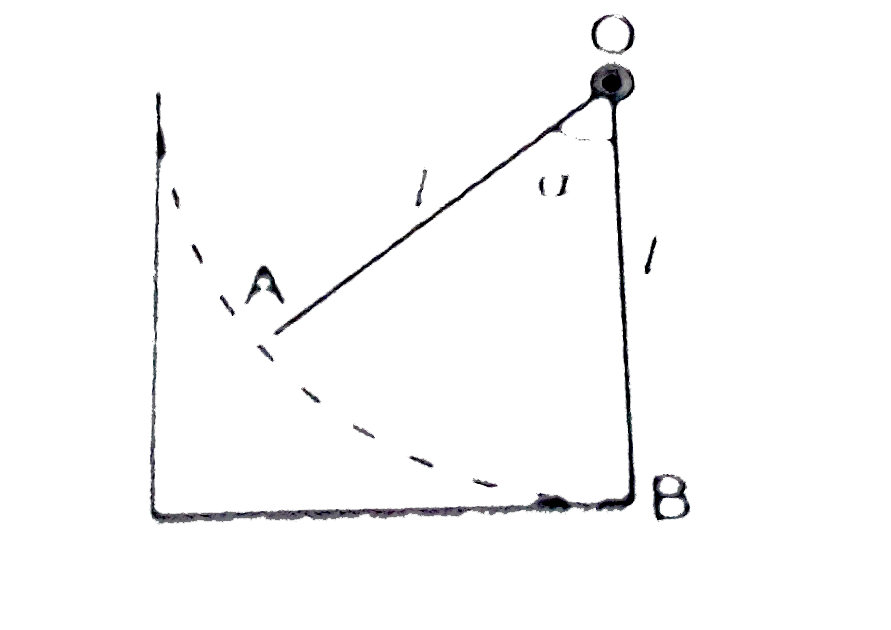
View SolutionAn electrometer consister of a fixed vertical metal bar OB at the top of which is attached a thin rod OA which gets deflected from the bar under the action of an electric charge (fig.). The rod can rotate in vertical plane about fixed horizontal axis passing through O. The reading is taken on a quadrant graduated in degrees. The length of the rod is l and its mass is m. what will be the charge when the rod of such an electrometer is deflected through an angle α in equilibrium. Find the answer using the following two assumptions :
The charge on the electrometer is equally distributed between the bar & the rod and the charges are concentrated at point A on the rod & at point B on the bar.
View SolutionElectrical resistance of certain materials, known as superconductors, changes abruptly from a nonzero value of zero as their temperature is lowered below a critical temperature TC(0). An interesting property of super conductors is that their critical temperature becomes smaller than TC(0) if they are placed in a magnetic field, i.e., the critical temperature TC(B) is a function of the magnetic field strength B. The dependence of TC(B) on B is shown in the figure.
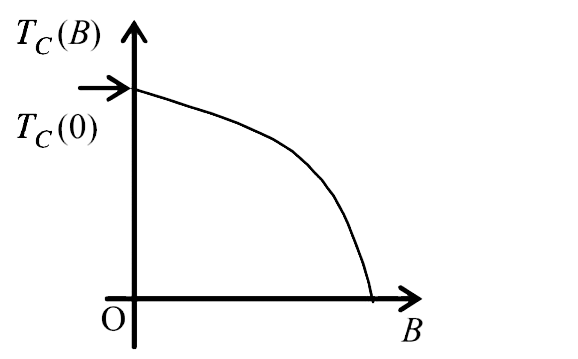 .
.
In the graphs below, the resistance R of a superconductor is shown as a function of its temperature T for two different magnetic fields B1(solid line) and B2 (dashed line). If B2 is larget than B1 which of the following graphs shows the correct variation of R with T in these fields?
View SolutionElectrical resistance of certain materials, known as superconductors, changes abruptly from a nonzero value of zero as their temperature is lowered below a critical temperature TC(0). An interesting property of super conductors is that their critical temperature becomes smaller than TC(0) if they are placed in a magnetic field, i.e., the critical temperature TC(B) is a function of the magnetic field strength B. The dependence of TC(B) on B is shown in the figure.
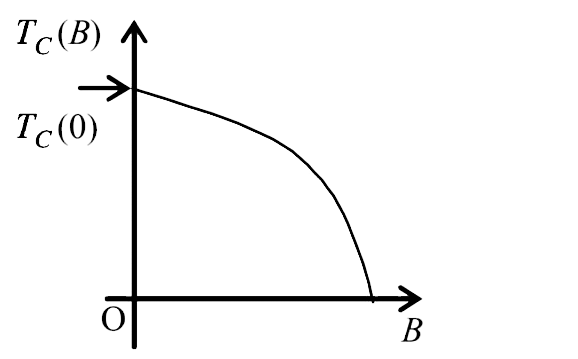 .
.
A superconductor has TC(0)=100K. When a magnetic field of 7.5 Tesla is applied , its TC decreases to 75 K. For this material one can difinitely say that when
View SolutionWhich of the following gases has the least value of critical temperature (T_(c )) and critical pressure (p_(c )) ?
View SolutionCritical temperature (TC) will be maximum for the following gas ?
View SolutionThe temperature 30.98^(@)C is called critical temperature (T_(C)) of carbon dioxide. The critical temperature is the
View SolutionSelect the correct order of the following temperature: {:("Boyl tempe.","Critical temp.","Inversion temp.",),(" "T_(B)," "T_(C)," "T_(I),):}
View SolutionWhich of the following relation is correct ?
(where Ti = Inversion temperature, Tc = Critical temperature)
View SolutionElectrical resistance of certain materials, known as superconductors, changes abruptly from a nonzero value to zero as there is lowered below a critical temperature TC(0). An interseting property of supercoductors is that their critical temperature becomes smaller than TC(0) if they are placed in a magnetic field , i.e., the critical temperature TC(B) on B si shown in the figure.
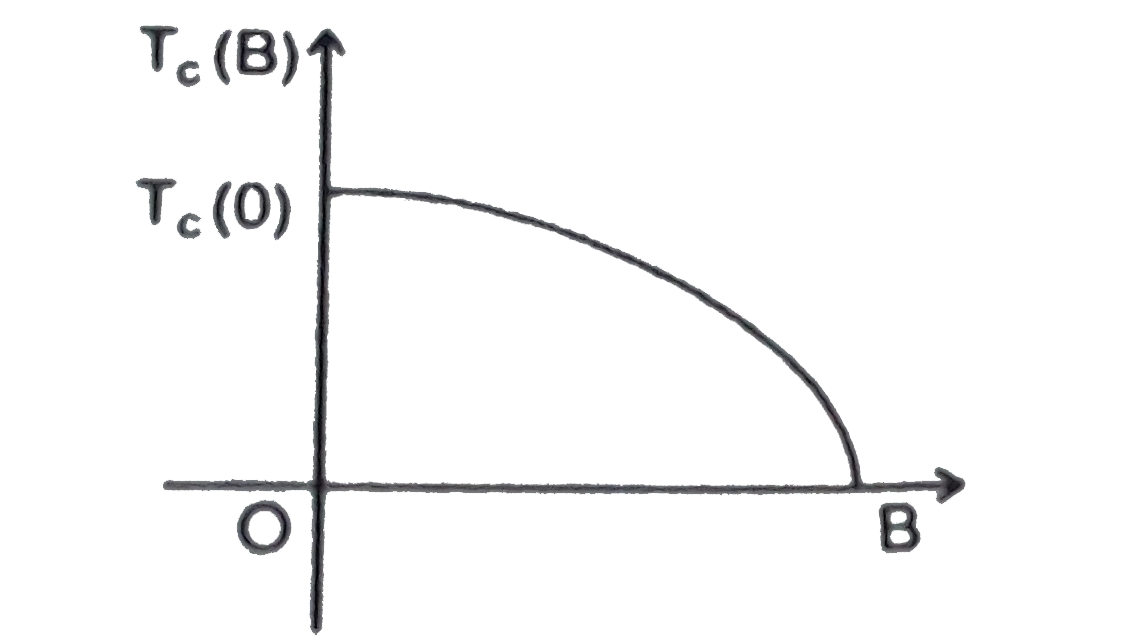
A superconductor has TC(0)=100K. When a magnetic field of 7.5 Tesla is applied , its TC decreases to 75 . For this material one can definitely say that when :
View Solutionक्रांतिक ताप ता अतिचालक किसे कहते हैं?
View Solutionकिसी पदार्थ का प्रतिरोध, जो कि अतिचालक है, इसका ताप क्रांतिक ताप TC(0) से कम करने पर अचानक अशून्य मान से शून्य तक परिवर्तित हो जाता है।
अतिचालक का एक रूचिकर गुण यह है कि यदि इन्हें चुम्बकीय क्षेत्र में रखा जाय तब, इनका क्रांतिक ताप TC(0) से घटने लगता है, अर्थात् क्रांतिक ताप TC(B), चुम्बकीय क्षेत्र की तीव्रता B का फलन होता है। TC(B) की B पर निर्भरता चित्र में प्रदर्शित है।

नीचे दिये गये ग्राफ में, दो भिन्न मान के चुम्बकीय क्षेत्रों B1 (सरल रेखा) तथा B2 (बिन्दुवत रेखा) के लिये अतिचालक के प्रतिरोध R को इसके ताप के फलन के रूप में दिखाया गया है। यदि B2 का मान B1 से बड़ा है तब इन चुम्बकीय क्षेत्रों में कौनसा ग्राफ R में T के साथ उचित परिवर्तन प्रदर्शित करता है
View SolutionA solid whose temperature t_(1)^(0)C It has a zero temperature chamber whose temperature t_(2)""^(@)C(t_(2) gt gt t_(1)) Is placed in. The rate of heat absorption by the body will be proportional
View Solution
