you have learnt that a travelling wave in one dimension is represented by a function y=f(x,t) where x and t must appear in the combination ax±bt or x−vt or x+vt,i.e. y=f(x±vt). Is the converse true? Examine if the folliwing function for y can possibly represent a travelling wave
(a) (x−vt)2
(b) log[(x+vt)/x0]
(c) 1/(x+vt)
The correct Answer is:The converse is not true. An obvious requirement for an acceptable function for a travelling wave is that it should be finite everywhere and at all times. Only funcation © satisfies this condition, the remaining funcations cannot possibly represent a travelling wave.
Step by step video solution for you have learnt that a travelling wave in one dimension is represented by a function y = f(x,t) where x and t must appear in the combination ax +- bt or x - vt or x + vt,i.e. y = f (x +- vt). Is the converse true? Examine if the folliwing function for y can possibly represent a travelling wave (a) (x - vt)^(2) (b) log[(x + vt)//x_(0)] (c) 1//(x + vt) by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- TRAVELLING WAVESBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - TRAVELLING WAVESEXERCISE - Exercise- 1 PART I
23 Videos
- TRAVELLING WAVESBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - TRAVELLING WAVESEXERCISE - Exercise- 1 PART II
30 Videos
- TRAVELLING WAVESBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - TRAVELLING WAVESEXERCISE - Solved Miscellaneous Problems
7 Videos
- TEST SERIESBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - TEST SERIESEXERCISE - PHYSICS
130 Videos
- WAVE ON STRING BOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - WAVE ON STRING EXERCISE - Exercise- 3 PART II
7 Videos
Similar Questions
Consider the wave y=(5mm)sin[1cm−1x−(60s−1)t]. Find (a) the amplitude, (b) the angular wave number, ( c ) the wavelength, (d) the frequency, (e) the time period and (f) the wave velocity.
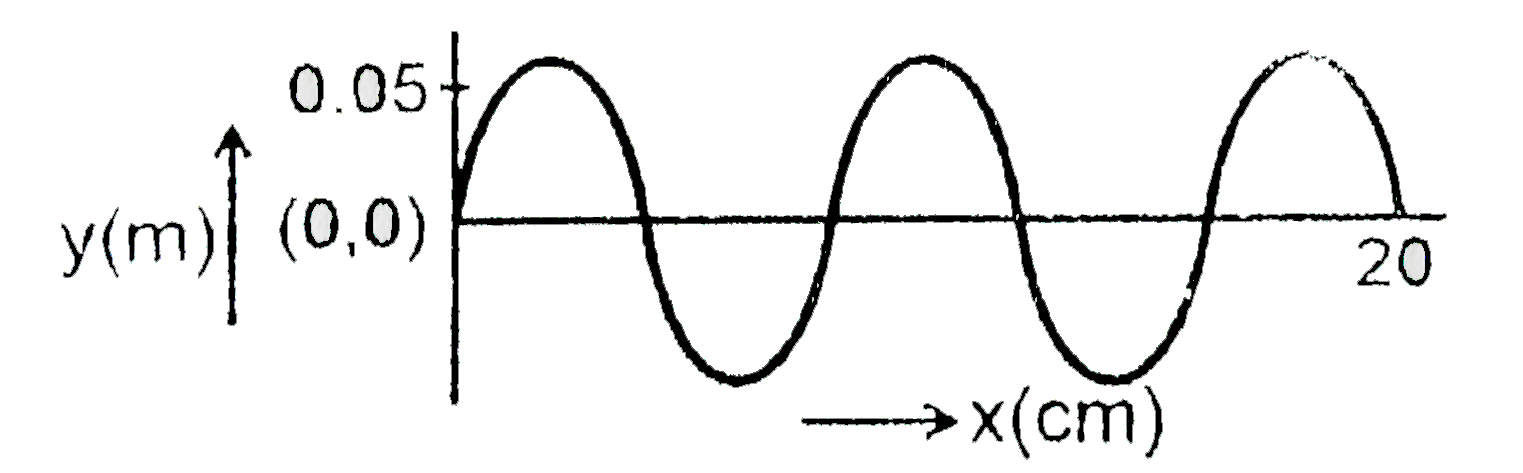
View SolutionFor the wave shown in figure, the equation for the wave, travelling along +x acis with velocity 350ms−1 when its position at t=0 is as shown
View SolutionA wave pulse moving along the x axis is represented by the wave function
y(x,t)=2(x−3t)2+1
where x and y are measured in cm and t is in seconds.
(i) in which direction is the wave moving ?
(ii) Find speed of the wave.
View SolutionA time varying voltage is applied across A & B such that voltage across capacitor is given by VC=2sin2t. What is maximum potential difference across the reistance?

View SolutionA string is stretched betweeb fixed points separated by 75.0cm. It observed to have resonant frequencies of 420Hz and 315Hz. There are no other resonant frequencies between these two. The lowest resonant frequency for this strings is
View SolutionDoes a travelling wave in one dimension represented by a function of a linear combination of x and t,i.e., y=f(ax+-bt) represented a travelling wave?
View SolutionCan the wave functions y=r(x-vt) or y=rlog(x+vt), y=rsqrt(vt-x) represent a wave motion?
View SolutionYou have learnt that a travelling wave in a dimension is represented by a funcation y = f(x,t) where x and t must appear in the combination x-vt or x + vt , i.e y = f(x+- upsilon t) . Is the coverse true? (Examine if the following funcations for y can possibly represent a travelling wave : (a) (x - vt)^(2) (b) log [(x + v)//x_(0)] (c) 1//(x + v)
View SolutionYou have learnt that a travelling wave in one dimension is represented by a function y=f(x,t) where x and t must appear in the combination x−vt or x+vt, i.e., y=f(x±vt). Is the converse true ? Examine if the following function for y can possibly represent a travelling wave :
(a) (x−vt)2
(b) log[(x+vt)/x0]
(c ) 1/(x+vt)
View SolutionYou have learnt that a travelling wave in a dimension is represented by a funcation y=f(x,t) where x and t must appear in the combination x−vt or x+vt, i.e y=f(x±υt). Is the coverse true? (Examine if the following funcations for y can possibly represent a travelling wave :
(a) (x−vt)2
(b) log[(x+v)/x0]
(c) 1/(x+v)
View SolutionYou have learnt that a travelling wave in a dimension is represented by a funcation y=f(x,t) where x and t must appear in the combination x−vt or x+vt, i.e y=f(x±υt). Is the coverse true? (Examine if the following funcations for y can possibly represent a travelling wave :
(a) (x−vt)2
(b) log[(x+v)/x0]
(c) 1/(x+v)
View SolutionYou have learnt that a travelling wave in one dimension is represented by a function y= f(x, t) where x and t must appear in the combination x-v t or x + v t , i.e., y= f (x +- v t) . Is the converse true? Examine if the following functions for y can possibly represent a travelling wave: (a) (x-vt)^(2) (b) log [(x + vt)//x_(0)] (c ) 1//(x + vt)
View SolutionYou have learnt that a travelling wave in one dimension is represented by a function y= f(x, t) where x and t must appear in the combination x-v t or x + v t , i.e., y= f (x +- v t) . Is the converse true? Examine if the following functions for y can possibly represent a travelling wave: (a) (x-vt)^(2) (b) log [(x + vt)//x_(0)] (c ) 1//(x + vt)
View Solutionyou have learnt that a travelling wave in one dimension is represented by a function y=f(x,t) where x and t must appear in the combination ax±bt or x−vt or x+vt,i.e. y=f(x±vt). Is the converse true? Examine if the folliwing function for y can possibly represent a travelling wave
(a) (x−vt)2
(b) log[(x+vt)/x0]
(c) 1/(x+vt)
View SolutionCheck whether, the following equations can represent a progressive (travelling wave)
(a) y=Acos(x3−vt)(b)x=Ae(vt−y)(c)y=Alog(xv−t)
View SolutionYou have learnt that a travelling wave in one dimension is represented by a function y= f(x, t) where x and t must appear in the combination x−vtorx+vt, i.e., y=f(x±vt). Is the converse true? Examine if the following functions for y can possibly represent a travelling wave:
(a) (x−vt)2
(b) log [(x+vt)/x0]
(c ) 1/(x+vt)
View Solution

