XSn/HCl−−−−→NaNO2−−−−→HClZCuCN−−−→Δ(P)H3O−−→Ph−COOH correct options is/are:
X is Ph−NH2
Y is Ph−NO2
Z is Ph−NH2
P is Ph-CN
The correct Answer is:D
To solve the problem step by step, we will analyze the transformations occurring from compound X to the final product Ph-COOH.
Step 1: Identify Compound X
The first reagent is Sn/HCl, which is a reducing agent. It is used to reduce nitro groups (NO2) to amine groups (NH2). Therefore, we can conclude that:
- X = Ph-NO2 (Nitrobenzene)
Step 2: Reduction of X to Y
When X (Ph-NO2) is treated with Sn/HCl, it is reduced to an amine:
- Y = Ph-NH2 (Aniline)
Step 3: Diazotization of Y to Z
Next, Y is treated with NaNO2 in HCl. This reaction is known as diazotization, where an amine is converted to a diazonium salt:
- Z = Ph-N2^+ Cl^- (Benzene diazonium chloride)
Step 4: Reaction of Z with CuCN to form P
The diazonium salt Z is then treated with CuCN, which introduces a cyanide group (CN) to the aromatic ring:
- P = Ph-C≡N (Benzene cyanide)
Step 5: Hydrolysis of P to form the final product
The final step involves the hydrolysis of P (Ph-C≡N) using H3O^+. This reaction converts the nitrile group (C≡N) into a carboxylic acid (COOH):
- Final Product = Ph-COOH (Benzoic acid)
Summary of the transformations:
- X = Ph-NO2
- Y = Ph-NH2
- Z = Ph-N2^+ Cl^-
- P = Ph-C≡N
- Final Product = Ph-COOH
Correct Option
From the analysis, we can conclude that the only correct statement is:
- P is Ph-C≡N, which is correct.
The first reagent is Sn/HCl, which is a reducing agent. It is used to reduce nitro groups (NO2) to amine groups (NH2). Therefore, we can conclude that:
- X = Ph-NO2 (Nitrobenzene)
When X (Ph-NO2) is treated with Sn/HCl, it is reduced to an amine:
- Y = Ph-NH2 (Aniline)
Next, Y is treated with NaNO2 in HCl. This reaction is known as diazotization, where an amine is converted to a diazonium salt:
- Z = Ph-N2^+ Cl^- (Benzene diazonium chloride)
The diazonium salt Z is then treated with CuCN, which introduces a cyanide group (CN) to the aromatic ring:
- P = Ph-C≡N (Benzene cyanide)
The final step involves the hydrolysis of P (Ph-C≡N) using H3O^+. This reaction converts the nitrile group (C≡N) into a carboxylic acid (COOH):
- Final Product = Ph-COOH (Benzoic acid)
- X = Ph-NO2
- Y = Ph-NH2
- Z = Ph-N2^+ Cl^-
- P = Ph-C≡N
- Final Product = Ph-COOH
From the analysis, we can conclude that the only correct statement is:
- P is Ph-C≡N, which is correct.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- AROMATIC COMPOUNDS BOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - AROMATIC COMPOUNDS EXERCISE - Section -2 (one or more than one options correct type)
5 Videos
- AROMATIC COMPOUNDS BOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - AROMATIC COMPOUNDS EXERCISE - Section-4: Comprehension type(Only one options correct)
1 Video
- AROMATIC COMPOUNDS BOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - AROMATIC COMPOUNDS EXERCISE - PART-II: NATIONAL STANDARD EXAMINATION IN CHEMISTRY (NSEC) STAGE-I
31 Videos
- ATOMIC STRUCTUREBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - ATOMIC STRUCTUREEXERCISE - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Fundamental Concept )
16 Videos
Similar Questions
Complete the following reaction
View Solution
Compound 'Z' is:
View SolutionCompound A is chiral and has the molecular formula C8H11N. When A reacts nitrous acid then occurs a brisk evolution of N2 gas. A dissolves in aqueous HCl. What is the identity of A ?
View SolutionThe magnetic moment of .25Mn in ionic state is √15B.M, then Mn is in:
View SolutionpH−OH∣C∣Me−NH3∣C∣Me−MeNaNO2,HCl−−−−−−−→Δ?
Major product is
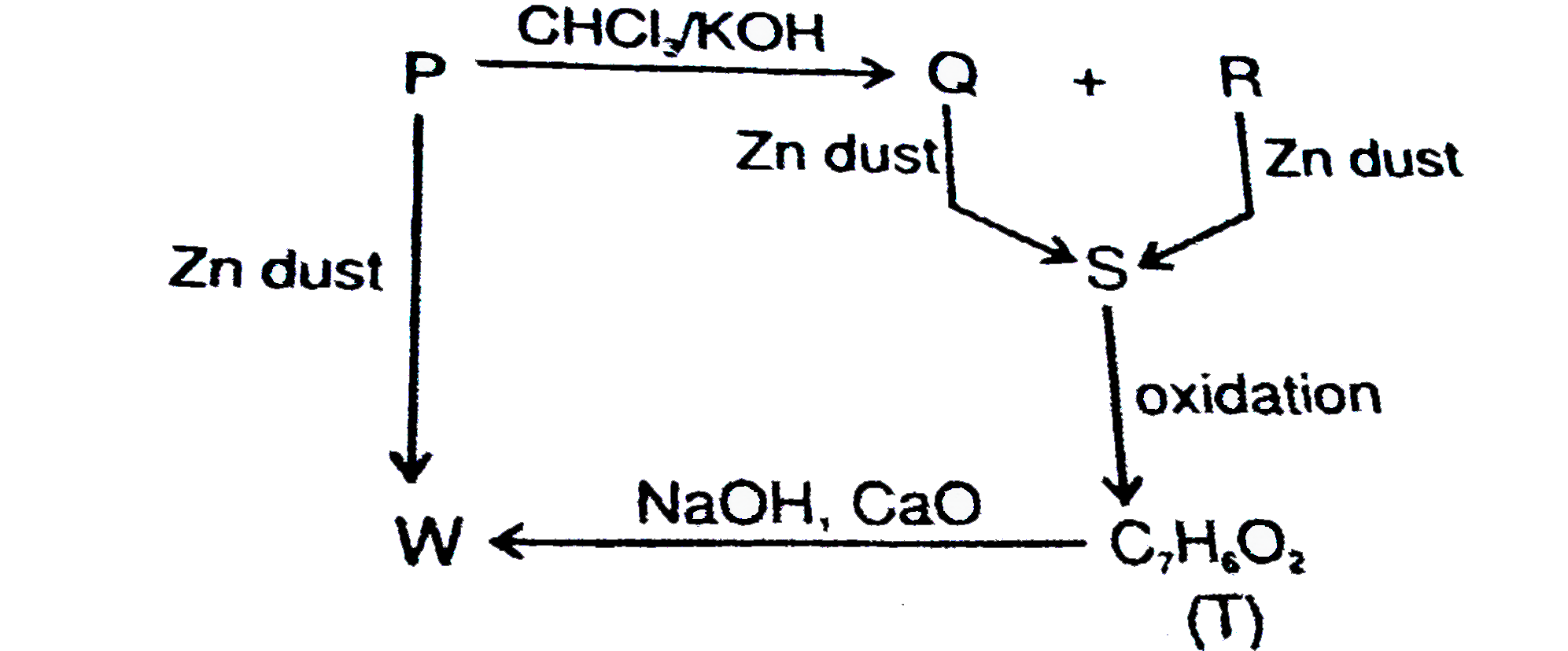
View Solutionunderset(("Monosubsitituted benzene"))(P)overset(Na(Hg))underset(+conc. H_(2)SO_(4))rarr Q overset(NaNO_(2))underset(+HCl.0^(@).5^(@)C)rarr R overset(KCN)underset(CuCN)rarr S overset(SnCl_(2))underset(HCl)rarr T Correct statement are :
View SolutionPh-overset(O)overset(||)(C)-CH_(3) overset(NaNO_(2))underset(HCl)(to) (A) underset("heat")overset(AC_(2)O)(to) (B)overset(H_(3)O^(+))(to)(C) Product (C) of the above reaction is :
View Solutionunderset((X))("p-Nitro phenol")underset((1))overset((C_2H_5)_2SO_4//NaOH)tounderset((2))overset(Sn//HCl)to(Y)underset((3))overset(NaNO_3//HCl)tounderset((4))overset(C_6H_5OH)to product is :
View SolutionXSn/HCl−−−−→NaNO2−−−−→HClZCuCN−−−→Δ(P)H3O−−→Ph−COOH correct options is/are:
View Solutionunderset(HCl)overset(NaNO_(2))(to)Aoverset(CuCN)(to)Boverset(H_(3)O^(+))(to)C .C is identified as
View Solutionइन अभिक्रियाओं को पूरा कीजिये एव A व B को पहचानिये।
C6H5NO2Sn/HCl−−−−→6H[A]NaNO3+HCl−−−−−−−−→[B]
View SolutionWhat is the major product (Z) of the reaction? PhCOOH underset(H_2SO_4)overset(HNO_3)(rarr) overset(Sn//HCl)(rarr)underset(HCl)overset(NaNO_2)(rarr)underset(Delta)overset(H_2O)(rarr)
View SolutionGive the structures of A, B and C in the following reactions:
(i) CH3CH2lNaCN−−−→AOH−−−−−−−−−−→Partial hydrolysisBNaOH+Br2−−−−−−−→C
(ii)C6H5N2ClCuCN−−−→AH2O∣H+−−−−−→BNH3−−→ΔC
(iii) CH3CH2BrKCN−−→ALiAH4−−−→BHNO2−−−→0∘CC
(iv) C6H5NO2Fe/HCl−−−−→ANaNO2+HCl−−−−−−−−→273KBH2∅H+−−−−→ΔC
(v) CH3COOH−NH3−−→ΔANaOBr−−−→BNaNO2/HCl−−−−−−−→C
View SolutionGive the structures of A and B in the following sequence of reactions:
(a) CH3COOHNH3−−→ΔANaOBr−−−→B
(b) C6H5NO2Fe/HCl−−−−→ANaNO2+HCl−−−−−−−−→0∘−5∘CB
(c ) C6H5N+2Cl−CuCN−−−→ΔAH2∅H+−−−−→B
View SolutionGive the structures of A, B and C in the following reactions : (i) C_(6)H_(5)N_(2)^(+)Cl^(-) overset(CuCN)(rarr)A overset(H_(2)O""//H^(+))(rarr)B underset(Delta)overset(NH_(3))(rarr)C (ii) C_(6)H_(5)NO_(2) overset(Sn+HCl)(rarr)A underset(273K)overset(NaNO_(2)+HCl)(rarr)B underset(Delta)overset(H_(2)O""//H^(+))(rarr)C
View Solution

