Which of the following reactions are completed through free radical intermediate ?
(CH3)3CH+Br2hv−−→(CH3)3CBr+HBr
(CH3)3C=CH2+Br2→CH3−Br∣C∣CH3−Br∣CH2
CH3−CH=CH2+Cl2hv−−→C∣ClH2−CH=CH2
Ph−CH=CH2+HBrR2O2−−→hvPh−CH2−C∣BrH2
The correct Answer is:A, C, D
To determine which reactions are completed through free radical intermediates, we will analyze each of the given reactions step by step.
1. Identify the Reactions: We have four reactions to analyze.
- Reaction 1: Bromination in the presence of light
- Reaction 2: Electrophilic addition on alkene
- Reaction 3: Chlorination in the presence of light
- Reaction 4: Another reaction involving hydrogen peroxide and light
2. Analyze Reaction 1 (Bromination in presence of light):
- This reaction involves the bromine molecule (Br2) undergoing homolytic cleavage due to the presence of light, forming two bromine radicals (Br•).
- These bromine radicals can then react with alkanes to form alkyl bromides.
- Conclusion: This reaction proceeds through a free radical mechanism.
Hint: Look for the presence of light and homolytic cleavage in the mechanism.
3. Analyze Reaction 2 (Electrophilic addition on alkene):
- This reaction involves the addition of electrophiles to alkenes, typically resulting in the formation of cyclic intermediates (like bromonium ions).
- There is no free radical formation in this process.
- Conclusion: This reaction does not proceed through a free radical mechanism.
Hint: Electrophilic addition typically involves cyclic intermediates rather than free radicals.
4. Analyze Reaction 3 (Chlorination in presence of light):
- Similar to bromination, chlorination in the presence of light involves the homolytic cleavage of Cl2 to form chlorine radicals (Cl•).
- These radicals can then react with alkanes to produce alkyl chlorides.
- Conclusion: This reaction proceeds through a free radical mechanism.
Hint: Check for the presence of light and radical formation from diatomic molecules.
5. Analyze Reaction 4 (Reaction with hydrogen peroxide and light):
- This reaction involves the cleavage of a double bond in the presence of hydrogen peroxide and light, leading to the formation of free radicals.
- The presence of light causes the homolytic cleavage of bonds, resulting in radical intermediates.
- Conclusion: This reaction proceeds through a free radical mechanism.
Hint: The presence of hydrogen peroxide and light often indicates a free radical pathway.
Final Conclusion:
The reactions that proceed through free radical intermediates are:
- Reaction 1: Bromination in presence of light
- Reaction 3: Chlorination in presence of light
- Reaction 4: Reaction with hydrogen peroxide and light
Answer: Reactions 1, 3, and 4 are completed through free radical intermediates.
- Reaction 1: Bromination in the presence of light
- Reaction 2: Electrophilic addition on alkene
- Reaction 3: Chlorination in the presence of light
- Reaction 4: Another reaction involving hydrogen peroxide and light
- This reaction involves the bromine molecule (Br2) undergoing homolytic cleavage due to the presence of light, forming two bromine radicals (Br•).
- These bromine radicals can then react with alkanes to form alkyl bromides.
- Conclusion: This reaction proceeds through a free radical mechanism.
- This reaction involves the addition of electrophiles to alkenes, typically resulting in the formation of cyclic intermediates (like bromonium ions).
- There is no free radical formation in this process.
- Conclusion: This reaction does not proceed through a free radical mechanism.
- Similar to bromination, chlorination in the presence of light involves the homolytic cleavage of Cl2 to form chlorine radicals (Cl•).
- These radicals can then react with alkanes to produce alkyl chlorides.
- Conclusion: This reaction proceeds through a free radical mechanism.
- This reaction involves the cleavage of a double bond in the presence of hydrogen peroxide and light, leading to the formation of free radicals.
- The presence of light causes the homolytic cleavage of bonds, resulting in radical intermediates.
- Conclusion: This reaction proceeds through a free radical mechanism.
The reactions that proceed through free radical intermediates are:
- Reaction 1: Bromination in presence of light
- Reaction 3: Chlorination in presence of light
- Reaction 4: Reaction with hydrogen peroxide and light
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS - IIBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS - IIExercise:APSP Part - 2
Explore 42 Videos
- MOLE CONCEPTBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:MOLE CONCEPTExercise:ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(BASIC CONCEPTS)
Explore 27 Videos
- ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVExercise:APSP PART-3
Explore 22 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Which of the following reactions involve free radical as intermediate?
A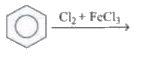 B
B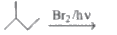 C
C D
D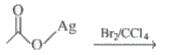
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of a free radical?
AIt has a positive chargeBIt has a negative chargeCIt has all paired electrons.DIt has an unpaired electron.Which of the following reactions involve benzyne intermediate?
A B
B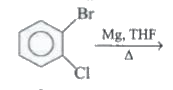 C
C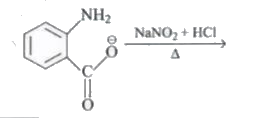 D
D
Which of the following reactions involve carbanion enolalte as reactive intermediate?
View SolutionHow many reactions will proceed through free radical addition mechanism ?
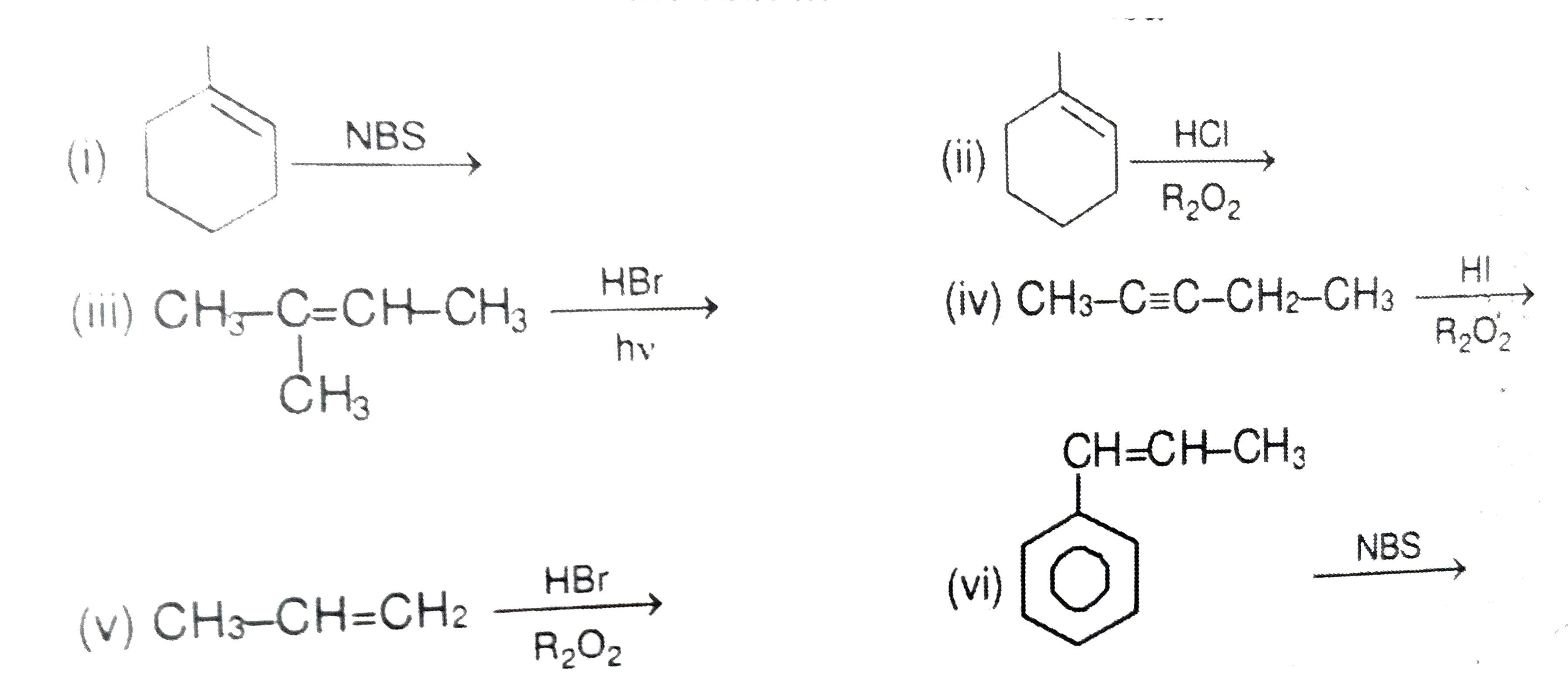
View SolutionFree radicals are formed through
View SolutionWhich of the following is true about the cycloheptatrienyl free radical ?
View SolutionWhich of the following is the correct order of stability of free radicals ?
View Solution
