CH3−CH3∣C∣H−CH2BrAlKOH−−−−→Δ Alkene,
Alkene is -


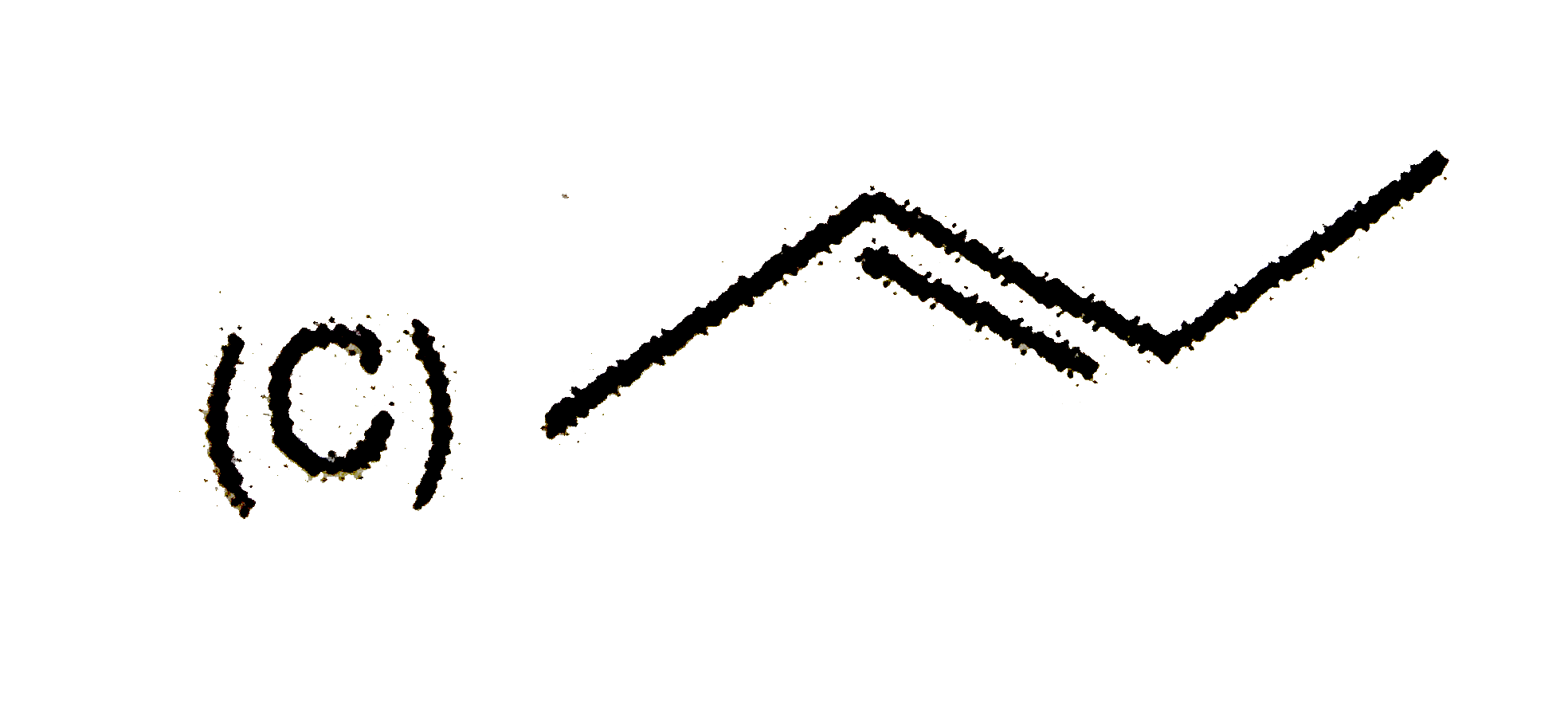
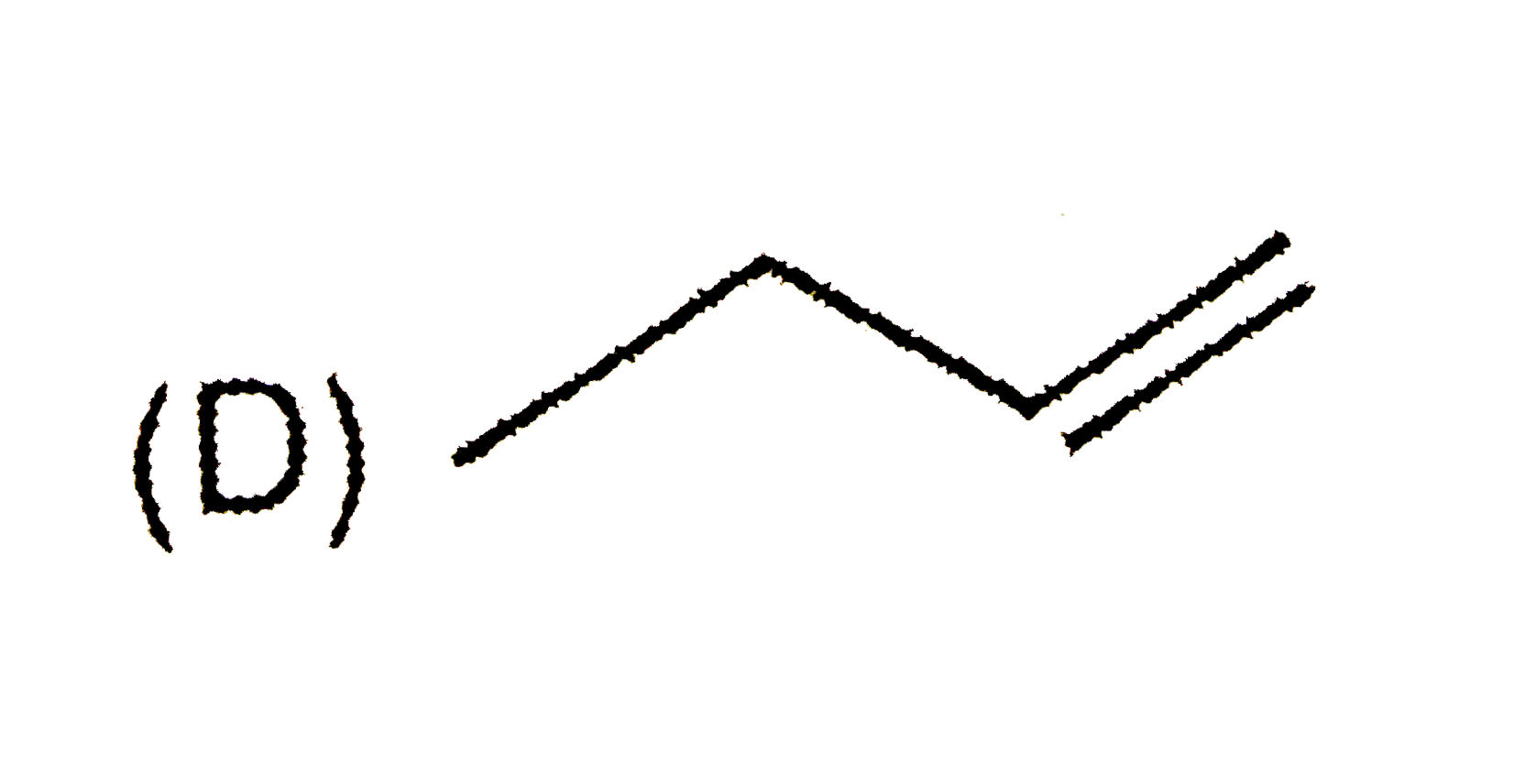
The correct Answer is:A
To solve the problem of determining the alkene formed from the reaction of 2-bromobutane with alcoholic KOH upon heating, we can follow these steps:
1. Identify the Reactant:
The compound given is 2-bromobutane, which can be represented as:
CH3−CH(Br)−CH2−CH3
2. Understand the Reaction Conditions:
The reaction is conducted with alcoholic KOH and involves heating. Alcoholic KOH promotes elimination reactions, specifically dehydrohalogenation.
3. Dehydrohalogenation Mechanism:
In this reaction, we will eliminate a hydrogen atom (H) and a bromine atom (Br) from adjacent carbon atoms:
- The bromine (Br) is a leaving group.
- A hydrogen atom from the adjacent carbon will also be removed.
4. Identify the Atoms to be Eliminated:
- From the 2-bromobutane, we can eliminate the Br from the second carbon and an H from the adjacent (first or third) carbon.
- For example, we can remove H from the first carbon (CH3) and Br from the second carbon.
5. Formation of the Alkene:
After the elimination of H and Br, a double bond will form between the first and second carbon atoms:
CH3−CH=CH−CH3
This results in the formation of 1-butene.
6. Final Structure of the Alkene:
The alkene formed can be represented as:
CH2=CH−CH2−CH3
7. Conclusion:
The alkene produced from the reaction of 2-bromobutane with alcoholic KOH is 1-butene.
Final Answer:
The alkene formed is 1-butene.
The compound given is 2-bromobutane, which can be represented as:
CH3−CH(Br)−CH2−CH3
The reaction is conducted with alcoholic KOH and involves heating. Alcoholic KOH promotes elimination reactions, specifically dehydrohalogenation.
In this reaction, we will eliminate a hydrogen atom (H) and a bromine atom (Br) from adjacent carbon atoms:
- The bromine (Br) is a leaving group.
- A hydrogen atom from the adjacent carbon will also be removed.
- From the 2-bromobutane, we can eliminate the Br from the second carbon and an H from the adjacent (first or third) carbon.
- For example, we can remove H from the first carbon (CH3) and Br from the second carbon.
After the elimination of H and Br, a double bond will form between the first and second carbon atoms:
CH3−CH=CH−CH3
This results in the formation of 1-butene.
The alkene formed can be represented as:
CH2=CH−CH2−CH3
The alkene produced from the reaction of 2-bromobutane with alcoholic KOH is 1-butene.
The alkene formed is 1-butene.
टॉपर्स ने हल किए ये सवाल
- ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVExercise:Exercise-1 Part-3
Explore 2 Videos
- ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVExercise:Exercise-2 Part-1
Explore 11 Videos
- ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IVExercise:APSP PART-3
Explore 22 Videos
- ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS - IIBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS - IIExercise:APSP Part - 3
Explore 22 Videos
- PERIODIC TABLE & PERIODICITYBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:PERIODIC TABLE & PERIODICITYExercise:ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(BASIC CONCEPTS)
Explore 24 Videos
समान प्रश्न
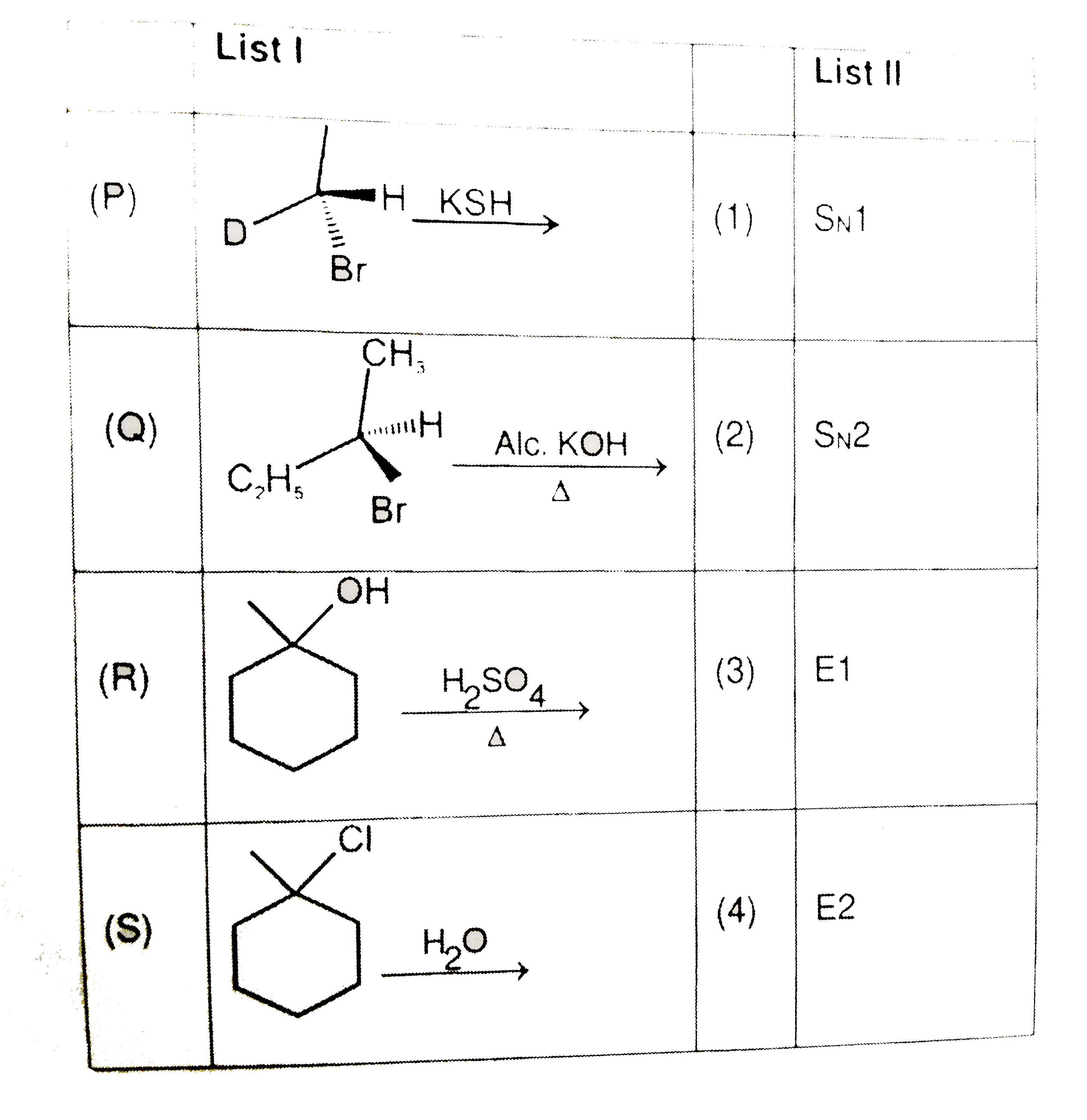
Match List I (Reaction) with List II (Type of reaction ) and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists :
View SolutionThe relative rate of acid catalysed dehydration of following alcohols would be
I.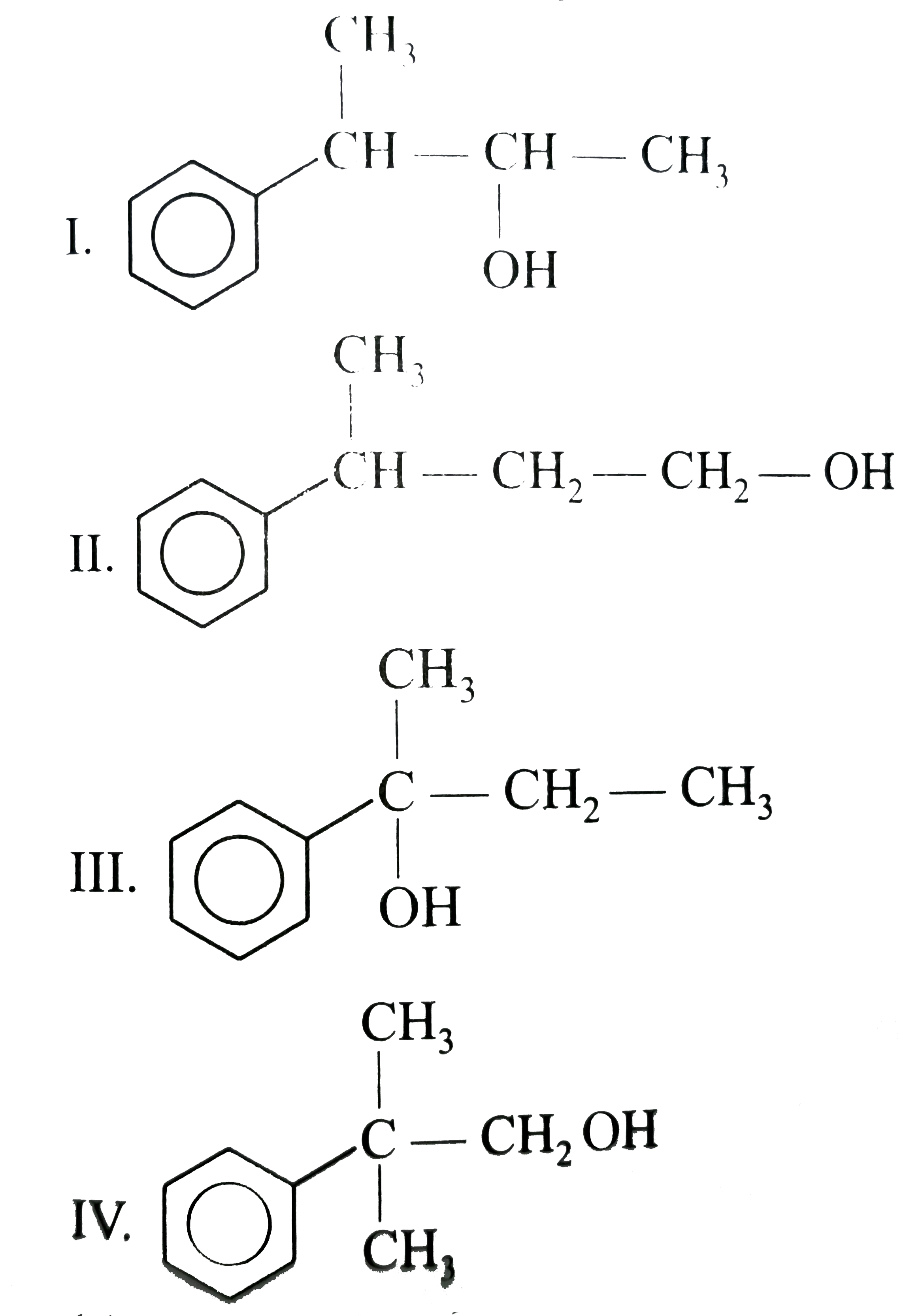
View SolutionRate of Bimolecular elimination (E2) reaction for the following :

View Solution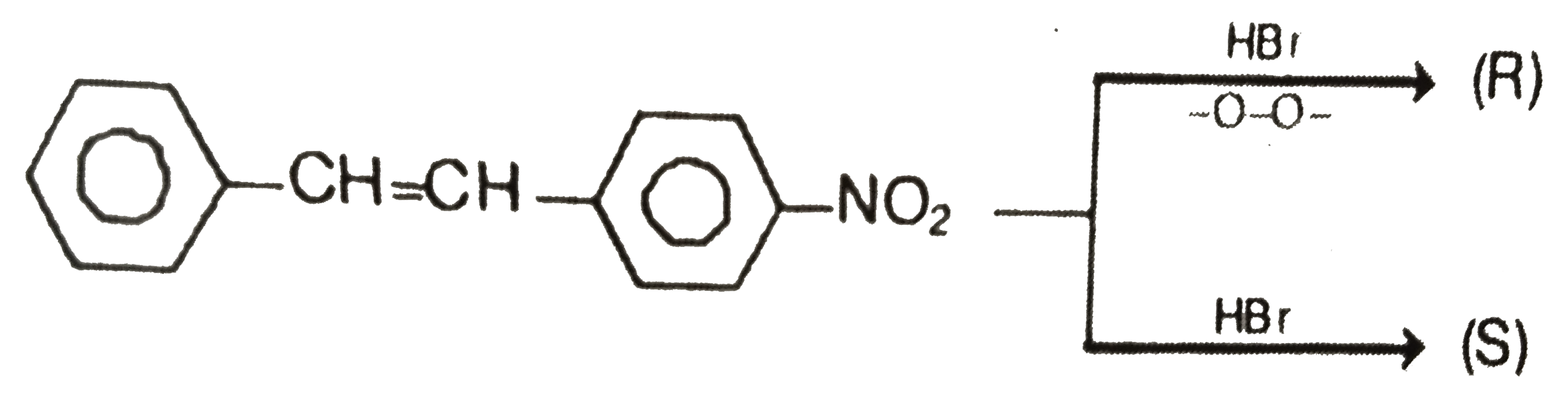
R & S are :
View SolutionAn element with atomic number 107 has recently been discovered. Its block, group number, period and outshell electronic configuration respectively are :
View SolutionCH_3-undersetunderset(O)(||)C-(CH_2)_4-undersetunderset(O)(||)C-CH_3 " " underset(H^+)overset(Ooverset(Theta)H//Delta)toAoverset(Ph-MgBr)toBunderset(Conc.HCl)overset(Zn-Hg)toC The product 'C' is:
View SolutionWhich of the following statement are correct for give reaction. CH_3-undersetunderset(CH_3)(|)C=CH-CH_3+HBr overset("Peroxide")toCH_3-undersetunderset(CH_3)(|)oversetoverset(Br)(|)C-CH_2-CH_3 " " CH_3-undersetunderset(CH_3)(|)CH-oversetoverset(Br)(|)CH-CH_3
View SolutionCH3−CH3∣C∣H−CH2BrAlKOH−−−−→Δ Alkene,
Alkene is -
View SolutionCH3−C∣CH3H−Cl∣CH−CH3t−BuO−−−−→Δ Major Product is :
View SolutionIn following compound - CH3−CH2−CH3∣C∣CH3−C∣CH3H−CH3∣CH−CH2−CH3
The correct lowest set of locants are :
View SolutionThe name of CH_3-undersetunderset(CH_3)(|)oversetoverset(CH_3)(|)C-CH_2-oversetoverset(CH_3)(|)CH-CH_3 is :
View SolutionCH3−C∣ CH3H−CH3∣C∣CH3−C∣CH3H−CH2−CH3 का IUPAC पद्धति में नाम है:
View SolutionConsider following reactions, I.CH_3CH_2undersetunderset(OH)|CHCH_3 overset(H^+)to A (major ) II. CH_3undersetunderset(CH_3)|oversetoverset(CH_3)|C-undersetunderset(OH)|CHCH_3 overset(H^+)to B (major ) A and B (both alkenes ) are respectively :
View SolutionCH_3underset(CH_3)underset(|)oversetoverset(CH_3)|C-undersetunderset(OH)|CHCH_3 overset(HBr)to A (predominant), A is
View SolutionThe reaction CH3−CH3∣C∣CH3−ONa+CH3CH2−Cl−NaCl−−−−→CH3−CH3∣C∣CH3−O−CH2−CH3 is called .
View Solution
