Reduction of an isonitrile gives a
primary amine
secondary amine
tertiary amine
quaternary ammonium salt.
The correct Answer is:B
To determine the product of the reduction of an isonitrile, we can follow these steps:
1. Identify the Structure of Isonitrile:
- Isonitriles have the general formula R-N≡C, where R is an alkyl or aryl group. For example, let's consider an isonitrile like CH3-CH2-N≡C.
2. Choose a Reducing Agent:
- Common reducing agents for the reduction of isonitriles include hydrogen gas (H2) in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel (Ni) or platinum (Pt).
3. Understand the Reduction Mechanism:
- During the reduction, the isonitrile undergoes a reaction where the carbon-nitrogen triple bond is reduced. The nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons, which can participate in the reaction.
4. Nucleophilic Attack:
- The carbon atom in the isonitrile is negatively charged and acts as a nucleophile. It attacks a proton (H+) from the reducing agent, leading to the formation of a new bond.
5. Formation of the Amine:
- As the reaction proceeds, the triple bond between carbon and nitrogen is broken. The nitrogen atom, which has a lone pair, can now bond to another hydrogen atom, resulting in the formation of a secondary amine.
6. Final Product:
- The final product of the reduction of isonitrile is a secondary amine. For the example CH3-CH2-N≡C, the product would be CH3-CH2-CH2-NH2, which is a secondary amine.
Conclusion:
The reduction of an isonitrile gives a secondary amine.
---
- Isonitriles have the general formula R-N≡C, where R is an alkyl or aryl group. For example, let's consider an isonitrile like CH3-CH2-N≡C.
- Common reducing agents for the reduction of isonitriles include hydrogen gas (H2) in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel (Ni) or platinum (Pt).
- During the reduction, the isonitrile undergoes a reaction where the carbon-nitrogen triple bond is reduced. The nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons, which can participate in the reaction.
- The carbon atom in the isonitrile is negatively charged and acts as a nucleophile. It attacks a proton (H+) from the reducing agent, leading to the formation of a new bond.
- As the reaction proceeds, the triple bond between carbon and nitrogen is broken. The nitrogen atom, which has a lone pair, can now bond to another hydrogen atom, resulting in the formation of a secondary amine.
- The final product of the reduction of isonitrile is a secondary amine. For the example CH3-CH2-N≡C, the product would be CH3-CH2-CH2-NH2, which is a secondary amine.
The reduction of an isonitrile gives a secondary amine.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- REDUCTION, OXIDATION & HYDROLYSIS REACTIONSBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - REDUCTION, OXIDATION & HYDROLYSIS REACTIONSEXERCISE - Part-III : High Level Problems (Subjective Questions)
6 Videos
- REDUCTION, OXIDATION & HYDROLYSIS REACTIONSBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - REDUCTION, OXIDATION & HYDROLYSIS REACTIONSEXERCISE - Only One Option Correct Type
4 Videos
- REDUCTION, OXIDATION & HYDROLYSIS REACTIONSBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - REDUCTION, OXIDATION & HYDROLYSIS REACTIONSEXERCISE - Additional problems for self Practice (Part-1)
30 Videos
- PERIODIC TABLE & PERIODICITYBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - PERIODIC TABLE & PERIODICITYEXERCISE - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(BASIC CONCEPTS)
24 Videos
- S BLOCK ELEMENTSBOOK - RESONANCE ENGLISHCHAPTER - S BLOCK ELEMENTSEXERCISE - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Biomolecules & Polymer)
4 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
The Birch reduction of benzoic acid gives :
A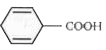 B
B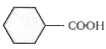 C
C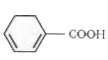 D
D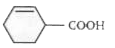
Assertion : Catalytic reduction of butanal gives butanol.
Reason: Aldehydes on reduction give corresponding primary alcohols.Aif both assertioon and reason are true and reason is the corrct explanation of assertion.BIf both assertion and reason are ture but reason is not the corrcet explanation of assertion.CIf assertion is true but reason is false .Dif both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: Esters which contain α−hydrogens undergo Claisen condensation.
Reason : LiAIH4 reduction of esters gives acids
View SolutionReduction by LiAlH4 of hydrolysed product of an ester gives
View SolutionReduction of nitrobenzene with H2 in presence of platinum gives nitrosobenzene––––––––––––––––.
View SolutionWhich of the following reduction reactions does not give an amine as product?
View SolutionReduction of nitrobenzene in the presence of Zn/NH4Cl gives
View SolutionMalachite on calcination gives →'A'+CO2+H2O.
Compound 'A' on reduction with carbon gives →CO+'B'
Here 'A' and 'B' are
View Solution

