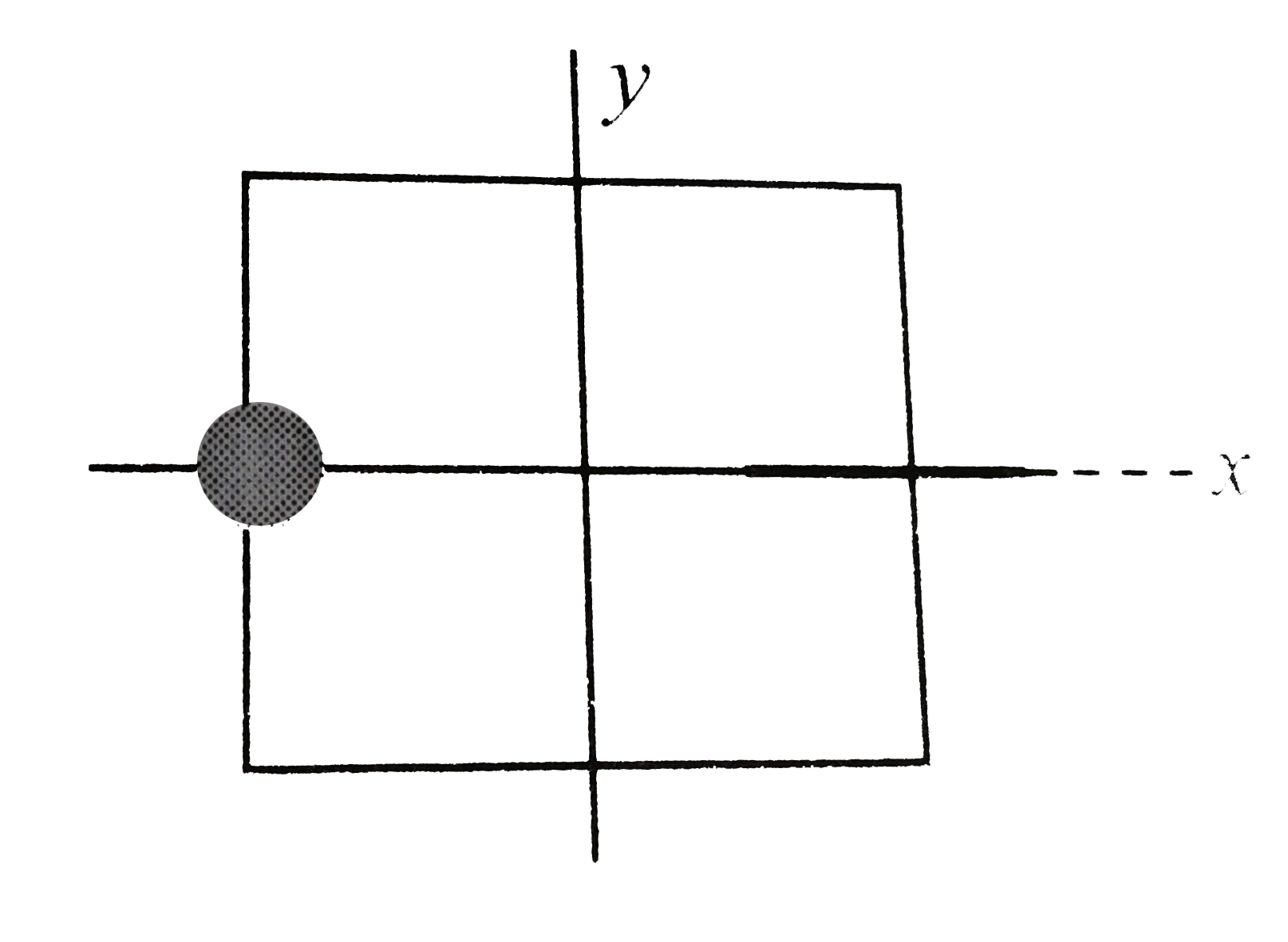
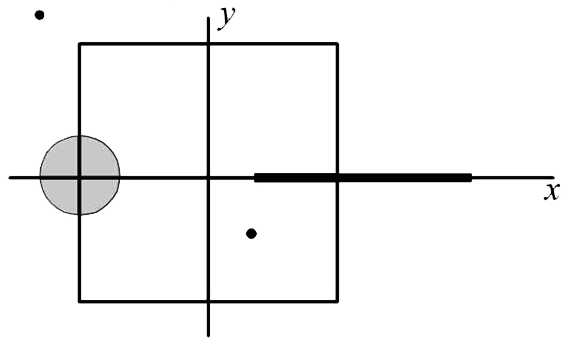
A disk of radius a/4 having a uniformly distributed charge 6 C is placed in the xy plane with its center at (−a/2,0,0). A rod of length carrying a uniformly distributed charge 8 C is placed on the x-axis from x=a/4→x=5a/4. Two point charges −7Cand3C are placed at (a/4,−a/4,0)and(−3a/4,3a/4,0), respectively. Consider a cubical surface formed by six surfaces x=±a/2,y=±a/2,z=±a/2. The electric flux through this cubical surface is
−2Cε0
2Cε0
10Cε0
12Cε0
The correct Answer is:A
Step by step video solution for A disk of radius a//4 having a uniformly distributed charge 6 C is placed in the xy plane with its center at (-a//2,0,0). A rod of length carrying a uniformly distributed charge 8 C is placed on the x-axis from x = a//4 to x = 5a//4. Two point charges -7C and 3C are placed at (a//4,-a//4,0) and (-3a//4,3a//4,0), respectively. Consider a cubical surface formed by six surfaces x = +-a//2, y = +-a//2, z = +-a//2. The electric flux through this cubical surface is by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- ELECTROSTATICSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROSTATICSExercise:Part - II
Explore 23 Videos
- ELECTROSTATICSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROSTATICSExercise:HLP
Explore 38 Videos
- ELECTROSTATICSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROSTATICSExercise:Part - IV
Explore 9 Videos
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONExercise:A.l.P
Explore 19 Videos
- EXPERIMENTAL PHYSICSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:EXPERIMENTAL PHYSICSExercise:PART -II
Explore 10 Videos
Similar Questions
An electric charge 10−3μC is placed at the origin (0, 0) of xy-coordinate system. Two points A and B are situated at (√2,√2)and(2,0), respectively. The potential difference between the points A and B will be
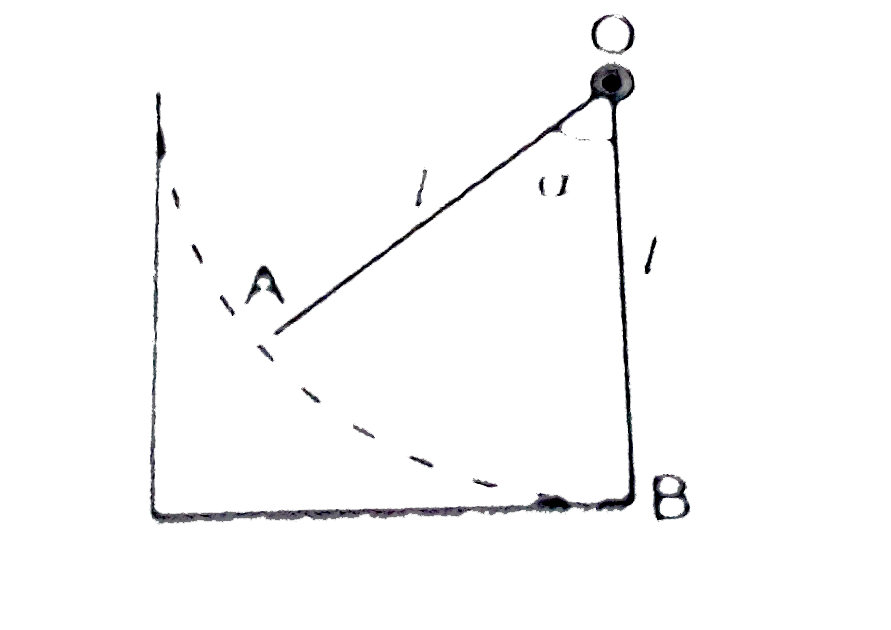
View SolutionAn electrometer consister of a fixed vertical metal bar OB at the top of which is attached a thin rod OA which gets deflected from the bar under the action of an electric charge (fig.). The rod can rotate in vertical plane about fixed horizontal axis passing through O. The reading is taken on a quadrant graduated in degrees. The length of the rod is l and its mass is m. what will be the charge when the rod of such an electrometer is deflected through an angle α in equilibrium. Find the answer using the following two assumptions :
The charge on the electrometer is equally distributed between the bar & the rod and the charges are concentrated at point A on the rod & at point B on the bar.
View SolutionA leaf electroscope is a simple apparatus to detect any charge on a body. It consist of two metal leaves OA and OB, free to rotate about O. Initially both are very slighty separted. When a charged object is touched to the metal knob at the top of the conduction re, charge flows from knob to the top of the conduction rod, charge flows from knob to the leaves through the conducting rod, charge flows from knob to the leaves through the conduction rod. As the leaves are now charged similarly, they start repelling each other and tet separted (deflected by certain angle).
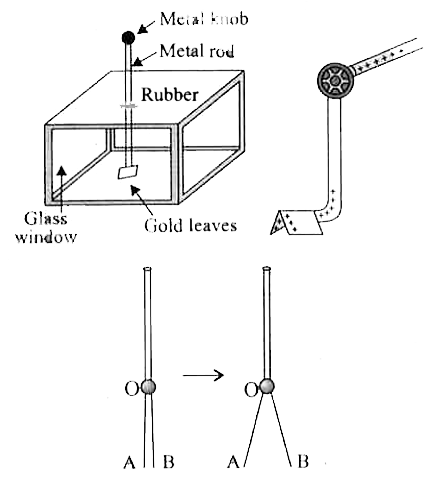
The angle of deflection in static equilibrium is an indicator of the amount of charge on the charged boy.
When a+20C rod is touched to the knob, the deflection of leaves was 5∘, and when an identical rod of −40C is touched, the deflection was found to be 9∘. If an identical rod of +30C is touched, then the deflection may be:
View SolutionA long thin wire carrying a varying current I=i0sinωt lies at a distance y above one edge of a rectangular wire loop of length LandW lying in the x−z plane. What emf is induced in the loop?

View SolutionTwo full turns of the circular scale of a screw gauge cover a distance of 1 mm on its main scale. The total number of division on the circular scale is 50. Further, it is found that the screw gauge has a zero error of −0.03 mm while measuring the diameter of a thin wire, a student notes the main scale reading of 3 mm and the number of circular scale division in line with the main scale as 35. The diameter of the wire is
View SolutionA disc of radius a/4 having a uniformly distributed charge 6C is placed in the x-y plane with its centre at (−a/2,0,0). A rod of length a carrying a uniformly distributed charge 8C is placed on the x-axis from x=a/4 to x=5a/4. Two point charges −7C and 3C are placed at (a/4,−a/4,0) and (−3a/4,3a/4,0), respectively. Conisder a cubical surface formed by isx surfaces x=±a/2, y=±a/2, z=±a/2. The electric flux through this cubical surface is
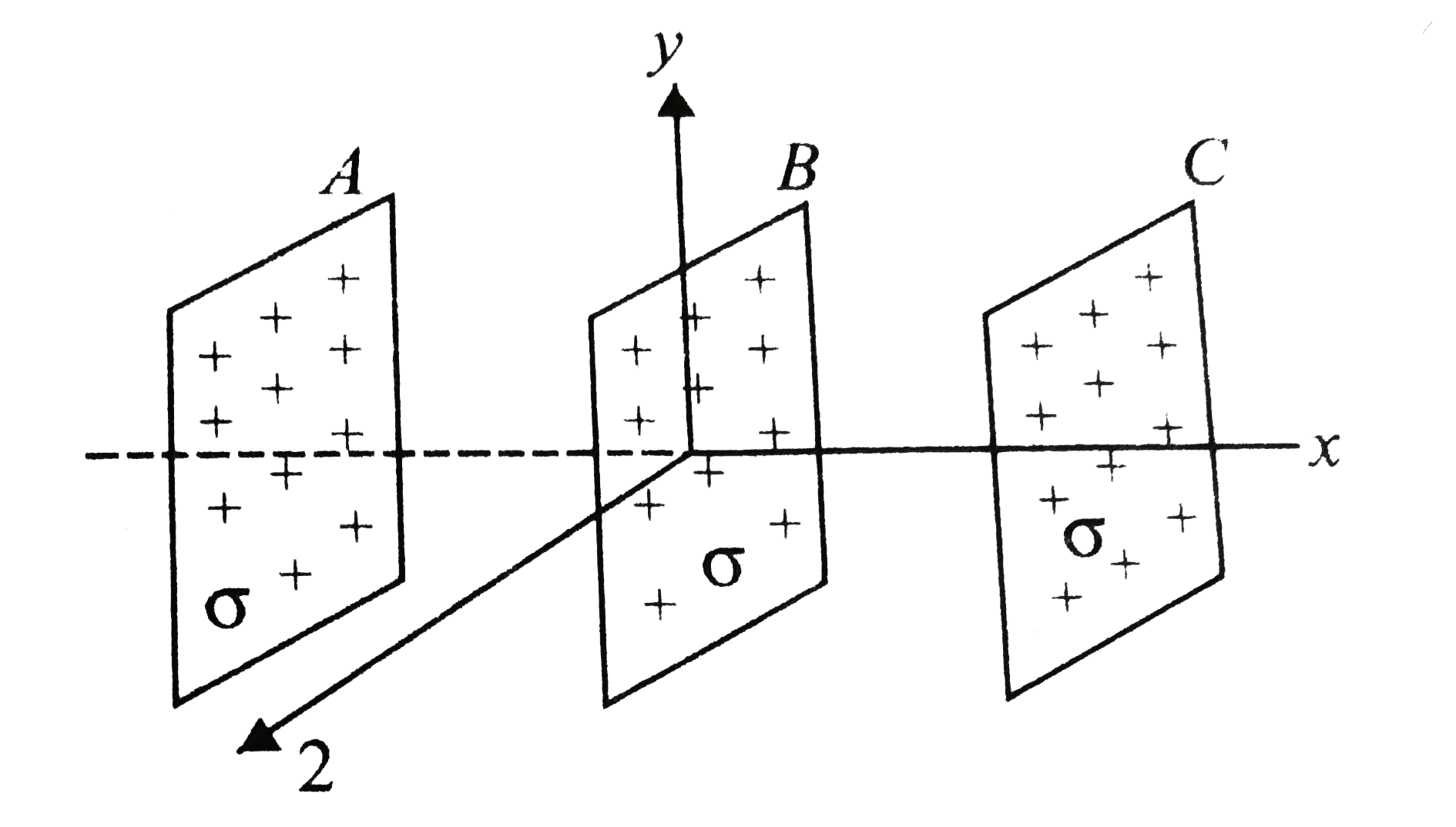
View SolutionThree infinite planes have a uniform surface charge distribution σ on its surfaces. All charges are fixed. On each of the three infinite planes, parallel to the yz plane placed at x=−a,x=0,andx=a, there is a uniform surface charge of the same density, σ. The potential difference between A and C is
View Solutionyz-तल में रखे R त्रिज्या के किसी रिंग का केन्द्र मूलबिंदु (origin ) पर स्थिर है। रिंग पर आवेश Q एक-समान रूप से (uniformaly ) वितरित है ।
View Solutionत्रिज्या R के एक वलय पर आवेश q एकसमान रूप से वितरित है। इसकी अक्ष पर केन्द्र से x दूरी पर स्थित बिन्दु पर विद्युत् क्षेत्र की तीव्रता ज्ञात कीजिए।
View SolutionContinuous charge distribution(linear, surface and volumetric), Electric field due to slender rod, Electric field on the axis of a uniformly charged ring and disk
View SolutionA disc of radius a/4having a uniformly distributed charge 6C is placed in X−Y plane with its centre at (−a/2,0,0).A rod of length a carrying a uniformly distributed charge 8C is placed on the X-axis from x=a/4 to x=6a/4. Two point charges −7C and 3C are placed at (a4,−a4.0) and (−3a4,0) respectively. Consider a cubical surface formed by six surfaces x=±a2,y=±a2,z=±a2. The electric flux throgh the cubical surface is
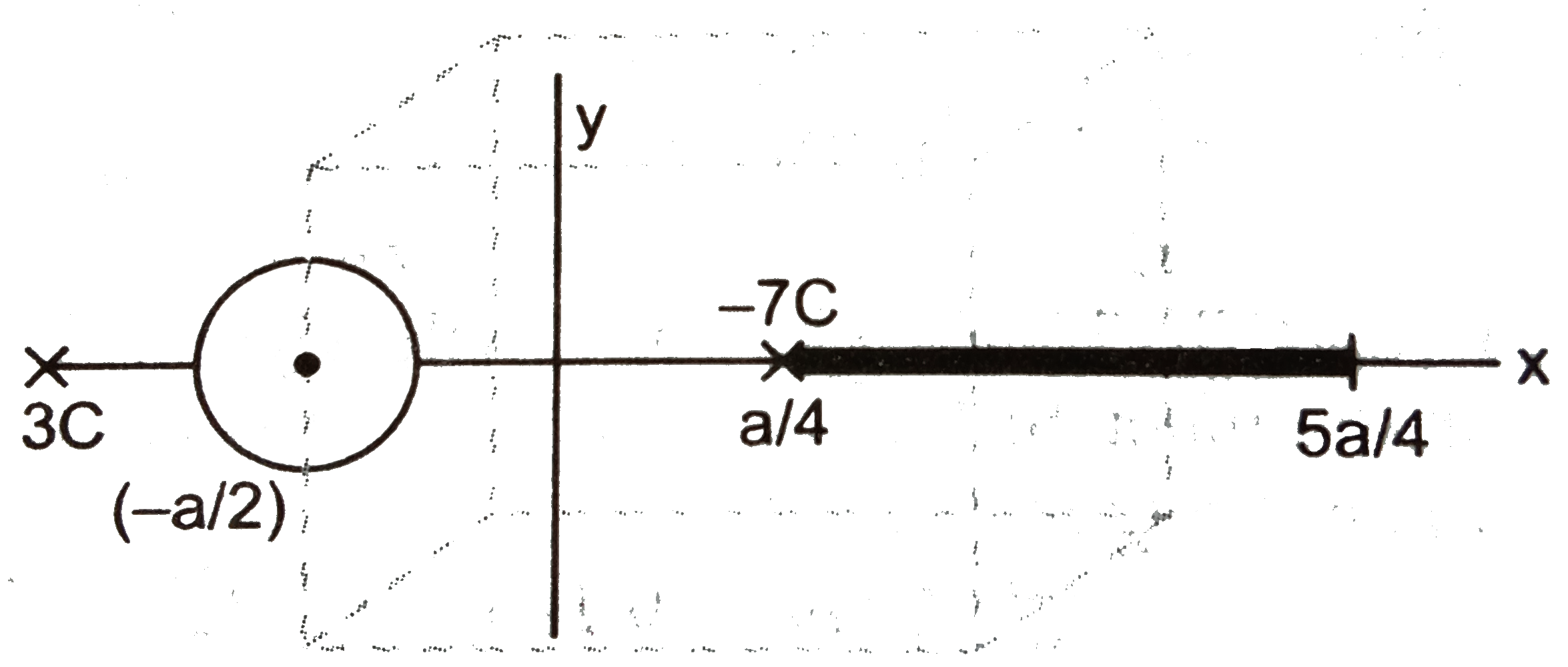
View Solutionत्रिज्या a/4 की एक डिस्क पर एक समान रूप से वितरित 6C आवेश है और यह x-y तल में इस प्रकार रखी है कि इसका केन्द्र (-a/2, 0, 0) पर है। लम्बाई की छड़ जिस पर एक समान रूप से वितरित 8C आवेश है, x-अक्ष पर x = a/4 से x =5a/4 तक रखी है। दो बिन्दु आवेश -7C तथा 3C क्रमश: {a/4, - a/4, 0) तथा (−3a4,3a4,0) पर रखे हैं। एक घनीय सतह 6 सतहों x=±a/2,y=+a/2,z=±a/2 से बनी है। इस घनीय सतह से गुजर रहा वैद्युत फ्लक्स है।
View SolutionA ring of radius a contains a charge q distributed. uniformly ober its length. Find the electric field at a point. on the axis of the ring at a distance x from the centre.
View SolutionA ring of radius R has charge Q distributed uniformly on it. At a distance x (!=0) from centre on its axis. (consider axial points only)
View SolutionR त्रिज्या की चक्रिका के पृष्ठ पर आवेश Q एकसमान रूप से वितरित है। इस आवेश के कारण चक्रिका की अक्ष पर विभव परिकलित कीजिए।
View Solutionएक बिन्दुवत् आवेश Q, R त्रिज्या एवं एक समान रूप से वितरित -Q आवेश के स्थिर पतले वलय के केन्द्र पर रखा है। वलय के अक्ष पर केन्द्र से x दूरी पर स्थित बिन्दु पर विधुत क्षेत्र की तीव्रता का परिमाण ( x>>R के लिए) ........... है |
View Solution
