The electric field E is measured at a point P (0, 0, d) generated due to various charge distributions and the dependence of E on d is found to be different for different charge distributions. Column I contains different relations between E and d. Column II describes different electric charge distributions, along with their locations. Match the functions in Column I with the related charge distribution(s) in Column II.

P→5,Q→3,4,R→1,S→2
P→5,Q→3,R→1,4,S→2
P→5,Q→3,R→1,2,S→4
P→4,Q→2,3,R→1,S→5
The correct Answer is:B
Step by step video solution for The electric field E is measured at a point P (0, 0, d) generated due to various charge distributions and the dependence of E on d is found to be different for different charge distributions. Column I contains different relations between E and d. Column II describes different electric charge distributions, along with their locations. Match the functions in Column I with the related charge distribution(s) in Column II. by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- ELECTROSTATICSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROSTATICSExercise:Part - II
Explore 23 Videos
- ELECTROSTATICSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROSTATICSExercise:HLP
Explore 38 Videos
- ELECTROSTATICSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROSTATICSExercise:Part - IV
Explore 9 Videos
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONExercise:A.l.P
Explore 19 Videos
- EXPERIMENTAL PHYSICSBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:EXPERIMENTAL PHYSICSExercise:PART -II
Explore 10 Videos
Similar Questions
An electric charge 10−3μC is placed at the origin (0, 0) of xy-coordinate system. Two points A and B are situated at (√2,√2)and(2,0), respectively. The potential difference between the points A and B will be
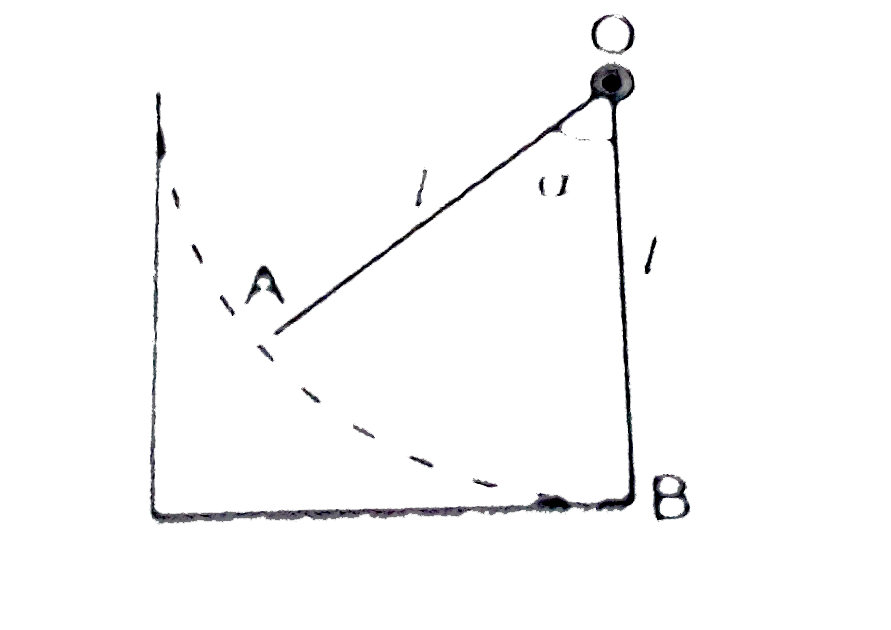
View SolutionAn electrometer consister of a fixed vertical metal bar OB at the top of which is attached a thin rod OA which gets deflected from the bar under the action of an electric charge (fig.). The rod can rotate in vertical plane about fixed horizontal axis passing through O. The reading is taken on a quadrant graduated in degrees. The length of the rod is l and its mass is m. what will be the charge when the rod of such an electrometer is deflected through an angle α in equilibrium. Find the answer using the following two assumptions :
The charge on the electrometer is equally distributed between the bar & the rod and the charges are concentrated at point A on the rod & at point B on the bar.
View SolutionA leaf electroscope is a simple apparatus to detect any charge on a body. It consist of two metal leaves OA and OB, free to rotate about O. Initially both are very slighty separted. When a charged object is touched to the metal knob at the top of the conduction re, charge flows from knob to the top of the conduction rod, charge flows from knob to the leaves through the conducting rod, charge flows from knob to the leaves through the conduction rod. As the leaves are now charged similarly, they start repelling each other and tet separted (deflected by certain angle).
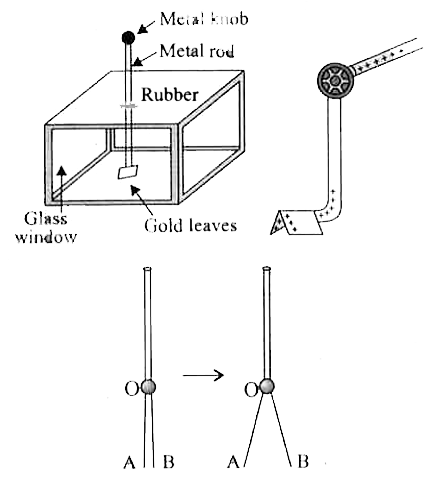
The angle of deflection in static equilibrium is an indicator of the amount of charge on the charged boy.
When a+20C rod is touched to the knob, the deflection of leaves was 5∘, and when an identical rod of −40C is touched, the deflection was found to be 9∘. If an identical rod of +30C is touched, then the deflection may be:
View SolutionA long thin wire carrying a varying current I=i0sinωt lies at a distance y above one edge of a rectangular wire loop of length LandW lying in the x−z plane. What emf is induced in the loop?

View SolutionTwo full turns of the circular scale of a screw gauge cover a distance of 1 mm on its main scale. The total number of division on the circular scale is 50. Further, it is found that the screw gauge has a zero error of −0.03 mm while measuring the diameter of a thin wire, a student notes the main scale reading of 3 mm and the number of circular scale division in line with the main scale as 35. The diameter of the wire is
View SolutionColumn I shows different charge distributions and short electric dipole at a distance x from the charge distributions. Column II gives the dependence of force acting on the dipole as of function of x.

View SolutionColumn-I shows different charge distributions. Cloumn-II gives corresponding electric dipole moments.
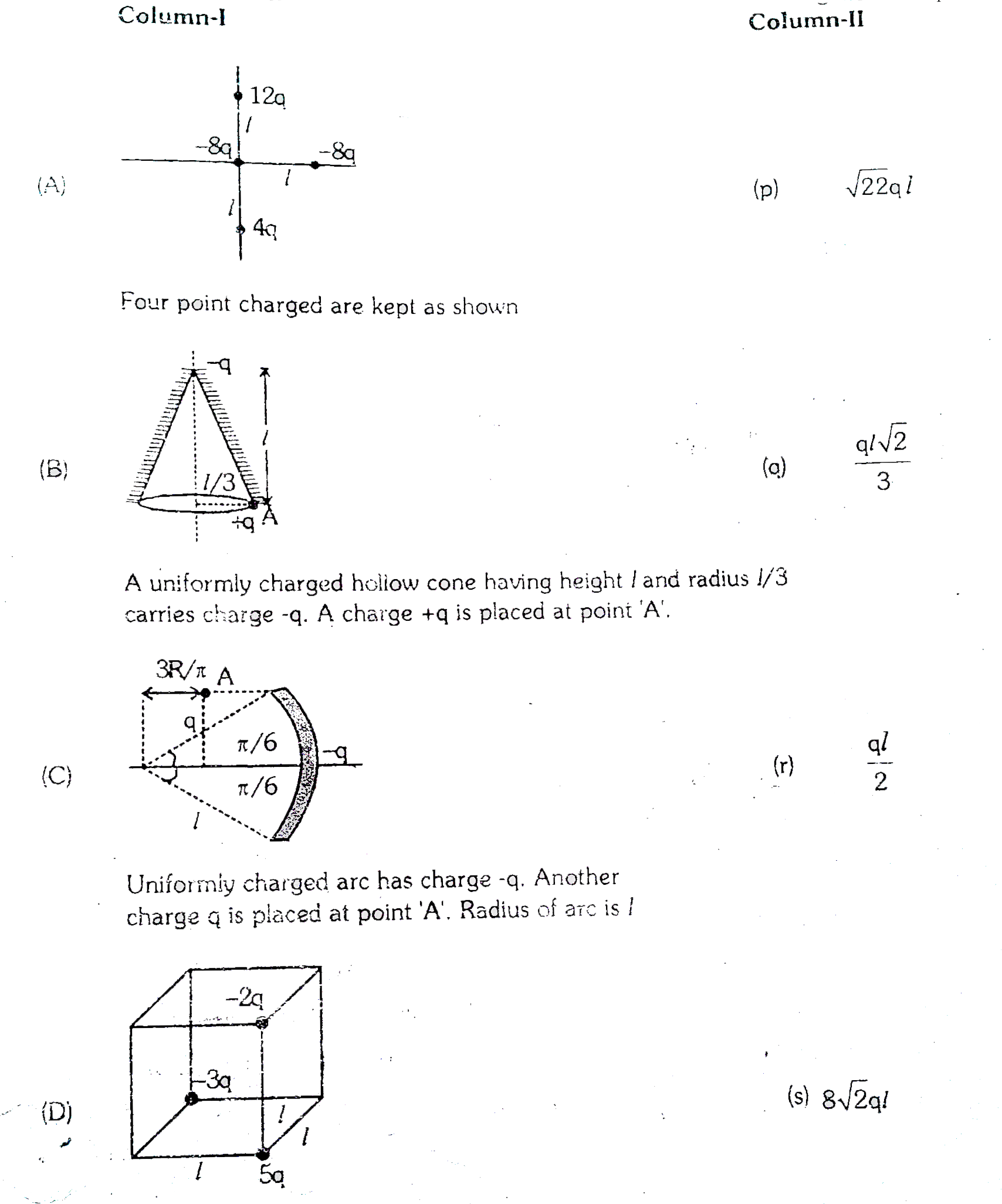
View SolutionThe electric field is measured at a point 0,0, generated due to various charge distributions and the dependence of on is found to be different for different charge distributions. List-I contains different relations between E and . List-II describes different electric charge distributions, along with their locations. Match the functions in List-I with the related charge distributions in List-II.
View SolutionColumn I represents a charged particle being thrown in different combinations of magnetic and electric field: Column II represents the path followed by the charged particle
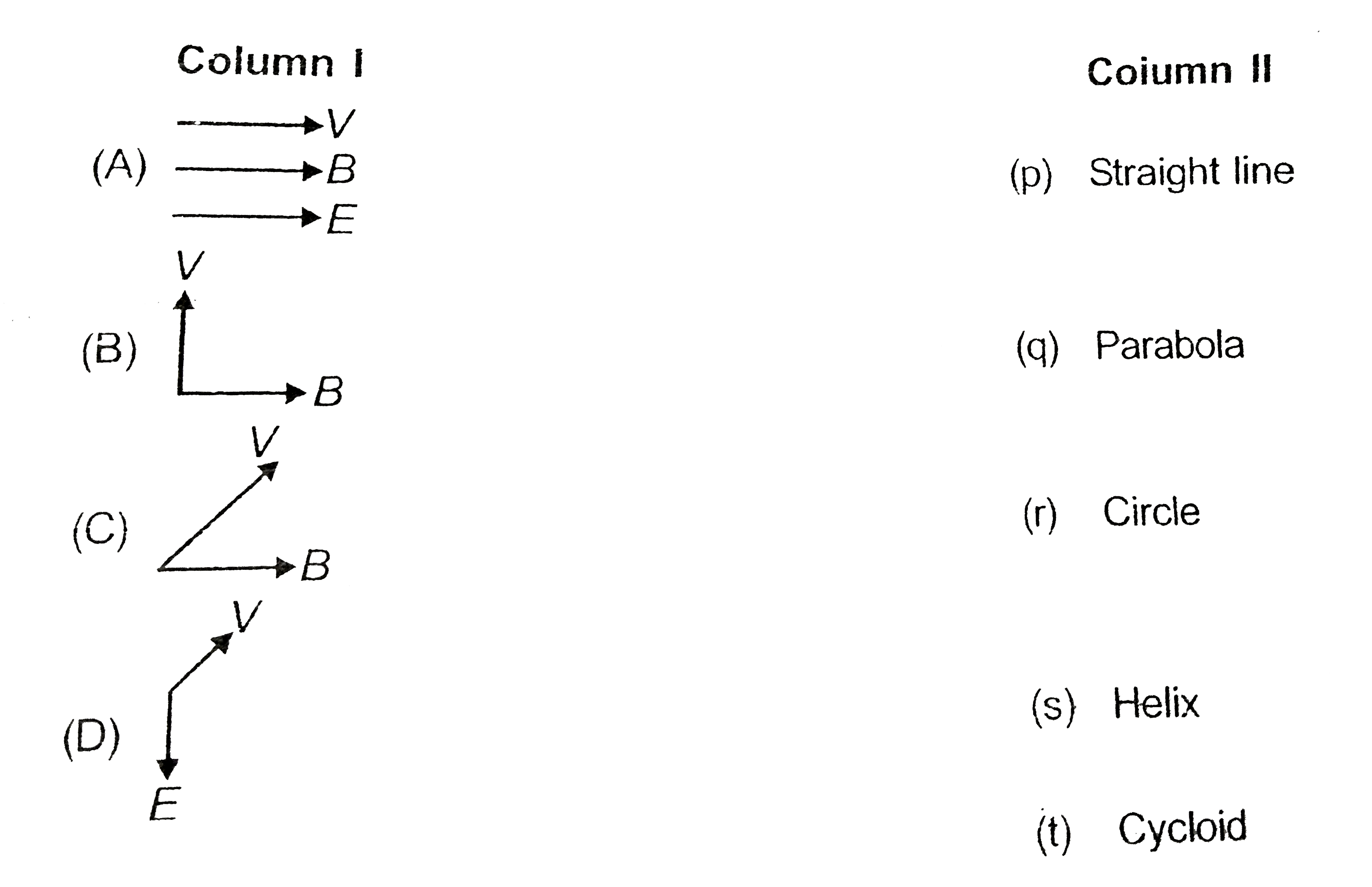
View SolutionColumn I shows charge distribution and column II shows electrostatic field created by that charge at a point r distance from its centre. {:(,"Column I ",,"Column II"),((A),"A stationary point charge",(p),E prop r^(0)),((B),"A stationary uniformly long charge rod",(q),Eprop r^(1)),((C ), "A stationary electric dipole",(r ),E prop r^(*-1)),,(s),E prop r^(-2) ),(,,(t ),E propr^(-3)):}
View SolutionColumn I shows distributionof electric field liness and column II shows charge distribution . Match the columns. {:(,"Column I ",,"Column II"),((A),"Straight lines but not parallel",(p),"Uniformly distributed charged shell"),((B), "Straight lines but parallel ",(q),"Uniformly distributed charged long rod"),((C ),"Curved lines",(r ),"Uniformly distributed infinite charged sheet"),((D), "Some regions where no lines are present",(s),"Electric dipole"),(,,(t),"Any conducting material"):}
View Solutionविभिन्न आवेश वितरणों से उत्पन्न होने वाले विधुत क्षेत्र E का एक बिन्दु P(0,0,d) और मापन किया जाता है और इस विधुत क्षेत्र E की d पर निर्भरता अलग-अलग पायी जाती है सूची I में E और d के बीच में अलग-अलग सम्बन्ध दिए गए है। सूची II विभिन्न प्रकार के आवेश वितरणों और उनके स्थानों को बताती है। सूची I के फलनों का सूची II से सम्बन्धित आवेश वितरणों से सुमेल कीजिए।


View Solutionकॉलम - I में कुछ आवेशित वस्तुओं के कारण वैधुत क्षेत्र E की दूरी R पर निर्भरता बताई गई है और कॉलम -II में ये वस्तुएँ दर्ज हैं।
कॉलम - I की प्रविष्टियों को कॉलम - II की प्रविष्टियों से मिलाएँ।

View SolutionMatch the appropriate Column I with Column II.
Column IColumn II(A) Same dimension of mass(P) electric charge(B) Negative dimension of mass(Q) electric potential(C) Zero dimension of mass(R) electric capacity(D) Dimension of length is±D(S) energy density
View SolutionConsider the figure given below
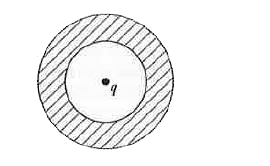
A charge Q is placed inside the Spherical conductor shell. In the given table, column 1 shows different charges, column 2 shows the positions of the electric charge and column 3 shows the different types of charge distribution.

In which case will the charge distribution be non-uniform ?
View SolutionConsider the figure given below
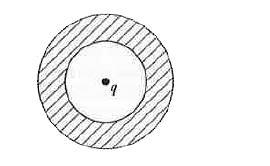
A charge Q is placed inside the Spherical conductor shell. In the given table, column 1 shows different charges, column 2 shows the positions of the electric charge and column 3 shows the different types of charge distribution.

In which case will the Charge distribution be uniform ?
View Solution
