How many of the following will volatilize on heating leaving no solid residue ?
(i)NaNO3 (ii)NH4NO3 (iii)Ca(H2PO2) (iv)NH4HCO3
(v)N2H5HSO3 (vi)AlCl3 (vii)[Cu(NH3)4]SO4 (viii)FeSO4,7H2O
The correct Answer is:ii,iv,v,vi
To determine how many of the given compounds will volatilize on heating leaving no solid residue, we will analyze each compound one by one.
1. NaNO₃ (Sodium Nitrate):
- On heating, NaNO₃ decomposes to form NaNO₂ (sodium nitrite) and O₂ (oxygen gas).
- Reaction: 2 NaNO₃ → 2 NaNO₂ (s) + O₂ (g)
- Conclusion: Solid residue (NaNO₂) remains.
2. NH₄NO₃ (Ammonium Nitrate):
- On heating, NH₄NO₃ decomposes to form N₂O (nitrous oxide) and O₂ (oxygen gas).
- Reaction: 2 NH₄NO₃ → N₂O (g) + O₂ (g)
- Conclusion: No solid residue remains.
3. Ca(H₂PO₂)₂ (Calcium Dihydrogen Phosphate):
- On heating, it decomposes to form calcium hydroxide, O₂, and P₄ (phosphorus).
- Reaction: Ca(H₂PO₂)₂ → Ca(OH)₂ (s) + O₂ (g) + P₄ (s)
- Conclusion: Solid residue (Ca(OH)₂ and P₄) remains.
4. NH₄HCO₃ (Ammonium Bicarbonate):
- On heating, it decomposes to form ammonia gas and CO₂ (carbon dioxide).
- Reaction: NH₄HCO₃ → NH₃ (g) + CO₂ (g)
- Conclusion: No solid residue remains.
5. N₂H₅HSO₃ (Hydrazine Sulfite):
- On heating, it decomposes to form N₂H₄ (hydrazine), O₂, and SO₂ (sulfur dioxide).
- Reaction: N₂H₅HSO₃ → N₂H₄ (g) + O₂ (g) + SO₂ (g)
- Conclusion: No solid residue remains.
6. AlCl₃ (Aluminum Chloride):
- On heating, it sublimates to form gaseous AlCl₃.
- Conclusion: No solid residue remains.
7. (Cu(NH₃)₄)SO₄ (Copper(II) Ammonium Sulfate):
- On heating, it decomposes to form solid copper sulfate, ammonia, and O₂.
- Reaction: (Cu(NH₃)₄)SO₄ → CuSO₄ (s) + NH₃ (g) + O₂ (g)
- Conclusion: Solid residue (CuSO₄) remains.
8. FeSO₄·7H₂O (Iron(II) Sulfate Heptahydrate):
- On heating, it loses water and decomposes to form FeSO₄ (solid) and O₂.
- Reaction: FeSO₄·7H₂O → FeSO₄ (s) + O₂ (g)
- Conclusion: Solid residue (FeSO₄) remains.
Now, let's summarize the results:
- Compounds that leave no solid residue upon heating: NH₄NO₃, NH₄HCO₃, N₂H₅HSO₃, AlCl₃.
- Compounds that leave solid residue: NaNO₃, Ca(H₂PO₂)₂, (Cu(NH₃)₄)SO₄, FeSO₄·7H₂O.
Final Count: 4 compounds will volatilize on heating leaving no solid residue.
- On heating, NaNO₃ decomposes to form NaNO₂ (sodium nitrite) and O₂ (oxygen gas).
- Reaction: 2 NaNO₃ → 2 NaNO₂ (s) + O₂ (g)
- Conclusion: Solid residue (NaNO₂) remains.
- On heating, NH₄NO₃ decomposes to form N₂O (nitrous oxide) and O₂ (oxygen gas).
- Reaction: 2 NH₄NO₃ → N₂O (g) + O₂ (g)
- Conclusion: No solid residue remains.
- On heating, it decomposes to form calcium hydroxide, O₂, and P₄ (phosphorus).
- Reaction: Ca(H₂PO₂)₂ → Ca(OH)₂ (s) + O₂ (g) + P₄ (s)
- Conclusion: Solid residue (Ca(OH)₂ and P₄) remains.
- On heating, it decomposes to form ammonia gas and CO₂ (carbon dioxide).
- Reaction: NH₄HCO₃ → NH₃ (g) + CO₂ (g)
- Conclusion: No solid residue remains.
- On heating, it decomposes to form N₂H₄ (hydrazine), O₂, and SO₂ (sulfur dioxide).
- Reaction: N₂H₅HSO₃ → N₂H₄ (g) + O₂ (g) + SO₂ (g)
- Conclusion: No solid residue remains.
- On heating, it sublimates to form gaseous AlCl₃.
- Conclusion: No solid residue remains.
- On heating, it decomposes to form solid copper sulfate, ammonia, and O₂.
- Reaction: (Cu(NH₃)₄)SO₄ → CuSO₄ (s) + NH₃ (g) + O₂ (g)
- Conclusion: Solid residue (CuSO₄) remains.
- On heating, it loses water and decomposes to form FeSO₄ (solid) and O₂.
- Reaction: FeSO₄·7H₂O → FeSO₄ (s) + O₂ (g)
- Conclusion: Solid residue (FeSO₄) remains.
- Compounds that leave no solid residue upon heating: NH₄NO₃, NH₄HCO₃, N₂H₅HSO₃, AlCl₃.
- Compounds that leave solid residue: NaNO₃, Ca(H₂PO₂)₂, (Cu(NH₃)₄)SO₄, FeSO₄·7H₂O.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)Book:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)Exercise:One Or More Than One Options Correct Type
Explore 6 Videos
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)Book:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)Exercise:Comprehension
Explore 3 Videos
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)Book:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS (ANION)Exercise:Match The Column
Explore 1 Video
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSISBook:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:QUALITATIVE ANALYSISExercise:INORGANIC CHMISTRY(Qualitative analysis)
Explore 35 Videos
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS PART 1Book:RESONANCE ENGLISHChapter:QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS PART 1Exercise:A.L.P
Explore 37 Videos
Similar Questions
Heating which of the following salts in a dry test tube may cause a change in their colour ?
View SolutionA common test to find the genotype of a hybrid is by
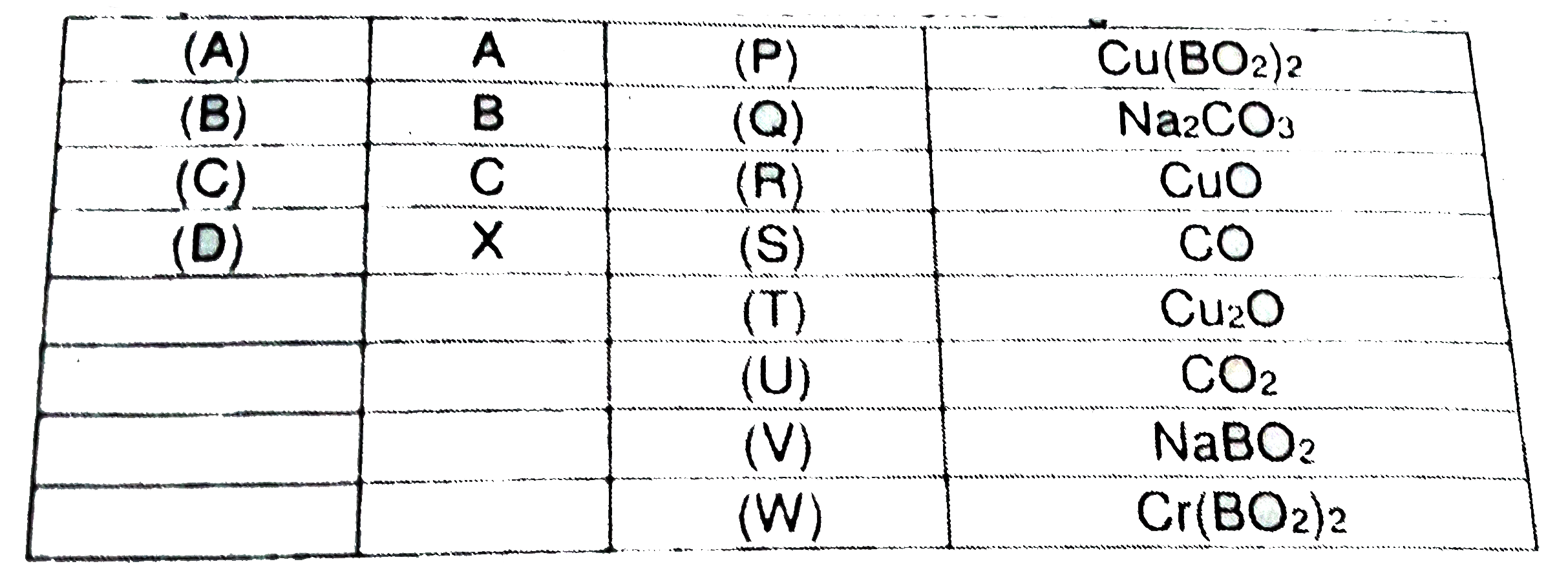
View SolutionCuCO3 was strongly heated to obtain a residue A and gas B. The residue obtained was treated with a salt of sodium 'X' and oxide Y, which produced a blue colored glassy compound C on heating in oxidising flame. The same combination of x and Y gave a green colored glassy compound D when Cr2(SO4)3 was heated with them in oxidizing flame. Match the following accordingly :
View SolutionS1: Silver iodide is fairly soluble in hypo solution.
S2: Heavy metal chloride like AgCl,HgCl2 etc. also respond to Chromyl chloride test.
S3: Bromine reacts with KI liberating violet vapours of iodine.
S4: Diphenylamine reagent test is also given by nitrites chlorates, bromates, iodates, etc. in addition to NO−3
View SolutionA red solide is insoluble in water. However it becomes soluble if some KI is added to water. On heating the red solid in a test tube, there is liberation of some violet coloured fumes and droplets of a metal appear on the cooler parts of the test tube. The red solid is :
View SolutionDescribe a simple test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds
(i) (A) [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4 and (B) [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br
(ii) (A) [Cr(H2O)6]CI3 and (B)[Cr(H2O)5CI]CI2H2O
(iii) (A) cis[PtCI2(NH3)2] and (B) trans [PtCI2(NH3)2]
(iv) (A) and (B) Two enantiomers of [Co(en)2(NH3)2]
(V) (A) (A) [Cr(NH3)6][Cr(NH3)2(NO2)4]
(vi) (A) [Pt(NH3)2CI2] and (B) [Pt(NH3)6]CI2
(vii) (A) [Co(NH3)5CI]SO4 and (B) [Co(NH3)5SO4]CI .
View SolutionWhich of the following is a Bronsted base ? (i) NH_(3) , (ii) CH_(3)NH_(2) (iii) HCO_(3)^(-) , (iv) SO_(4)^(2-)
View Solution{:((A)NH_(3),,,,(i)CO_(3)^(2-)),((B)HCO_(3)^(-),,,,(ii)NH_(4)^(+)),((C)H_(2)O,,,,(iii)H_(3)O^(+)),((D)HSO_(4)^(-) ,,,,(iv)H_(2)SO_(4)),((E)H_(2)CO_(3) ,,,,):}
View SolutionHow many compounds liberate NH3 on heating from the following ?
(i) (NH4)2SO4 (ii)(NH4)2CO3 (iii)NH4Cl
(iv) NH4NO3 (v)(NH4)2Cr2O7
View SolutionNumber of ions which are identified by dil. HCl from the following. (i) SO_(4)^(2-) " " (ii) CO_(3)^(2-) " " (iii) SO_(3)^(2-) " " (iv) HCO_(3)^(-) (v) SO_(3)^(2-) " " (vi) NO_(3)^(-) " " (vii) CH_(3)CO O^(-) " " (viii) PO_(4)^(3-)
View SolutionHow many of the following will volatilize on heating leaving no solid residue ? (i) NaNO_(3) " " (ii) NH_(4)NO_(3) " " (iii)Ca(H_(2)PO_(2)) " " (iv) NH_(4)HCO_(3) (v) N_(2)H_(5)HSO_(3) " " (vi)AlCl_(3) " " (vii) [Cu(NH_(3))_(4)]SO_(4) " " (viii) FeSO_(4), 7H_(2)O
View SolutionTotal number of paramagnetic complexes which are inner orbital complexes : (i) [Cr(NH_(3))_(6)]Cl_(3) " " (ii)[Co(NH_(3))_(6)](NO_(3))_(2)" " (iii)[Ni(NH_(3))_(6)]SO_(4) (iv) K_(2)[PtCl_(6)]. " " (v) [V(H_(2)O)_(6)]SO_(4) " " (vi) [Mn(NH_(3))_(6)]SO_(4) (vii)[Fe(H_(2)O)_(5)(NO)]SO_(4) " " (viii)K_(3)[CuCL_(4)]" " Na_(4)[Fe(CN)_(5)(NOS)]
View SolutionWhich of the following on heating will produce an oxide of nitrogen (NH_(4))_(2)SO_(4), (NH_(4))_(2)Cr_(2)O_(7), NH_(4)NO_(3), KNO_(3), Pb(NO_(3))_(2), (NH_(4))_(2)HPO_(4), NH_(4)Cl, NH_(4)NO_(2)
View SolutionCalculate the equivalent weight of following assuming molecular weight M
(i) H3BO3
(ii) H3PO2
(iii) FeSO4.(NH4)2.6H2O
(iv) K2SO4Cr2(SO4)3.24H2O
(v) Al2O3
(vi) HNO3
(vii) MgCO3
(Viii) CaSO4
View SolutionOn the basis of VSEPR theory, predict the shapes of the following molecules molecules /ions ? (i)SiF_(4) (ii) NH_(2)^(-) (iii) NH_(4)^(+) (iv) C_(2) H_(2) (v) H_(3)O^(+) (vi) F_(2)O (vii) PCl_(3) (viii) PF_(5) .
View Solution
