Two identical conducting rods are first connected independently to two vessels, one containing water at 100∘C and the other containinf ice at 0∘C . In the second case, the rods are joined end to end and connected to the same vessels. Let q1andq2gs−1 be the rate of melting of ice in two cases respectively. the ratio of q1q2 is
The correct Answer is:4
Tem perature differencethem alresistance=L(dmdt)
dmdt∝1Them alresistance,q∝1R
The rods are in parallel in the first case and they are in series in the seconds case. q1q2=2R(R/2)=4
Topper's Solved these Questions
- PROPERTIES OF MATTERBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - PROPERTIES OF MATTEREXERCISE - Level -2
50 Videos
- PROPERTIES OF MATTERBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - PROPERTIES OF MATTEREXERCISE - JEE Main (Archive) Level - 1
48 Videos
- PROPERTIES OF MATTERBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - PROPERTIES OF MATTEREXERCISE - JEE Advanced (Archive) Level - 2 (MATRIX MATCH TYPE)
1 Video
- MOVING CHARGES & MAGNETISM BOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - MOVING CHARGES & MAGNETISM EXERCISE - IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE-K
10 Videos
- QUIZBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - QUIZEXERCISE - PHYSICS
29 Videos
Similar Questions
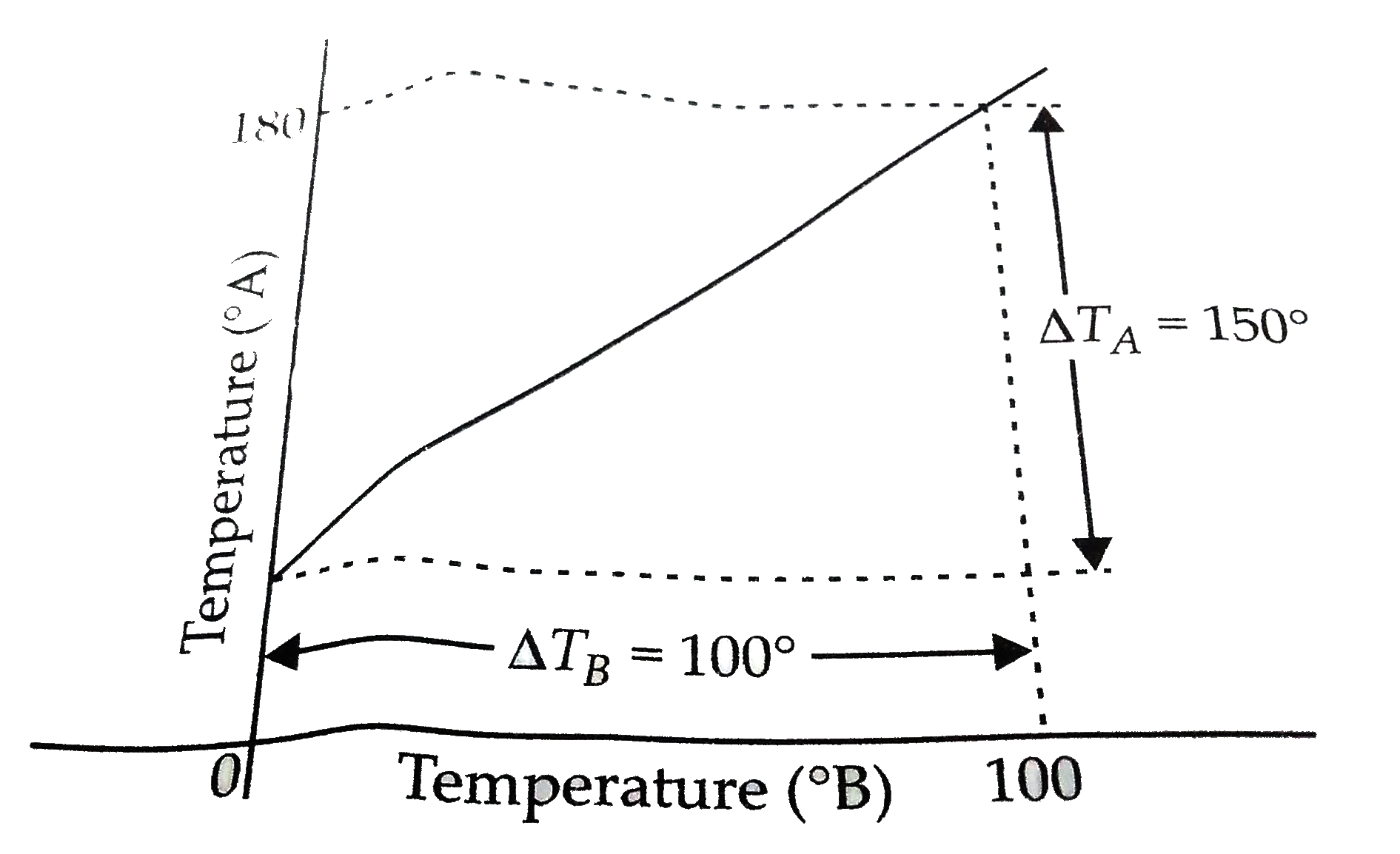
The graph between two temperature scales A and B is shown in figure. Between upper fixed point and lower fixed point there are 150 equal division on scale A and 100 on scale B. The relationship for conversion between the two scales is given by
View SolutionTwo spheres of the same material have radii 1 m and 4 m, temperature 4000K and 2000K respectively. Then the ratio of energy radiated per second by the first sphere as compared to that by the second is
View SolutionColumn I gives some devices and Column II given some processes on which the functioning of these devices depends. Match the devices in Column I with the processes in column II.

View SolutionThe angle of dip is the angle
View SolutionA mass m of radius r is rolling horizontally without any slip with a linear speed v. It then rolls up to a height given by 34v2g
View SolutionTwo identical conducting rods are first connected independently to two vessels, one containing water at 100∘C and the other containing ice at 0∘C. In the second case, the rods are joined end to end and connected to the same vessels. Let q1andq2 gram per second be the rate of melting of ice in the two cases respectively. The ratio q1q2 is
(a) 12 (b)21 (c)41 (d)14
View SolutionTwo identical rods are connected between two containers. One of them is at 100^(@)C containing water and another is at 0^(@)C containing ice. If rods are connected in parallel then the rate of melting of ice is q_(1)g//s . If they are connected in series then teh rate is q_(2)g//s . The ratio q_(2)//q_(1) is
View SolutionTwo large , parallel conducting plates X and Y , kept close to each other , are given Q1 and Q2(Q1>Q2). The four surfaces of the plates are A,B,C and D , as shown
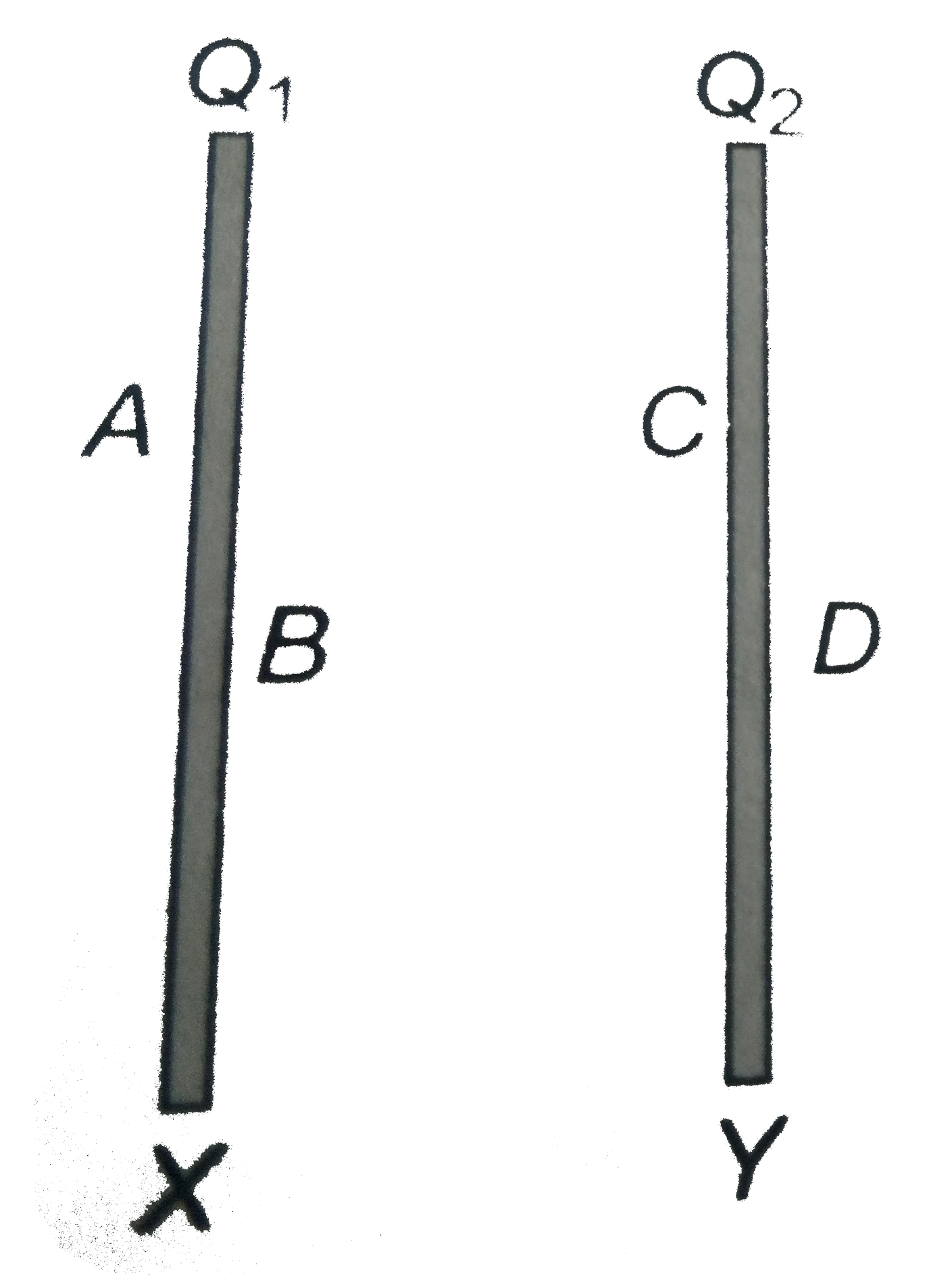
(i) The charge on A is 12(Q1+Q2)
(ii) The charge on B is 12(Q1−Q2)
(iii) The charge on C is 12(Q2−Q1)
(iv) The charge on D is 12(Q1+Q2)
View SolutionTwo conducting spheres of radii r1 and r2 having charges Q1 and Q2 respectively are connected to each other. There is
View SolutionTwo identical conducting rods are first connected independently to two vessels, one containing water at 100∘C and the other containing ice at 0∘C. In the second case, the rods are joined end to end connected to the same vessels. Let m1andm2 g/s be the rate of melting of ice in the two cases respectively, the ratio m1m2 is
View SolutionTwo identical rods are connected in parallel. One end of the rods is maintained at 100∘C and other end is kept in 0∘C ice . The rate at which the ice melts is Q1 gm/sec . Now the rods are connected in series . The ends are again maintained at 100∘C and kept in 0∘C ice . Now the rate at which ice melts is Q2 gm/sec . Then Q2/Q1 is
View SolutionTwo identical conducting rods are first connected independently to two vessels, one containing water at 100∘C, and the other containing ice at 0∘C. In the second case, the rods are joined end to end and connected to the same vessels. Let q1,q2 gram/sec be the rate of melting of ice in the two cases respectively. The ratio q1/q2 is :
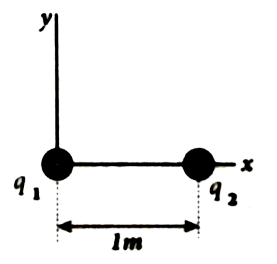
View SolutionConsider two point charges q1 and q2 at rest as shown in the figure. They are separated by a distance of 1 m. Calculate the force experienced by the two charges for the following cases:
(a) q1=+2μ C and q2=+3μC
(b) q1=+2μC and q2=−3μ C
(c) q1=+2μC and q2−3μ C kept in water (εr=80)
View Solutionदो समरूप चालक छड़ें प्रारम्भ में दो बर्त्तनों से अलग-अलग जुड़ी हैं, एक बर्तन में 100∘C पर पानी एवं दूसरे बर्तन में 0∘C पर बर्फ रखा है। बाद में द्नों छड़ों के सिरों को आपस में जोड़कर दिये गये दो बर्तन से जोड़ा जाता है। यदि इन दोनों स्थितियों में बर्फ के पिघलने की दर क्रमश: q1 एवं q2 gm/s हो तो q1/q2 का मान है
View SolutionTwo identical rods are connected independently to two different pots. in a pot 100^@C In water and other vessels 0^@C Is kept ice. The two rods are then connected to each other and connected to the same vessel. If in both cases per second q_1 and q_2 Rate at which ice melts q_1/q_2 What will be the value of?
View Solutionदो समरूप चालक छड़ें प्रारम्भ में दो बर्तनों से अलग-अलग जुड़ी हैं, एक बर्तन में 100∘C पर पानी एवं दूसरे बर्तन में0∘C पर बर्फ रखा है। बाद में दोनों छड़ों के सिरों को आपस में जोड़कर दिये गये दो बर्तन से जोड़ा जाता है। यदि इन दोनों स्थितियों में बर्फ के पिघलने की दर क्रमशः q1 एवं q2 ग्राम/से हो तो q1/q2का मान है
View Solution

